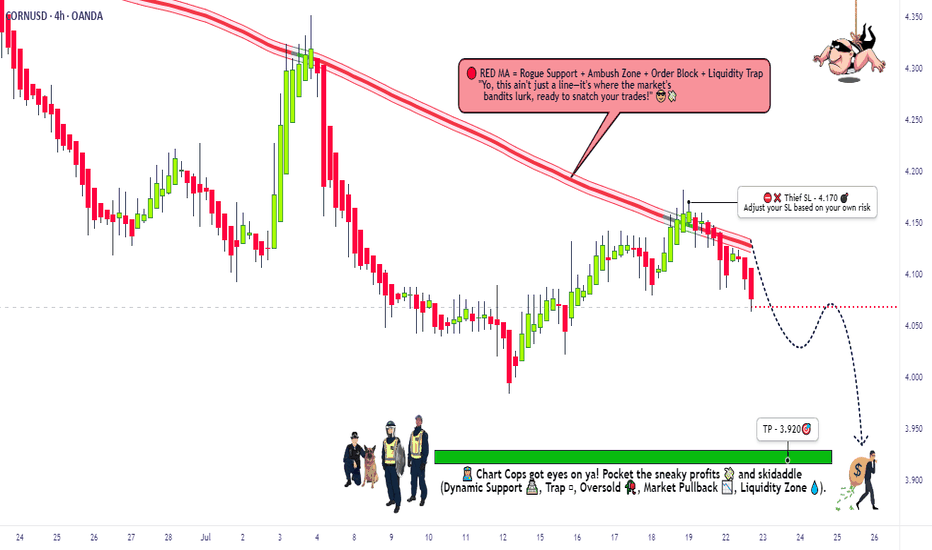
CORN Heist: Steal Short Profits Before Bulls React!🚨 CORN HEIST ALERT: Bearish Raid Ahead! 🚨 Swipe the Loot Before Cops Arrive! 🌽🔻
🌟 Attention, Market Bandits & Profit Pirates! 🌟
🔥 Thief Trading Intel Report 🔥
The 🌽 CORN CFD market is setting up for a bearish heist—time to short-swipe the loot before the bulls rally their defenses! Police barricade (resistance) is holding strong, but oversold conditions + consolidation hint at a trend reversal trap. High-risk, high-reward—just how we like it!
🎯 Heist Strategy (Swing/Day Trade)
Entry (Bearish Raid) 🏴☠️
"Vault’s unlocked! Swipe shorts at any price—OR set sell limits *near 15M/30M pullbacks for a cleaner steal!"*
Stop Loss (Escape Route) 🛑
Thief’s SL at nearest 4H swing high (4.170)—adjust based on your risk tolerance & lot size.
Pro Tip: Tighten SL if trading multiple orders!
Target (Profit Escape) 🎯
3.920 (or bail early if cops (bulls) show up!)
🌽 Market Snapshot: Why CORN is Ripe for a Raid
Neutral trend leaning bearish—consolidation breakout likely!
Key Drivers:
Macro pressure (USD strength, crop reports)
COT data hinting at big players positioning short
Seasonal trends favoring downside
Want full intel? 🔍 Check COT reports & intermarket analysis!
🚨 Trading Alerts (Avoid the Cops!)
News = Volatility Trap! 📰🚔
Avoid new trades during high-impact news.
Trailing stops to lock profits on running heists!
💥 Boost This Heist! 💥
"Like & boost this idea to fuel our next raid! More steals = more profits for the gang! 🏴☠️💰
Stay tuned—another heist drops soon! 🚀🤝
CORN
Weather and Corn: Understanding the Precipitation Factor1. Introduction: Rain, Grain, and Market Chain Reactions
In the world of agricultural commodities, few forces carry as much weight as weather — and when it comes to corn, precipitation is paramount. Unlike temperature, which can have nuanced and sometimes ambiguous effects depending on the growth stage, rainfall exerts a more direct and consistent influence on crop performance. For traders, understanding the role of rainfall in shaping market sentiment and price behavior isn't just an agricultural curiosity — it's a trading edge.
This article unpacks the relationship between weekly rainfall levels and corn futures prices. By leveraging normalized weather data and historical returns from Corn Futures (ZC), we aim to translate weather signals into actionable market insights. Whether you're managing large agricultural positions or exploring micro futures like MZC, precipitation patterns can provide vital context for your trades.
2. Corn’s Moisture Dependency
Corn is not just sensitive to water — it thrives or suffers because of it. From the moment seeds are planted, the crop enters a delicate dance with precipitation. Too little moisture during the early stages can impair root development. Too much during germination may lead to rot. And during pollination — particularly the tasseling and silking stages — insufficient rainfall can cause the plant to abort kernels, drastically reducing yield.
On the other hand, excessive rainfall isn't necessarily beneficial either. Prolonged wet periods can saturate soil, hinder nutrient uptake, and encourage fungal diseases. Farmers in the U.S. Corn Belt — particularly in states like Iowa, Illinois, and Nebraska — know this well. A single unexpected weather shift in these regions can send ripple effects across global markets, causing speculators to reassess their positions.
For traders, these weather events aren’t just environmental footnotes — they are catalysts that influence prices, volatility, and risk sentiment. And while annual production is important, it's the week-to-week rhythm of the growing season where short-term trades are born.
3. Our Data-Driven Approach: Weekly Rainfall and Corn Returns
To understand how rainfall impacts price, we collected and analyzed decades of historical weather and futures data, aligning weekly precipitation totals from major corn-growing regions with weekly returns from Corn Futures (ZC).
The weather data was normalized using percentiles for each location and week of the year. We then assigned each weekly observation to one of three precipitation categories:
Low rainfall (<25th percentile)
Normal rainfall (25th–75th percentile)
High rainfall (>75th percentile)
We then calculated the weekly percent change in corn futures prices and matched each return to the rainfall category for that week. The result was a dataset that let us measure not just general trends but statistically significant shifts in market behavior based on weather. One key finding stood out: the difference in returns between low-rainfall and high-rainfall weeks was highly significant, with a p-value of approximately 0.0006.
