Price overextension: misconceptions and common mistakesPrice overextension remains a widely misunderstood concept in trading, causing both novice and seasoned traders to make errors in their decision-making. This misinterpretation often leads to placing trades in the wrong direction or, equally detrimental, overlooking profitable opportunities.
In essence, price overextension signifies that the market has undergone a rapid and excessive movement in one direction. Such movements are often perceived as unsustainable. Numerous indicators, such as Stochastic, RSI, Bollinger Bands and many other, attempt to identify such "abnormal" price movements so traders could capitalize on them. Despite variations in statistical methods and calculations, their common goal is to detect instances where price went or down too much and is likely to reverse.
In this discussion, I will use Relative-Strength-Index (RSI), a popular indicator, to convey my perspective on price overextension. While some traders argue for customization, the elusive question of "how" often remains unanswered. From my experience, there are no universally perfect settings that consistently yield optimal results.
I’ll draw my examples from the recent SPY bar chart (February 2024).
The first misconception
The first misconception is that if price is overextended it is time to immediately start looking for a trade in the opposite direction. The most important phrase here is “start looking”. Many beginners misinterpret this as an invitation to commence trading, leading to the premature initiation of short positions during perceived market "overextension" and vice versa.
So, the first and foremost important advice is to never try guessing top/bottom based on one indicator or gut feeling. Simple as it seems I remember many times breaking this rule myself because the temptation was too strong. It rarely ended up well.
On the graph, I've highlighted three recent instances where the RSI exceeded 70 (indicating overbought conditions). What stands out is that, following each occurrence, the price surged significantly before consolidation set in, inflicting losses upon short traders.
Even experienced traders, who look for confluence of signals, may fall into this trap. In the first two examples, bearish candlestick patterns failed to prevent subsequent price increases. Most likely, those candles were “created” by weak hands traders, who tried to short market, while it was actually controlled by strong buyers.
These instances could have been avoided by considering the daily graph, revealing a robust bullish context – price was in an uptrend, one-time-framing up on weekly. There were couple of moments when bears gained short term control (Tuesdays 13th and 20th) but they never could take the previous week low; bulls always confirmed their control.
The second advice is to avoid trading against higher level context. While sometimes those trades might work the result is usually mediocre and most of the times you’ll simply lose. If you really wish to trade against context you need to construct a solid dossier of evidence, supporting your trade.
The second misconception
What is the second misconception? It is that when price overextended it is not time to go with the market. In this scenario, traders refrain from initiating long trades after RSI indicates overbought conditions, potentially causing them to miss profitable opportunities. It might not hurt your account but who likes missing good opportunities?
Surprisingly, seizing these trades correctly is not much harder than any other trade. It simply requires prudence and discipline and getting rid-off cognitive biases. For example, in the second example on the graph a trader could win up to 1% if he played off gap-up open after seeing that the new price has found acceptance.
Conclusion
It is possible to build a profitable strategy that relies on “price overextension” concept. However, it demands more than a cursory examination of a single indicator and adherence to textbook candle patterns. Personally, I reached a point where I entirely abandoned the use of RSI and similar tools because, instead of providing clarity, they seemed to cloud my thinking.
Opting for a more effective approach involves keenly observing actual market behavior, which often defies conventional expectations. Study of high-level contexts, understanding key levels, and discerning confluence in price action signals on lower timeframes consistently prove invaluable. This method helps steer clear of common pitfalls and contributes to enhancing overall trading results.
Overbought-oversold
Introducing the Dynamic Fusion OscillatorHello, it's Stock Justice here! In our latest video, we delve into the world of the Dynamic Fusion Oscillator (DFO) - a tool that blends the power of the Relative Strength Index and the Stochastic Oscillator. I walk you through how it works, from understanding these two base components to how we fuse them to create a balanced and sensitive tool for identifying market trends and reversals.
We dive deep into how the DFO uses moving averages to signal potential bullish or bearish trends, and how divergence within the DFO can indicate trend reversals or continuations. I also touch on the DFO's capacity for multi-timeframe analysis, giving you the bigger picture of market trends.
Wrapping up, I remind you of the DFO's value as a versatile trading tool, but also emphasize the importance of using it alongside proper risk management and other technical analysis components. All in all, this video is a must-watch for traders aiming to enrich their toolkit and navigate the market more effectively!