4. What the Numbers Tell Us
The results are striking. During low-rainfall weeks, corn futures often posted higher average returns, suggesting that the market responds to early signs of drought with anticipatory price rallies. Traders and institutions appear to adjust positions quickly when weather models hint at below-normal moisture during key growth stages.
In contrast, high-rainfall weeks displayed lower returns on average — and greater variability. While rain is essential, excess moisture raises fears of waterlogging, planting delays, and quality issues at harvest. The futures market, ever forward-looking, seems to price in both optimism and concern depending on the volume of rain.
Boxplots of these weekly returns reinforce the pattern: drier-than-usual weeks tend to tilt bullish, while wetter periods introduce uncertainty. For discretionary and algorithmic traders alike, this insight opens the door to strategies that incorporate weather forecasts into entry, exit, and risk models.
📊 Boxplot Chart: Weekly corn futures returns plotted against precipitation category (low, normal, high). This visual helps traders grasp how price behavior shifts under varying rainfall conditions.
5. Strategy: How Traders Can Position Themselves
With the clear statistical link between rainfall extremes and price behavior in corn futures, the logical next step is applying this insight to real-world trading. One straightforward approach is to incorporate weather forecast models into your weekly market prep. If a key growing region is expected to receive below-normal rainfall, that could serve as a signal for a potential bullish bias in the upcoming trading sessions.
This doesn’t mean blindly buying futures on dry weeks, but rather layering this data into a broader trading thesis. For example, traders could combine weather signals with volume surges, technical breakouts, or news sentiment to form confluence-based setups. On the risk management side, understanding how price behaves during extreme weather periods can inform smarter stop-loss placements, position sizing, or even the use of option strategies to protect against unexpected reversals.
Additionally, this information becomes particularly valuable during the planting and pollination seasons, when the corn crop is most vulnerable and the market reacts most strongly. Knowing the historical patterns of price behavior in those weeks — and aligning them with current forecast data — offers a clear edge that fundamental and technical analysis alone may not reveal.
🗺️ Global Corn Map Screenshot: A world map highlighting major corn-growing regions with weather overlay. This helps illustrate the geographic variability in rainfall and how it intersects with key production zones.
6. Corn Futures Contracts: Speculating with Flexibility
For traders looking to act on this kind of seasonal weather intelligence, CME Group provides two practical tools: the standard-size Corn Futures contract (ZC) and the Micro Corn Futures contract (MZC).
Here are some quick key points to remember:
Tick size for ZC is ¼ cent (0.0025) per bushel, equating to $12.50 per tick.
For MZC, each tick is 0.0050 equating to $2.50 per tick.
Standard ZC initial margin is approximately $1,000 and MZC margins are around $100 per contract, though this can vary by broker.
Micro contracts are ideal for those who want exposure to corn prices without the capital intensity of full-size contracts. They’re especially helpful for weather-based trades, where your thesis may rely on shorter holding periods, rapid scaling, or position hedging.
7. Conclusion: Rain’s Role in the Corn Trade
Precipitation isn’t just a farmer’s concern — it’s a trader’s opportunity. Our analysis shows that weather data, especially rainfall, has a statistically significant relationship with corn futures prices. By normalizing historical precipitation data and matching it to weekly returns, we uncovered a clear pattern: drought stress tends to lift prices, while excessive moisture creates volatility and downside risk.
For futures traders, understanding this dynamic adds another layer to market analysis.
As part of a broader series, this article is just one piece of a puzzle that spans multiple commodities and weather variables. Stay tuned for our upcoming releases, where we’ll continue exploring how nature’s forces shape the futures markets.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
THE GREAT CORN GRAB! (Bearish CFD Heist)🌽 THE CORN HEIST: Bearish Raid Plan (Swing/Day Trade) 🚨💰
🌟 Attention, Market Robbers & Money Makers! 🌟
(Hola! Oi! Bonjour! Hallo! Marhaba!)
🔥 Based on the ruthless Thief Trading Style (TA + FA), we’re plotting a bearish heist on the CORN Commodities CFD Market! Time to short like a bandit and escape with profits before the bulls catch us! 🏴☠️💸
🎯 MASTER HEIST PLAN (BEARISH RAID)
Entry Point (Sell Limit / Market):
"The vault is open—swipe the bearish loot at any price!"
🔹 *For safer heists, set sell limits near pullbacks (15M/30M).*
Stop Loss (Escape Route):
📌 Thief SL at nearest swing high (1D timeframe) – 4.4000
📌 Adjust SL based on risk, lot size, & multiple orders.
Profit Target (Escape Before Cops Arrive):
🎯 4.1000 (or exit early if the trap snaps shut!)
🌽 MARKET TREND: NEUTRAL (BEARISH OPPORTUNITY!)
Consolidation zone = Thief’s playground!
Oversold? Maybe. But the real trap is where bullish robbers get slaughtered.
High risk = High reward—only for cold-blooded traders!
📡 FUNDAMENTAL INTEL (DON’T SKIP THIS!)
🔗 Get full reports (COT, Macro, Seasonals, Sentiment, Intermarket Analysis) in our bio0!
🚨 TRADING ALERT: NEWS = DANGER ZONE!
❌ Avoid new trades during news!
🔐 Use trailing stops to lock profits & escape alive!
💥 BOOST THIS HEIST! (HELP US ROB THE MARKET!)
🔥 Hit LIKE & FOLLOW to strengthen our robbery squad!
💸 More heists = More profits. Stay tuned for the next raid!