Tips to Help Demystify the RSIPrimary Chart: Tips to Help Demystify the RSI
Introduction to Momentum Indicators
Many indicators exist for technical analysis. And a number of them focus on momentum, which is distinguishable from other core technical concepts such as trend, support and resistance, volatility, and standard deviation. Momentum tools measure the velocity of a directional price move. Using a train as an analogy, momentum considers the speed, velocity and magnitude of the train's movement in a given direction, e.g., north or south. In a sense, it helps determine the strength and speed of the directional travel of the train.
By contrast, trend analysis considers whether a price move is consistently heading in a given direction. A trend can be valid despite corrective retracements, where price retraces a portion of the prior move, consolidates a portion of the prior move, and then resumes movement in the trend's direction. Using the same train analogy, trend analysis considers how effectively and persistently the train is moving in a given direction, such as north or south. Momentum, though, considers the train's speed and velocity in whatever direction the train is moving.
Many momentum indicators also are not limited to analyzing momentum and may have utility as a trend gauge as well. For example, Stochastics, MACD and RSI all have the additional capacity to help analyze trends.
Basic Concepts and Calculation of RSI
Created by J. Welles Wilder, the RSI is one of the most widely used and well-known momentum indicators. The acronym "RSI" means relative strength index. RSI should not be confused with the concept of relative strength, which compares one instrument or security against another to determine its outperformance or underperformance. Some other common momentum indicators that have been in use for many years include the Rate-of Change, Chande Momentum Oscillator, Stochastics, MACD, and CCI. Most momentum indicators, including RSI, share some conceptual aspects, such as overbought and oversold conditions and divergences, even though they may vary in the way they are calculated and interpreted.
Reviewing the way an indicator is calculated can sometimes help to sharpen one's understanding of it and interpret it more effectively. RSI's calculation is not as complex as some indicators. So reviewing its calculation remains an accessible exercise, but this is not essential to mastering the indicator. TradingView's RSI description contains a useful summary of how the indicator is calculated. See the Calculation section of the RSI description at this link: www.tradingview.com(close%2C%2014).
Another excellent description of how RSI is calculated may be found on this reputable technical-analysis website: school.stockcharts.com
To summarize, RSI's basic formula is as follows: RSI = 100 – (100 / 1 + RS), where RS = average gain / average loss.
Using the default lookback period of 14 (note that any lookback period can be selected), the calculation then proceeds to include 14 periods of data in the RS portion of the calculation (average gain / average loss). So the average gain over the past 14 periods is divided by the average loss over the past 14 periods to derive "RS," and then this RS value is plugged into the formula at the start of this paragraph. The subsequent calculations also have a lookback of 14 periods (using the default settings) but smooth the results.
Smoothing of these values then occurs by (1) multiplying the previous average gain by 13 and adding the current period's gain, if any, and dividing that sum by 14, and (2) multiplying the previous average loss by 13 and adding the current period's loss, if any, and dividing that sum by 14. If the lookback period is adjusted from the default of 14, then the formula and smoothing techniques will have to adjust for that different period.
In short, the calculation reveals that RSI's core function is to compare the size of recent gains against the size of recent losses and then normalize that result so the indicator's values may fluctuate between 0 to 100. Note that if a daily period is used, for example, the average day's gain is compared against the average day's loss over the lookback period selected. Similarly, if hours are used, the average hour's gain is compared against the average hour's loss over the relevant lookback period.
RSI can be used on any timeframe, including a 1-minute or 5-minute chart, and simply calculates its values based on the period to which the indicator is applied, based on a default using closing prices for the period specified. With TradingView's RSI indicator, traders have a great deal of flexibility in adjusting such defaults to some other preferred value, so the closing price need not be used—the default can be changed to the open, the high, the low, high+low/2, high+low+close/3, or several other options.
Interpreting RSI's Overbought and Oversold Signals
With some exceptions, the higher-probability RSI overbought (OB) and oversold (OS) signals align with the direction of the trend. The old trading adage remains valid for RSI as with other forms of technical analysis: the trend is your friend. In the chart below, consider the yellow circles flagging OS signals that could have been effective in the Nasdaq 100's uptrend in 2021.
Supplementary Chart A: Example of RSI OS Conditions That Align with an Uptrend and Key Support
As with other technical trade signals, countertrend setups should be avoided in the absence of overwhelming confirmation from other technical evidence. If a countertrend setup is traded, use extra caution and smaller position size. In this context, trading RSI signals against the trend means selling or entering a short or bearish position in an uptrend when an OB signal appears, or it means buying or entering bullish positions in a downtrend when an OS signal appears. It may also mean trading counter-trend positions as soon as RSI begins exiting an OB or OS zone.
Stated differently, trading overbought and oversold signals against the trend will likely result in mounting losses. Countertrend trades require much technical experience and significant trading expertise—and even the most experienced trading veterans and technical experts say that the counter-trend trades tend to be low probability setups. In short, never trade the RSI's OB and OS signals mechanically without considering any other technical evidence.
Supplementary Chart B: NDX OB Condition in an Uptrend
In the chart above, note how the Nasdaq 100 (NDX) reached a fairly high daily RSI reading of 77.17 on July 7, 2021. This chart shows an example of how even very high OB conditions can persist much longer than expected. RSI remained above 70 for over a trading week. And the ensuing pullback was not that significant, and it didn't reverse the uptrend at all. The risk-reward for mechanically trading this setup would have been poor, and stops would probably have been ignored at some point in the days following the signal. For an experienced trader with small position size, perhaps the second RSI peak immediately following the July 7, 2021 peak would have worked for a short-term trade given that a divergence arose (higher price high coinciding with a lower RSI high). But it would still have been a difficult trade requiring excellent timing and precision.
In summary, OB / OS signals should not be interpreted and traded mechanically. The trend and other technical evidence should always be considered. OB / OS signals work best when aligned with the direction of the trend on the relevant time frame. They also work best when taken at crucial support or resistance.
Consider several other tips and tricks when interpreting OB / OS signals on RSI.
1. The importance of an OB / OS signal depends not only on the context of the trend in which it arises but also on the time frame on which it appears and the lookback period used in its calculation. This is intuitive, but it helps to keep this in mind. For example, an OB / OS reading has a greater effect on the weekly or monthly chart than on the daily, and an OB / OS reading has a greater effect on daily chart than on the hourly or other intraday chart. Furthermore, if the RSI lookback period is set to 5 periods on a given time frame, the effect of an OB / OS reading will less significant than if the RSI lookback period is set to 14 (the default setting).
2. Consider past OB / OS readings for the same security or index being considered (using the same time frame for past and current OB / OS readings). Each security or index may have OB / OS levels that differ somewhat from other securities or indices. In addition, the OB / OS readings that are typical for a given a security, index or instrument may vary over time in different market environments. It may help to draw support or resistance lines on the RSI indicator within the same market environment and trend to determine what RSI OB / OS levels are typical. RSI support or resistance levels in an uptrend should not drawn to be applied and used in a downtrend for the same index or security.
Supplementary Chart C.1: RSI Support and Resistance Levels for NDX in 2021 on Daily Chart
Supplementary Chart C.2: Two RSI Downward Trendlines Drawn on BTC's Weekly Chart to Help Identify Resistance
3. Divergences can strengthen the effect of an OB / OS signal. Stated simply, a divergence occurs when the RSI and price are in conflict. For example, consider two or three subsequent higher highs in price that occur (this can happen in an uptrend or a bear rally or in a trading range). When price makes the second or third high, a divergence arises if RSI makes a lower high. Or consider two or three subsequent lower lows in price. When price makes the second or third lower low, a divergence arises if the RSI makes a higher low. A greater number of divergences presents a stronger signal than a lower number of divergences. And having divergences on multiple time frames can also be helpful. Finally, a divergence should not be traded until confirmation comes from price itself, i.e., a trendline or other support / resistance violation.
Supplementary Chart D: Example of RSI Bearish or Negative Divergence at NDX's All-Time High in November 2021
4. OB / OS signals also can be helpful in chop when they arise at the upper boundary of a well-defined trading range. In choppy trading ranges, one has a better trading edge at the edge. OB / OS signals that arise at the edge (at critical support / resistance) are the most useful. But depending on the trading strategy, setups in choppy trading ranges can be more difficult and lower probability than setups in strong trends.