🐱👤 See you in the shadows, bandits! 🤑🚀
ZCU25 CORN... It ALWAYS comes down to cornAND I'M BACK AND DUMBER THAN EVER
Listen up Honkies, this trade has a 93% probability based on the historical data over the last 30 years. So I bet Muhammad my 3rd ex-wife and a half of my second step child. The reason this trade works is easy! We all have felt and understand FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt) and how the market reacts, I understood this on my second ex-wife when she got a boyfriend. So in late June pollination season occurs with corn and the yield is unknown for the next year, this is a very simple way of looking at the agricultural industry and how the market corrects. The trade is set up in two stages in order to maximize profit. The first stage, with the FUD in pollination season typically results in a 15-20% drop, I split the difference at 17% lets make it easier than my first divorce. This usually occurs around June 26th and can extend to July 17th. Around July 15th to the 20th the projected yield is shared and the market recorrects to the upside as the numbers represented due to the FUD don't represent the price action in the futures market, and because the futures market is speculatory (Adult Gambling) the degens will pump the contracts up looking for a quick buck like my third wife. Now in order to not go broke while you're trying to buy your ex wife's boyfriend's son a new car, you need to hedge the contract in a calendar spread aka intra-commodity spread, so do the opposite in combination on the march 2026 corn contract as the maintance is lower and the price action isn't there due to open interest in the market, so let that contract ride if it goes against you. SO! you short the ZCU25 while longing the ZCH26, then offset the contracts when direction changes and long ZCU25 and short ZCH26, it's as easy as 1,2,8. Had to repost this forgot the Tags my bad.
"all I need is one trade to pay all the alimony for this year."
-KewlKat
CORN.c CORN.c Short Trade Plan (Daily Timeframe)
📍 Trade Setup
Direction: Short
Entry: Instant / Current Market Price (CMP)
Stop Loss (SL): 465.97
Take Profit 1 (TP1): 403.36 (≈ 1:1 Risk-Reward)
Take Profit 2 (TP2): 387.00 (≈ 1:1.5 Risk-Reward)
📊 Technical Justification
Trend: Downtrend confirmed – price forming Lower Highs and Lower Lows.
Candle Pattern: Bearish shooting star near resistance – strong rejection signal.
🌽 Top 3 Bearish Fundamental Reasons
Favorable U.S. Weather Conditions
→ Ideal for crop growth → higher yield expectations → bearish pressure.
Weak Global Export Demand
→ Sluggish corn exports (e.g., China slowdown) → less global demand for U.S. corn.
Strong U.S. Dollar
→ Makes U.S. corn more expensive internationally → lowers export competitiveness.
🎯 Risk Management & Execution Plan
Risk-Reward (TP1): ~1:1
Risk-Reward (TP2): ~1:1.5
📌 Once TP1 is hit:
✅ Move SL to Entry (Breakeven) to protect capital and ride remaining position to TP2.
Corn at the Cliff Edge: Bearish Breakdown or Smart Money Trap?📉 1. Price Action & Technical Context (Weekly Chart – ZC1!)
Price is currently sitting around 439'0, after rejecting the 462'2 supply zone (gray block) and confirming rejection from the macro supply area between 472'6–480'0 (red block).
The last four weekly candles show a failed recovery attempt (three green candles trapped between two strong red ones), culminating in a bearish breakout below the intermediate demand zone (445'0–442'0).
Now, price is back inside the key demand zone between 439'0–433'4, an area with heavy volume and previous significant lows.
🔍 Technical takeaway: Bearish breakout confirmed. Price is testing the last major weekly support before opening the door toward the yearly lows (~420'0).
📊 2. Commitment of Traders (COT Report – May 27, 2025)
Non-Commercials (Speculators):
Long: 324,377 (▼ -17,952)
Short: 344,710 (▼ -9,171)
Net Position: -20,333 → Bearish, but the unwinding of both sides suggests profit-taking.
Commercials (Institutions):
Long: 766,211 (▲ +12,588)
Short: 713,647 (▼ -962)
Net Position: +52,564 → Increasing → Institutional accumulation.
🔎 Key observation: Commercials are increasing their net longs, while speculators are reducing exposure. This diverges from price action and may signal institutional accumulation under 440.
📉 3. Net Positioning vs Price (COT Chart)
The chart shows a clear decline in speculative longs since March, with a new low this week.
Meanwhile, commercials are gradually increasing their long exposure, positioning themselves against the current bearish trend.
💡 Combined view: While price keeps dropping, the "smart money" is accumulating → possible bottom forming, though not yet confirmed technically.
🌾 4. Seasonality
June Performance:
20-Year Avg: -4.25%
15-Year Avg: +12.31%
5-Year Avg: +1.15%
2-Year Avg: +28.61%
📈 Seasonal Conclusion: The seasonal bias has turned strongly bullish in the last 2–5 years. June–July is often a rally period for Corn following the late-May bottoms — likely tied to U.S. planting season dynamics.
Weather and Corn: A Deep Dive into Temperature Impact1. Introduction: Corn and Climate – An Inseparable Relationship
For traders navigating the corn futures market, weather isn't just a background noise—it's a market mover. Few agricultural commodities are as sensitive to environmental variables as corn, especially temperature. Corn is grown across vast regions, and its development is directly tied to how hot or cold the season plays out. This makes weather not just a topic of interest but a core input in any corn trader’s playbook.
In this article, we go beyond conventional wisdom. Instead of simply assuming “hotter equals bullish,” we bring data into the equation—weather data normalized by percentile, matched with price returns on CME Group's corn futures. The results? Useful for anyone trading ZC or MZC contracts.
2. How Temperature Affects Corn Physiology and Yields
At the biological level, corn thrives best in temperatures between 77°F (25°C) and 91°F (33°C) during its growth stages. During pollination—a critical yield-defining window—extreme heat (especially above 95°F / 35°C) can cause irreversible damage. When hot weather coincides with drought, the impact on yields can be catastrophic.
Historical drought years like 2012 and 1988 serve as powerful examples. In 2012, persistent heat and dryness across the US Midwest led to a national yield drop of over 25%, sending futures skyrocketing. But heat doesn't always spell disaster. Timing matters. A heat wave in early June may have little impact. That same wave during tasseling in July? Major consequences.
3. The Market Mechanism: How Traders Respond to Temperature Surprises
Markets are forward-looking. Futures prices don’t just reflect today’s weather—they reflect expectations. A dry June may already be priced in by the time USDA issues its report. This dynamic creates an interesting challenge for traders: separating noise from signal.