Using RSI as a Trend-Analysis Tool
While primarily a momentum tool, the RSI has trend-analysis aspects. Because the RSI will likely remain in overbought (OB) or oversold (OS) for extended periods, it helps evaluate the strength and duration of price trends.
In an uptrend or bull market, the RSI (daily) tends to remain in the 40 to 90 range with the 35-50 zone acting as support. In a downtrend or bear market the RSI (daily) tends to stay between the 10 to 60 range with the 50-65 zone acting as resistance. These ranges will vary depending on the RSI settings, time frame, and the strength of the security or market’s underlying trend. As mentioned above, RSI readings will also vary from one security or index to another. They also vary in different market environments, e.g., a strong uptrend vs. a weak uptrend will have different OB / OS readings.
So the RSI can help confirm the trend when it moves within the RSI range that is typical of that security or index when trending. As a hypothetical example example, if a major index appears to be making higher highs and lower highs, respecting trendline and other key supports, and showing technical evidence of an uptrend, then RSI can help confirm this trend analysis by marking OS lows within the 35-50 range (perhaps 30 on a volatile pullback). RSI can also help time entries and exits when reaching the area that has been where RSI has found support in its current market environment.
The following points summarize how RSI tends to operate during trending price action:
During an uptrend, RSI will trend within the upper half of the range (roughly), moving into OB territory frequently (and at times persisting in the OB zone) and finding support around 35-50. When RSI finds support around 35-50, this may represent tradeable a price pullback—a retracement of the recent trend’s price move—that may work as a bullish entry if other technical evidence confirms.
During a downtrend, RSI will trend within the lower half of the range (roughly), moving into OS territory frequently (and at times persisting in the OS zone) and finding resistance around 50-65. When RSI finds resistance around 50-65 (sometimes higher given the violent nature of short-squeeze induced bear rallies), this may represent tradeable a price bounce—a retracement of the recent trend’s price move —that may work as a bearish entry if other technical evidence confirms.
RSI, like other indicators, cannot produce perfectly reliable and consistently accurate signals. Like other indicators, it can help identify higher probability trade setups when used correctly and when confirmed with other technical evidence. When considering trade setups in terms of probabilities rather than certainties, traders will find position sizing and risk management to be a vital part of any strategy that relies in part on the RSI.
Wave exhaustionThe main purpose of analyzing waves is to understand when the current wave is exhausted aka overextended aka overbought aka oversold.
What is every1 seem to miss is that exhaustion is not based exclusively on "price gone too far", but also on "too much time passed" and "not much volume was traded" as well. That's one of the main reasons why your comparative analysis, divergences on so called "indicators" do not work properly. It simply can't. These methods do not gain time & volume information from the data.
When you analyze order flow on any resolution, be it 1 minute, 5 years or tick chart, you're interested in 2 waves: current wave and *the very last (previous) wave in the same direction .
* including the imaginary waves
Don't forget to turn in log scale when it's needed!
You compare these 2 as the current wave develops and keep updating the answer to the binary question, "which of these two waves is weaker". Strength of a wave = it's ability to continue. Every wave starts strong and goes weaker and weaker, the factors are:
1) Time. Horizontal size of a wave (in bars), more time (more bars) - weaker ;
2) Range. Vertical size of a wave, higher range - weake r;
3) Volume, or inferred volume. You sum up all the volume within a wave, or sum up all the bar sizes within a wave. Less volume - weaker .*
* in order not to sum up anything within a wave yourself, here you can turn in volume/range bars and simply count em.
And from that moment it's like "Best of 3" comparison.
1) Time. Wave A 10 bars, wave B 5 bars. Wave B is stronger;
2) Range. Wave A 546 points, wave B 890 points. Wave A is stronger;
3) Volume. Wave A 10k, wave wave B 8k. Wave A is stronger;
So at that point, wave A was stronger = wave B was weaker.
This will be giving you a binary answer which wave is weaker. When the current wave becomes weaker than the last wave in the same direction, current wave is considered exhausted.
P.S.: wave start in time (first bar of the wave) is the level origin itself or the first bar that touched a level if we talked about a new wave starting from an already positioned level, or about a wave started after clearing a positioned level.
The more you'll think about the more it'll make sense. An example. Remember seeing fast price jumps? After some, the price reverses very fast and goes back, after others prices continues in the direction of the jump. In most of the cases the current wave (the jump) gets exhausted in terms of price, but not exhausted in terms of time (the jump was very fast). So in terrms of time and price both waves are 50/50. What is different is volume. If the current wave (the jump) had a huge volume, overall it's still not exhausted, hence it continues. Sounds familiar? Sounds logical?
Just the last simple and obvious thing, in most cases you won't need to calculate sum volumes/ranges, usually at the moment of analysis the current wave is already longer and higher than the previous one in the same direction, hence the current wave is already exhausted.
Yessir
Overbought & OversoldIf you can identify overbought or oversold conditions, as a trader, this can be highly profitable. In particular, these are two definitions that refer to the extreme values of the price in addition to their intrinsic value. So, when these conditions appear, a reversal of the direction of the price is highly expected.
What is Overbought?
When something is ‘overbought’, it means that the price is thriving for a long peri. Because of this, it’s trading at a higher price than it actually should be. In other words, the asset is overly expensive and a sell-off is about to happen.
What is Oversold?
When something is ‘oversold’, it means the price is in a negative momentum for an extended period. Because of this, it’s trading at a lower price than it actually should be. In other words, the asset is overly cheap and an upward rise is about to happen.
Indicators
Moreover, there’re plenty of technical indicators which you could use in technical analysis. To confirm the Overbought and Oversold conditions the three indicators commonly used are:
Bollinger Bands,
Relative Strength Index and
Stochastics
Bollinger Bands
The Bollinger Bands appear as a channel. Specifically, the middle line is often a twenty-period moving average. On the other hand, the upper band is the moving average plus two times its standard deviation. Furthermore, the lower band is the moving average minus two times its standard deviation. As a result, the price seems to fluctuate in this channel and normally doesn’t move out of the bands. However, when the price tends to move out of the upper band the price can be considered as overbought. Likewise, the same thing happens when the price moves out of the lower band, the price can be considered oversold.
Relative Strength Index
The Relative Strength Index is a momentum oscillator where the horizontal axis appears as a function of time and the vertical axis as on a scale of 0 to 100. In addition, the standard amount of periods used for this indicator is 14.
So, the Relative Strength Index measures the magnitude and the speed of recent price action. The indicator compares a security strength on days when prices go up to its strength on days when prices go down. Yet when the Relative Strength Index has a value higher than 70 the price can be considered as overbought. When the opposite happens and the price drops down a value of 30 the price can be considered as oversold.
Stochastics
Stochastics is like the Relative Strength Index, a momentum oscillator where the horizontal axis appears as a function of time and the vertical axis is displayed on a scale of 0 to 100. However, the stochastic oscillator is predicated on the assumption that closing prices should move in the same direction as the current trend.
Meanwhile, the Relative Strength Index is measuring the magnitude and the speed of the current price action. The Stochastic oscillator does calculate this value and expresses this value into a %K.
In addition, the standard amount of periods used for this indicator is 14. When the %K crosses a value of 80 the price can be considered as overbought. When the opposite happens and the price drops down a value of 20 the price can be considered as oversold.
Combined
One indicator that matches the criteria for being ‘overbought’ or ‘oversold’ can suggest a small trend reversal. But once all 3 indicators combined are matching the criteria, the assumption of a trend reversal is very likely to happen. Therefore, for trading in general this can be a profitable and low-risk strategy.