During July and August—the critical reproductive phase—temperature updates from NOAA and private forecasters often trigger major moves. Rumors of an incoming heat dome? Corn futures might gap up overnight. But if it fizzles out, retracements can be just as dramatic. Traders who rely on headlines without considering what’s already priced in are often late to the move.
4. Our Analysis: What the Data Reveals About Corn and Temperature
To cut through the fog, we performed a percentile-based analysis using decades of weather and price data. Rather than looking at raw temperatures, we classified each week into temperature “categories”:
Low Temperature Weeks: Bottom 25% of the historical distribution
Normal Temperature Weeks: Middle 50%
High Temperature Weeks: Top 25%
We then analyzed weekly percentage returns for the corn futures contract (ZC) in each category. The outcome? On average, high-temperature weeks showed higher volatility—but not always higher returns. In fact, the data revealed that some extreme heat periods were already fully priced in, limiting upside.
5. Statistically Significant or Not? T-Tests and Interpretation
To test whether the temperature categories had statistically significant impacts on weekly returns, we ran a t-test comparing the “Low” vs. “High” temperature groups. The result: highly significant. Corn returns during high-temperature weeks were, on average, notably different than those during cooler weeks, with a p-value far below 0.01 (4.10854357245787E-13).
This tells us that traders can't ignore temperature anomalies. Extreme heat does more than influence the narrative—it materially shifts price behavior. That said, the direction of this shift isn't always bullish. Sometimes, high heat correlates with selling, especially if it’s viewed as destructive beyond repair.
6. Strategic Takeaways for Corn Traders
Traders can use this information in several ways:
Anticipatory Positioning: Use temperature forecasts to adjust exposure ahead of key USDA reports.
Risk Management: Understand that volatility spikes in extreme temperature conditions and plan stops accordingly.
Calendar Sensitivity: Prioritize weather signals more heavily in July than in May, when crops are less vulnerable.
Combining weather percentile models with weekly return expectations can elevate a trader’s edge beyond gut feel.
7. CME Group Corn Futures and Micro Corn Contracts
Corn traders have options when it comes to accessing this market. The flagship ZC futures contract from CME Group represents 5,000 bushels of corn and is widely used by commercial hedgers and speculators alike. For those seeking more precision or lower capital requirements, the recently launched Micro Corn Futures (MZC) represent just 1/10th the size.
This fractional sizing makes temperature-driven strategies more accessible to retail traders, allowing them to deploy seasonal or event-based trades without excessive risk exposure.
Here are some quick key points to remember:
Tick size for ZC is ¼ cent (0.0025) per bushel, equating to $12.50 per tick.
For MZC, each tick is 0.0050 equating to $2.50 per tick.
Standard ZC initial margin is approximately $1,000 and MZC margins are around $100 per contract, though this can vary by broker.
8. Wrapping Up: Temperature's Role in a Complex Equation
While temperature is a key driver in corn futures, it doesn't act in isolation. Precipitation, global demand, currency fluctuations, and government policies also play crucial roles. However, by quantifying the impact of extreme temperatures, traders gain a potential edge in anticipating market behavior.
Future articles will expand this framework to include precipitation, international weather events, and multi-variable models.
This article is part of a broader series exploring how weather impacts the corn, wheat, and soybean futures markets. Stay tuned for the next release, which builds directly on these insights.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Shady CORN Scheme: Bullish Plot or Market Trap?🌟 Ultimate CORN Heist Strategy: Swing Trade Plan 🌟
Greetings, Wealth Chasers & Market Mavericks! 🤑💸
Ready to pull off a legendary heist in the 🌽 CORN Commodities CFD Market? Our Thief Trading Style blends sharp technicals and fundamentals to craft a high-octane plan for massive gains. Follow the strategy below, stick to the chart, and aim to cash out near the high-risk Red Resistance Zone—an electrified level where overbought conditions, consolidation, or trend reversals could spark traps from bearish bandits. Let’s lock in profits and treat ourselves to the spoils! 💪🎉
📈 Entry Plan: Launch the Heist! 🚀
Wait for a breakout above the Moving Average at 4.5800 to ignite your long entry—bullish riches are calling!
Option 1: Set Buy Stop Orders just above the MA for breakout confirmation.
Option 2: Place Buy Limit Orders on a pullback to the most recent swing low/high within a 15- or 30-minute timeframe.
📢 Pro Tip: Set an alert on your chart to catch the breakout in real-time! ⏰
🛑 Stop Loss: Protect Your Loot! 🔒
For Buy Stop Orders, place your Stop Loss after the breakout confirms to avoid premature exits.
Thief SL Recommendation: Set at the recent swing low on the 4H timeframe (4.4300) for day/swing trades.
Adjust SL based on your risk tolerance, lot size, and number of open orders—play it smart! ⚠️
Feeling rebellious? Set your SL wherever you dare, but don’t blame us if the market bites back! 😎🔥
🎯 Target: Grab the Gold! 🏴☠️
Aim for 4.8000—take partial profits or exit fully before hitting this level.
Scalpers: Stick to long-side scalps. Got deep pockets? Jump in now. Otherwise, join swing traders for the full heist.
Use a trailing Stop Loss to lock in gains and keep your money safe. 💰
🌽 CORN Market Outlook: Why This Heist Works 🌟
The CORN CFD market is currently neutral but shows strong bullish potential, driven by:
📰 Fundamentals: Check macroeconomic data, COT reports, geopolitical events, and news sentiment for a full picture.
📊 Intermarket & Seasonal Analysis: Aligns with favorable positioning and future trend targets.
⚠️ Trading Alert: News & Position Management 🚨
Avoid new trades during major news releases to dodge volatility spikes.
Use trailing Stop Loss orders to secure profits and protect open positions.
Stay updated via reliable sources like Investing.com for real-time news impacting CORN prices.
💥 Boost the Heist! 🚀
Support our Thief Trading Style by hitting the Boost Button to amplify our robbery squad’s strength! 💪 Together, we’ll swipe profits effortlessly every day. Stay tuned for the next heist plan—more riches await! 🤑🐱👤
Let’s make this CORN heist legendary! 🌽💸🎉
The Golden Grain: Trading Corn in Global Markets🟡 1. Introduction
Corn isn’t just something you eat off the cob at a summer barbecue — it’s one of the most widely traded agricultural commodities in the world. Behind every kernel lies a powerful story of food security, global trade, biofuels, and speculative capital.
Whether you’re a farmer managing risk, a trader chasing macro trends, or simply curious about how weather affects global prices, corn futures sit at the crossroads of agriculture and finance. In this article, we’ll explore what makes corn a global economic driver, how it behaves as a futures product, and what traders need to know to approach the corn market intelligently.
🌎 2. Where Corn Grows: Global Powerhouses
Corn is cultivated on every continent except Antarctica, but a handful of countries dominate production and exports.
United States – By far the largest producer and exporter. The “Corn Belt” — spanning Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Nebraska, and parts of Ohio and Missouri — produces the majority of U.S. corn. U.S. exports also set global benchmarks for pricing.
Brazil & Argentina – These two South American powerhouses are crucial to the global corn supply, especially during the Northern Hemisphere’s off-season.
China – Though a top producer, China consumes most of its own supply and has become a key importer during deficit years.
Corn is typically planted in the U.S. between late April and early June and harvested from September through November. In Brazil, two crops per year are common — including the important safrinha (second crop), harvested mid-year.
Understanding where and when corn is grown is vital. Weather disruptions in any of these regions can ripple through the futures market within hours — or even minutes.
💹 3. Corn as a Futures Market Power Player
Corn is one of the most liquid agricultural futures markets in the world, traded primarily on the CME Group’s CBOT (Chicago Board of Trade). It attracts a diverse set of participants:
Producers and Commercials: Farmers, ethanol refiners, and food manufacturers use corn futures to hedge price risk.
Speculators and Funds: Hedge funds and retail traders speculate on corn price direction, volatility, and seasonal patterns.
Arbitrageurs and Spreads: Traders bet on relative price differences between contracts (e.g., old crop vs. new crop spreads).
The deep liquidity and relatively low tick size make corn accessible, but its price is highly sensitive to weather, government reports (like WASDE), and international trade policies.
🏗️ 4. CME Group Corn Futures: What You Can Trade
The CME Group offers both standard and micro-sized contracts for corn. Here’s a quick overview:
o Standard Corn
Ticker: ZC
Size = 5,000 bushels
Tick = 0.0025 = $12.50
Margin = ~$1,050
o Micro Corn
Ticker: XC
Size = 1,000 bushels
Tick = 0.0050 = $2.50
Margin = ~$105
⚠️ Always confirm margin requirements with your broker. They change with market volatility and exchange updates.
The availability of micro corn contracts has opened the door for smaller traders to manage risk or test strategies without over-leveraging.
📊 5. Historical Price Behavior & Seasonality
Corn is deeply seasonal — and so is its price action.
During planting season (April–May), traders watch weekly USDA crop progress reports and early weather forecasts like hawks. A wet spring can delay planting, leading to tighter supply expectations and early price spikes.
Then comes pollination (July) — the most critical stage. This is when heatwaves or drought can do serious damage to yield potential. If temperatures are unusually high or rainfall is scarce during this window, markets often react with urgency, bidding up futures prices in anticipation of reduced output.
By harvest (September–November), prices often stabilize — especially if production matches expectations. But early frost, wind storms, or excessive rain during harvest can still trigger sharp volatility.
Many experienced traders overlay weather models, soil moisture maps, and historical USDA data to anticipate season-driven price shifts.
Even international factors play a role. For example, when Brazil’s safrinha crop suffers a drought, global corn supply tightens — impacting CME prices even though the crop is thousands of miles away.
🧠 6. What Every New Trader Should Know
If you’re new to corn trading, here are some key principles:
Watch the Weather: It’s not optional. Daily forecasts, drought monitors, and precipitation anomalies can move markets. NOAA, Open-Meteo, and private ag weather services are your friends.
Know the Reports: The WASDE report (World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates), USDA Crop Progress, and Prospective Plantings reports can shake up pricing more than you might expect — even if changes seem small.
Mind the Time of Year: Seasonality affects liquidity, volatility, and trader behavior. March–August tends to be the most active period.
Understand Global Demand: The U.S. exports a huge portion of its crop — with China, Mexico, and Japan as major buyers. A tariff tweak or surprise Chinese cancellation can cause wild price swings.
🛠️ Good corn trading is 50% strategy, 50% meteorology.
🧭 This article is part of a broader educational series exploring the relationship between agricultural commodities and weather patterns. In the upcoming pieces, we’ll dive deeper into how temperature and precipitation affect corn, wheat, and soybeans — with real data, charts, and trading insights.
📅 Watch for the next release: “Breadbasket Basics: Trading Wheat Futures.”
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Front-loaded Exports has fuelled rally in Corn. Can it last?After President Trump instituted broad new tariffs on 2nd April 2025, corn futures initially wavered but then rallied sharply. While this may seem counterintuitive given tariffs' disruptive impact on trade, near-term support for corn comes from front-loaded U.S. exports, a weaker dollar, and lower-than-expected domestic supply.
However, prices are likely to face downward pressure as the U.S. harvest season approaches. This paper examines the short-term bullish factors, outlines the potential risks ahead, and presents a hypothetical trade setup involving a calendar spread on CME Micro Corn futures.
CME Corn futures gapped lower on 3rd April but quickly recovered, jumping 4.5% over the next three trading days to six-week highs by 9th April. This move aligns with the typical spring seasonal trend, as corn often firms in late spring during planting & strong demand season.
Surging Export Commitments Amid Tariffs
Export commitments have surged post-tariff announcement. USDA reports that U.S. exporters had already booked about 85% of the 2024/25 season target by early April, according to Reuters , well above the 5‐year average.
In the week ending 3rd April, net U.S. corn sales hit ~40.2 million bushels, reflecting heavy front-loading. Large private sales continue: for example, in early April exporters announced a 9.4-million-bushel sale of 2024/25 corn to Spain.