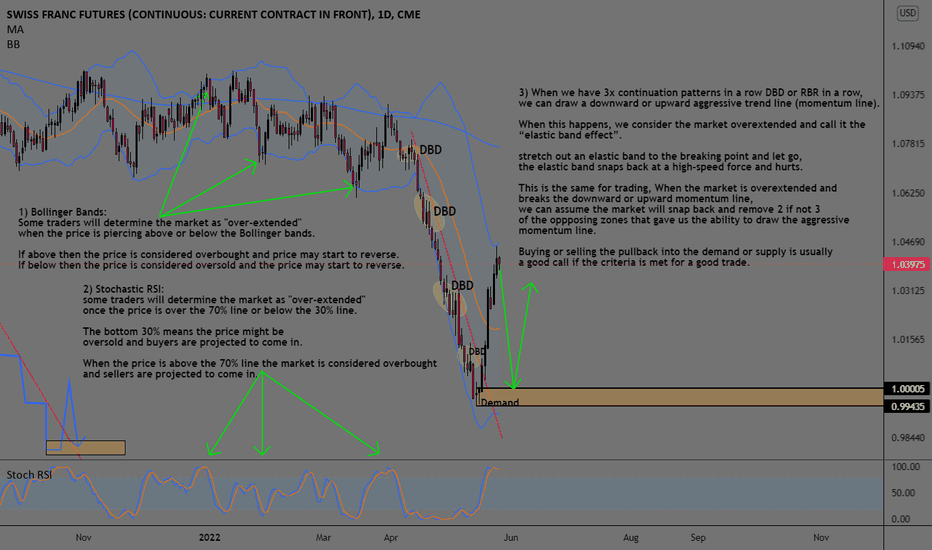
Overextended Markets (Overbought And Oversold)1) Bollinger Bands:
Some traders will determine the market as "over-extended"
when the price is piercing above or below the Bollinger bands.
If above then the price is considered overbought and price may start to reverse.
If below then the price is considered oversold and the price may start to reverse.
2) Stochastic RSI:
some traders will determine the market as "over-extended" once the price is over the 70% line or below the 30% line.
The bottom 30% means the price might be oversold and buyers are projected to come in.
When the price is above the 70% line the market is considered overbought and sellers are projected to come in.
3) Supply And demand
When we have 3x continuation patterns in a row DBD or RBR in a row, we can draw a downward or upward aggressive trend line (momentum line).
When this happens, we consider the market overextended and call it the “elastic band effect”.
stretch out an elastic band to the breaking point and let go, the elastic band snaps back at a high-speed force and hurts.
This is the same for trading, When the market is overextended and breaks the downward or upward momentum line, we can assume the market will snap back and remove 2 if not 3 of the opposing zones that gave us the ability to draw the aggressive momentum line.
Buying or selling the pullback into the demand or supply is usually a good call if the criteria are met for a good trade.
Volume Indicators Masterclass Part 1VOLUME INDICATORS
Volume is one piece of information that is often neglected by many market players, especially beginners.
However, learning to interpret volume brings many advantages and could be of tremendous help when it comes to analyzing the markets. The usage of volume indicators has long been restricted to just the Forex Markets. Thereby in the Volume Indicator Masterclass, we will be looking in-depth for a few volume indicators.
Traders often use volume which measures the number of shares traded during a particular time period as a way to assess the significance of changes in a security’s price.
Traders rely on it as a key metric because it lets them know the liquidity level of an asset, and how easily they can get into or out of a position close to the current price, which can be a moving target.
Volume analysis is a technique used to determine the trades you will make by discovering the relationships between volume and prices. In order words, it shows how many times the security has been bought or sold over a given timeframe. The time frame can be one minute, four hours, one day, or anything.
The volume transacted in the given timeframe is represented as a bar, which can be color-coded. The color of the bar shows whether the security’s price closes up or down.
A green bar is generally used to show that the security closed higher during the trading session
A red bar is used to indicate that the security closed lower
The height of the bar shows whether there’s an increase or a decrease in the volume of the security transacted a taller bar shows a higher volume while a shorter bar shows a lower volume.
Trend Confirmation :
If the volume increase with an increase in price or with a decrease in price, it indicates a strong buying or selling pressure.
Trend Non-Confirmation :
If the volume decrease with an increase in price or with a decrease in price, it indicates a weak buying or selling pressure.
There are various Volume Indicators, out of which we will be discussing the Money Flow Index in this Masterclass.
Money Flow Index
The Money Flow Index (MFI) is an oscillator that uses both price and volume to measure buying and selling pressure.
The indicator is synonymous with “volume-weighted RSI” as it integrates volume and mirrors the relative strength index (RSI) with respect to its mathematical formulation and categorical classification as a momentum oscillator MFI.