These front-loaded sales (especially to Mexico & Europe) suggest buyers are rushing to secure supply before possible trade disruptions. Overall, extraordinarily strong export pace and large “flash” sales are underpinning the market.
Supply is Weaker than Initially Thought
USDA’s April WASDE cut U.S. 2024/25 ending stocks to just 1.465 billion bushels – a 75 million bushels reduction – implying a stocks/use ratio around 9.6%. For context, that ratio is near multi-decade lows for corn. The USDA simultaneously raised exports to 2.55 billion bushels, a full 100 million bushels above the previous estimate.
On the supply side, USDA’s Prospective Plantings (March 2025) projected 95.3 million corn acres for 2025, roughly 5% higher than 2024, above expectations (highlighted by Mint Finance in a previous paper ). This suggests that while near-term stocks remain stressed the situation is likely to improve drastically following the harvest.
Weaker Dollar Supports Increased Corn Exports
A key bullish factor for U.S. corn exports is the recent weakness of the U.S. dollar. After the tariff announcement, the trade-weighted dollar tumbled – hitting fresh lows (e.g. a 10-year low versus the Swiss franc). Through April 10, the dollar was down ~2–3% on the week. A weaker dollar makes U.S. corn cheaper for overseas buyers, supporting export competitiveness. With dollar at multi-year lows, U.S. corn is more attractive globally, partly offsetting any Chinese retaliatory tariffs.
COT and Options Data
Managed-money funds have dramatically pared back their long corn bets since the beginning of March. CFTC COT data show net long positions peaking around 364,000 contracts in early February, then plunging to ~54,000 by the 8th April report. However, the pace of decline has slowed dramatically over the past few weeks and seems to be signalling an end of the cutback by asset managers.
Interestingly, despite the tariff introduction (2/April) and the WASDE release (10/April), implied volatility (IV) moderated. IV has since normalized from the spike observed in March. During this period, skew also declined, reaching a negative value on 8th April - indicating that put options briefly became more expensive than calls.
Although this trend has since reversed, skew remains near its lowest levels in 2025, suggesting sustained interest in put options among market participants.
Source: CME CVOL
OI shift over the past week also signals a cautious tone despite the rally. Near term options have seen an increase in put OI, suggesting participants remain cautious despite the rally.
Source: CME QuikStrike
Hypothetical Trade Setup
While bullish factors have driven a sharp rally in corn prices over the past two weeks, there are dark clouds on the horizon. Tariffs risk disrupting trade and as most importers have already loaded up on US corn, they could slow the pace of future purchases.
Additionally, a downbeat seasonal trend along with an expected bumper harvest signal that prices could reverse sharply from here. On the technical front, momentum remains solidly bullish but approaching a potential overbought level amid a slowing bullish trend.
Corn prices remain pressured from a bumper harvest expected in September. Along with expected trade disruptions and a slowdown in the pace of US exports, prices are likely to decline during the summer. Regardless, prices remain bullish in the near term from a weakening dollar and near-term front loading.
To express views on these converging trends, investors can deploy a calendar spread on CME Micro Corn futures consisting of a long position on the near-term May contract (MZCK2025) and a short position on the September contract (MZCU2025). A hypothetical trade setup providing a reward to risk ratio of 1.8x is mentioned below:
A calendar spread on CME Micro Corn Futures is highly capital efficient with the above trade requiring maintenance margin of just USD 23 as of 15/April. The position remains protected from near-term price increase but benefits from the eventual price decline in September during harvest season.
MARKET DATA
CME Real-time Market Data helps identify trading set-ups and express market views better. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs tradingview.com/cme .
DISCLAIMER
This case study is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment recommendations or advice. Nor are they used to promote any specific products, or services.
Trading or investment ideas cited here are for illustration only, as an integral part of a case study to demonstrate the fundamental concepts in risk management or trading under the market scenarios being discussed. Please read the FULL DISCLAIMER the link to which is provided in our profile description.
Inflation Leading Indicator Data with Agricultural Commodities Inflation leading indicator data is not derived solely from CPI numbers; more importantly, we must consider what drives these CPI numbers. By understanding this, we can stay ahead of the mass market.
Looking at past trends, we can observe that CPI numbers and agricultural commodities tend to move in tandem.
In this discussion, we will explore why agricultural commodities are an effective tool for projecting inflation direction and examine where these commodities may be heading.
Micro Agriculture Futures:
. Corn: MZC
. Wheat: MZW
. Soybean: MZS
. Soybean Oil: MZL
. Soybean Meal: MZM
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
Trading the Micro: www.cmegroup.com
Short Idea On ZC1! (Corn)1)On Cot data,we can see the commercials shorting at the extremes.
2)Seasonality gives us a short bias and quantitative data shows 80% win rate for shorts.
3) We overvalued on daily and weekly timeframe against several benchmarks
4) On weekly timeframe,the price rejected the EMA Forming a Pin bar reversal
5) I set the entry and stoploss on the supply structure as you can see in the picture
What Lies Beyond the Cornfield's Horizon?The narrative of corn in the global agricultural scene is not merely about sustenance but a complex ballet of economics, innovation, and policy. This staple crop stands at the intersection of international trade, with U.S. farmers gaining a foothold in Mexico's market through a significant legal victory against GMO corn restrictions, highlighting the nuanced dance between technology and trade agreements. Meanwhile, Brazil's agricultural strategies reveal a shift towards leveraging corn for ethanol, showcasing a potential future where corn could play an even more pivotal role in sustainable energy solutions.
In science and technology, the development of digital corn twins presents a frontier in crop breeding. This innovative approach could redefine how we think about plant resilience and efficiency, potentially leading to crops tailored to withstand the capricious whims of climate change. The challenge lies in translating theoretical models into practical, field-ready solutions that can benefit farmers and consumers alike.
However, the journey isn't without its threats. The unexpected rise of corn leaf aphids in 2024 serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing battle with nature's unpredictability. Farmers are now challenged to anticipate and manage these pests, pushing the boundaries of traditional farming practices into more predictive, data-driven methodologies. This situation beckons a broader inquiry into how agriculture can evolve not just to react but preemptively adapt to ecological shifts.
As we look beyond the cornfield's horizon, we see a landscape where policy, technology, and biology converge. The future of corn involves navigating this triad with foresight, ensuring that each step taken today not only secures current yields but also plants the seeds for a sustainable agricultural legacy. This exploration into corn's evolving role invites us to ponder how we can harness these developments for a future where food security and environmental stewardship walk hand in hand.
crypto is crypto, but do you need to buy corn? - If the trend line breaks, this is the beginning of a bullish trend.
- a Formulated is Golden Cross Moving Average
- the reason for the rise in corn prices is the decrease in the EU corn harvest in 2024/25. This is the third consecutive year of poor harvest.
If you have anything to add, please write in the comments.
Behind the Curtain: Economic Indicators Shaping Corn Futures1: Introduction
Corn Futures (ZC), traded on the CME, play a vital role in global markets, particularly in the agriculture and food industries. As a commodity with widespread applications, Corn Futures are influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from seasonal weather patterns to broader economic trends. Understanding these influences is critical for traders seeking to navigate the market effectively.
In this article, we leverage machine learning, specifically a Random Forest Regressor, to identify key economic indicators that have historically correlated with Corn Futures' price changes. By analyzing daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes, we aim to provide a clearer picture of how these indicators potentially shape market behavior and offer actionable insights for traders.
The findings are presented through visual graphs highlighting the top economic indicators across different timeframes. These insights can help traders fine-tune their strategies, whether for short-term speculation or long-term investment.
2: Understanding the Key Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide a glimpse into various facets of the economy, influencing commodity markets such as Corn Futures. Using the Random Forest model, the following indicators emerged as significant for Corn Futures on different timeframes:
Daily Timeframe:
Oil Import Price Index: Reflects the cost of importing crude oil, impacting energy costs in agriculture, such as fuel for equipment and transportation.
Durable Goods Orders: Tracks demand for goods expected to last three years or more, often signaling broader economic activity that can influence commodity demand.
Natural Gas Prices: Critical for the production of fertilizers, which directly impacts corn farming costs.
Weekly Timeframe:
China GDP Growth Rate: Indicates global demand trends, as China is a major consumer of agricultural products.
Housing Starts: Reflects construction activity, indirectly influencing economic stability and consumer behavior.
Corporate Bond Spread (BAA - 10Y): A measure of credit risk that can signal changes in business investment and economic uncertainty.
Monthly Timeframe:
Retail Sales (YoY): Gauges consumer spending trends, a crucial driver of demand for corn-based products.
Initial Jobless Claims: Acts as a measure of labor market health, influencing disposable income and consumption patterns.
Nonfarm Productivity: Indicates economic efficiency and growth, impacting broader market trends.
By understanding these indicators, traders can interpret their implications on Corn Futures more effectively.
3: How to Use This Information
The timeframes for these indicators provide unique perspectives for different trading styles:
Daily Traders: Indicators like the Oil Import Price Index and Natural Gas Prices, which are highly sensitive to short-term changes, are valuable for high-frequency trading strategies. Daily traders can monitor these to anticipate intraday price movements in Corn Futures.
Swing Traders (Weekly): Weekly indicators, such as the China GDP Growth Rate or Housing Starts, help identify intermediate-term trends. Swing traders can align their positions with these macroeconomic signals for trades lasting several days or weeks.
Long-Term Traders (Monthly): Monthly indicators, such as Retail Sales and Nonfarm Productivity, provide insights into overarching economic trends. Long-term traders can use these to assess demand-side factors impacting Corn Futures over extended periods.
Additionally, traders can enhance their strategies by overlaying these indicators with seasonal patterns in Corn Futures, as weather-related supply shifts often coincide with economic factors.
4: Applications for Risk Management
Understanding the relationship between economic indicators and Corn Futures also plays a critical role in risk management. Here are several ways to apply these insights:
Refining Entry and Exit Points: By correlating Corn Futures with specific indicators, traders can potentially time their entries and exits more effectively. For example, a sharp rise in the Oil Import Price Index might signal increased production costs, potentially pressuring corn prices downward.
Diversifying Trading Strategies: Leveraging daily, weekly, and monthly indicators allows traders to adapt their strategies across timeframes. Short-term volatility from energy prices can complement long-term stability signals from broader economic metrics like GDP Growth.
Mitigating Uncertainty: Tracking indicators such as Corporate Bond Spreads can provide early warnings of economic instability, helping traders hedge their Corn Futures positions with other assets or options.
Seasonal Hedging: Combining indicator-based insights with seasonal trends in Corn Futures can enhance risk-adjusted returns. For instance, aligning hedging strategies with both economic and weather-related factors could reduce downside exposure.
5: Conclusion
The analysis highlights how diverse economic indicators shape Corn Futures prices across multiple timeframes. From daily volatility influenced by energy costs to long-term trends driven by consumer spending and productivity, each indicator provides unique insights into market dynamics.
Traders can use this framework not only for Corn Futures but also for other commodities, enabling a more data-driven approach to trading. The combination of machine learning and economic analysis presents opportunities to refine strategies and improve outcomes in the competitive world of futures trading.
Stay tuned for the next article in this series, where we delve into another futures market and its relationship with key economic indicators.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
The Fed Signals Commodity TrendThe Fed signals that the commodity trend may be moving higher. In the latest FOMC meeting, the Fed lowered rates by a quarter point.
Contrary to the expectations of many analysts who anticipated more cuts in 2025, they signaled only two rate cuts next year, reflecting greater caution about the pace of further reductions in borrowing costs.
So, how is this being interpreted as an indication that the commodity trend may be moving higher?
Corn Futures & Options
Ticker: ZC
Minimum fluctuation:
1/4 of one cent (0.0025) per bushel = $12.50
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
Corn Futures: New All Time Highs Ahead 10x potential CBOT:ZC1! Straight forward MACRO LONG to new ALL TIME HIGH. Easy 2x upside to previous all time high within a year and 5-10x upside within the next couple of years. There is a huge fair value gap or unbalanced zone to the upside (yellow) to be filled. The 3 month chart has finally started to show signs of reversal as price retraced to a key high volume zone (gray) and printed a bullish hammer candle.