Calculation of the Money Flow Index:
Typical Price: (High + Low + Close) / 3
Money Flow: Typical Price x Volume
Positive Money Flow: The Money Flow on days where the Typical Price is greater than the previous day’s Typical Price.
Negative Money Flow: The Money Flow on days where the Typical Price is less than the previous day’s Typical Price.
Money Flow Ratio: 14-Period Positive Money Flow / 14-Period Negative Money Flow
Money Flow Index: 100 Money Flow Ratio / (1 + Money Flow Ratio)
Signal Generation
BUY When Money Flow Index crosses up 20 i.e. from the oversold region
SELL When Money Flow Index crosses down 80 i.e. from the overbought region
There a lot of more interesting Volume Indicators that can be used, about which we'll be talking in the next Masterclass of Volume Indicator.
STAY TUNED!
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Your questions and comments are most welcome.
If you find the post useful, please like, share, and follow to make sure that you get more information once published.
- Mudrex
Relative Strength Index Masterclass Part 1Relative Strenght Index(RSI)
RSI is a momentum oscillator, whereas the momentum is the rate of the rise or fall in price.
RSI is an oscillator ranging between two extremes, in the case of RSI, it ranges from 0 to 100.
The relative strength index is computed with: RSI = 100RS/(1+RS); where RS is relative strength.
RS= (Previous Average gain*13+Current gain)/(Previous Average loss*13+Current loss)
Relative Strength is a ratio of a stock price performance to a market average (index) performance.
RSI will rise as the number and size of positive close increases and will fall as the number and size of losses increase.
There are two terminologies for RSI:
Lookback period: The time frame that is used to calculate the relative strength, by default it is 14. A look-back period greater than 14 will give a smoother RSI signal while less than 14 will give a rough volatile RSI signal
Threshold Frequency: The oversold-overbought value ranges are the threshold frequency, default is 70-30 (which depend on various factors reasons such as risk factor), for eg. 80-20(less risk) and 66-33 (more risk)
RSI touching the overbought condition is a bearish sign (prices are likely to go down) while RSI attaining oversold condition is a bullish sign (prices are likely to increase)
There are many ways of using RSI as an indicator
Oversold-Overbought Region :
Oversold Region - The situation at which a lot of selling has happened and everyone who was willing to sell has sold, RSI value less than 30
Overbought Region - The situation at which a lot of buying has happened and everyone who was willing to buy has bought, RSI value greater than 70
In this, we have default values for the lookback period(14) and threshold frequency(70-30) which you can change according to your requirement and risk management.
A look-back period of more than 14 would be more interested in long term trend while less than 14 would be inclined towards short term trades. The look-back period can also be increased to smoothen out the RSI line.
A threshold of 80-20 (more-safer) or 66-33 (more-riskier) can be taken into consideration.
A Buy signal will be generated when RSI is less than 30 i.e. the oversold region while a Sell signal will be generated when RSI is greater than 70 i.e. overbought region.
50-Level RSI Midline
The overbought-oversold condition helps detect sudden changes in the momentum of price without providing much information about the overall trend of the market, therefore using the overbought-oversold strategy without getting information on the overall trend could be a bit risky.
Thus we use RSI with different timeframes and the threshold for trend information as well as signal generation.
In this we will have two different RSI:
A RSI with the look-back period of 20-days and 50-50 frequency, also called midline RSI. In an uptrend, this RSI is above 50 and below 50 for a downtrend.
A RSI with the look-back period of 5-days and 66-33 frequency, the look-back period is sufficiently low so that in a predominant trend, local maxima or minima can be used for generating buy or sell signal with the small look-back period RSI ensuring the signal is reactive to current price fluctuations.
Thereby, an uptrend is signaled if 20-RSI is greater than 50, with the buy signal being generated in the uptrend with 5-RSI in the oversold region while a downtrend is signaled if 20-RSI is less than 50, with the sell signal being generated in the downtrend with 5-RSI in the overbought region.
A buy signal is generated when 20-RSI is greater than 50 and 5-RSI is less than 33 while a sell signal is generated when 20-RSI is less than 50 and 5-RSI is greater than 66.
A lot more interesting things can be done using RSI, about which we'll be talking in the next Masterclass on RSI, STAY TUNED!
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Your questions and comments are most welcome.