Weekly timeframe is lacking strength and looking like it wants to retest the low $400's. Rather wait for a further retrace or jump in upon a break of previous highs.
Options Blueprint Series [Basic]: Corn Futures and PPI InsightsIntroduction to Corn Futures Market Sentiment
Corn Futures are capturing the interest of traders as technical indicators and economic fundamentals align in a potential bullish setup. Currently, the Corn Producer Price Index (PPI) shows a Commodity Channel Index (CCI) bullish crossover, indicating a possible uptrend in prices. Corn Futures have followed suit with an earlier CCI bullish crossover, adding strength to the view that Corn prices could see upward momentum in the coming months.
As Corn Futures reflect early signals of a shift in market sentiment, this article explores a straightforward yet effective Bull Call Spread strategy using June 2025 options. By leveraging these CCI signals and key resistance levels, traders could position themselves to benefit from a potential rise in Corn prices while maintaining a controlled risk profile.
Corn Futures Contract Specifications and Margin Requirements
Understanding the specifications of Corn Futures is essential for managing both position size and margin requirements effectively. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Price Tick Size: The minimum fluctuation is 0.0025 cents per bushel, equivalent to $12.50 per tick.
Margin Requirement: Approximately $1,000 per contract, although this can vary based on broker and market conditions.
Analysis of Key Indicators and Market Setup
Two primary indicators support the bullish case for Corn Futures: the CCI bullish crossover in both the Corn Futures and the Corn PPI. The CCI, a momentum-based indicator, identifies potential trend reversals by highlighting overbought and oversold conditions. The recent CCI bullish crossover in Corn Futures suggests early buying pressure, while the subsequent crossover in the Corn PPI confirms this trend on the economic front.
This alignment between technical and economic indicators provides a potentially unique opportunity for options traders to capture potential upward movement, particularly as Corn prices approach critical resistance levels in front of a potential breakout.
Identifying Key Resistance Levels for Corn Futures
Resistance levels play a crucial role in setting realistic targets and managing expectations. In the current Corn Futures landscape, the primary resistance level for the front contract is observed around 550. For our target contract, ZCN2025 (July 2025), this resistance translates to approximately 485 due to the effects of contango/backwardation.
These resistance levels serve as benchmarks for setting exit targets in a Bull Call Spread. If Corn prices rally towards this zone, it could provide a favorable exit opportunity while maintaining a controlled risk-to-reward structure.
The Bull Call Spread Strategy Setup
In this setup, we employ a Bull Call Spread using options with a June 20, 2025, expiration date. This strategy is ideal for capturing moderate upside movement while limiting downside risk through a capped loss. Here’s the specific setup:
Long Position: Buy the 460 Call for a premium of 25.41.
Short Position: Sell the 490 Call for a premium of 15.87.
By buying the 460 Call and simultaneously selling the 490 Call, we establish a Bull Call Spread that allows us to benefit from price increases up to the 490 strike level. This setup reduces the net cost of the trade while capping the profit potential at the 490 strike price, aligning with our outlook based on resistance levels.
Net Premium (Cost): 25.41−15.87=9.54.
Reward-to-Risk Analysis
A Bull Call Spread provides a straightforward way to define both maximum profit and loss at the outset. Here’s a closer look:
Maximum Profit: Achieved if Corn Futures price rises to or above the 490 strike level at expiration = (490−460)−9.54=20.46.
Maximum Loss: Limited to the net premium paid = 9.54.
Breakeven Point: 469.54, calculated by adding the net premium to the 460 strike.
This structure results in a reward-to-risk ratio of approximately 2.14:1.
Forward-Looking Trade Plan and Execution Strategy
This Bull Call Spread strategy is structured with specific entry and exit conditions in mind:
Entry Condition: Triggered once the ZC1! (continuous Corn Futures contract) surpasses the prior month’s high at 434'2. This confirmation aligns the technical breakout with the ongoing bullish trend indicated by the CCI and PPI crossovers.
Target Exit: Based on the resistance level, the target for this trade is 485 on the ZCN2025 contract. Reaching this level would allow for a strategic exit with a maximum profit potential.
Alternative Exit: If Corn Futures prices fail to sustain the breakout or if technical indicators weaken significantly, an early exit can be considered to limit losses or preserve gains.
By setting these clear parameters, the trade plan maintains discipline, helping traders avoid reactive decision-making and align with the predefined strategy.
Risk Management Essentials
Effective risk management is crucial, especially when trading options. Here are some best practices:
Stop-Loss Strategy: For options traders, a stop-loss can be set based on a percentage of the premium paid or by monitoring underlying futures price action.
Position Sizing: Limit the size of the position relative to the account balance to avoid overexposure. This is especially relevant for volatile markets like Corn.
Discipline and Emotional Control: Stick to the plan, avoid emotional reactions to market noise, and adhere to entry and exit conditions.
Risk management ensures that even if the trade does not perform as expected, losses are limited and capital is preserved for future opportunities.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies. Also, some of the calculations and analytics used in this article have been derived using the QuikStrike® tool available on the CME Group website.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Children Of The CornCorn Should go Up. exponential m.a. is popping. Wanted to do some Futures type here. This should be a decent, Steady gainer.
~Careful not to step on corn-flakes, you wouldn’t want to become a cereal-killer.
~The corn stalk decided to change careers. He went into a completely different field.
~Plain popcorn? I’m sorry, but you're going to have to do a lot butter than that.
This One should mint us some Green...
Corn Reversal: Classical 5 bar trend confirmed!Corn CBOT:ZC1! is showing signs of a reversal, and it has confirmed the following:
The daily trend was activated at yesterday's close, with enough momentum to push above 450.
The weekly trend is also active, following a classic five-bar trend pattern, indicating a strong reversal signal.
Once it reclaims 433, it should quickly move toward the first target of 466.
If everything aligns as expected, it could aim for a break of the current trend. For now, it’s important to take it level by level.