If you find the post useful, please like, share, and follow to make sure that you get more information once I publish it.
- Mudrex
Overbought to Oversold - Keep It Simple, Stupid!After exploring the depths of profit taker heaven and stop loss hell, after combining many different indicators, finding correlations with momentum, trend, volatility, you name it... After trying to adjust the strategies to different assets, asset classes, market conditions... After finding out that each of these steps are way more difficult than I thought and will require much more rigor and a start from scratch...
I remembered the golden rule of strategy...
"Keep it simple, stupid!"
When others are buying like rabid dogs, you sell...
When others are selling like mad monkeys, you buy...
When others are greedy, you are fearful... When others are fearful, you are greedy...
So, we trade from overbought to oversold. No profit takers, no stop losses, no optimization for a specific stock or time frame or asset class, no correlation with other indicators... Just overbought to oversold.
Win rate of 90+%, profit factor of over 5.0, compared to holding the stock indefinitely with a loss of 80%.
Happy trading!
XRPUSD 1H BEST %R MOMENTUM STRATEGYStep #1: Define the Trend. An Downtrend is defined by a Series of LH Followed by a Series of LL.
The definition of an downtrend is pretty much standard. In an downtrend, we look for a series of lower highs followed by a series of lower lows. Two LH followed by at least another two LL is enough to define an downtrend.
A lower high is simply a swing low point that is lower than the previous swing high. While a lower low is simply a swing low that is lower than the previous swing low.
All momentum traders know that the trend is our friend. But without momentum behind the trend, we might actually not have any trend.
For active traders, we also look at the actual price action in order to gauge momentum. Besides reading the best momentum indicator.
Step #2: In an Downtrend Look for Bold Candlesticks that Close Near the Lower End of the Candlestick .
A technical analysis concept is that you want to use multiple confirmation signs when buying and selling. This will increase the likelihood that’s a high probability trading setup.
In this regard, the momentum trading strategy besides using the best momentum indicator, also incorporates the price action.
A practical way to read momentum from a price chart is to simply look at the candlestick length. What we want to see in an downtrend is big, bold bearish candlesticks that close near the lower end of the candlestick.
Now, it’s time to focus on the Williams %R. This is the best momentum indicator. Which brings us to the next step of our momentum indicator strategy.
Step #3: Wait for the best Momentum Indicator to get overbought (above -20). Then rallies below the -50 level before Selling .
We’re going to use Williams %R, the best momentum indicator in a smart way. In an downtrend, we sell after the best momentum indicator has reached overbought conditions (above -20). And then rallied back below the -50 level.
Now, we have confirmation from both the price and the best momentum indicator. The real momentum is behind this trend and the probabilities are in favor of more downside prices from here on.
Note* If the best momentum indicator continually stays in oversold territory (below -80 level), it signals a strong momentum and conversely a strong trend. Inversely the same is true in a uptrend.
The next important thing we need to establish is where to place our protective stop loss.
Step #4: Place Your Protective Stop Loss above the Recent Lower Low.
We want to hide our protective stop loss. It is above the most recent lower low level that formed right before the best momentum trading strategy issue the sell signal.
Alternatively, you can also trail your stop loss above each most recent lower low. This strategy will allow you to lock-in the potential profits in case of a sudden market reversal.
Last but not least the momentum indicator strategy also needs a place where we need to take profits, which brings us to the last step of the best momentum trading strategy.
Step #5: You pick your own TP strategy or
Take Profit once we break above the Previous Lower Low
A trend in motion can stay in that state longer than anyone can anticipate. And since we want to maximize our potential profits we let the market tips it hands before liquidating our trades. In this regard, we look for a break in the trend structure. Respectively a break above the most recent lower low.
Alternatively, you can take profit once the best momentum indicator breaks above the -50 level.
Note** The above was an example of a SELL trade using the Best Momentum Trading Strategy. Use the same rules for a BUY trade.
Massive sequence of RSI-Renko DIVINE™ Scalps Following Iran NewsThere were a total of 250-270 points of NQ scalps after the Iran missile strikes going long. If you held the first contract long on the swing trade (1st trade in the direction of the new trend is always the swing trade, marked by a fat arrow) you would have gained another 270 points.