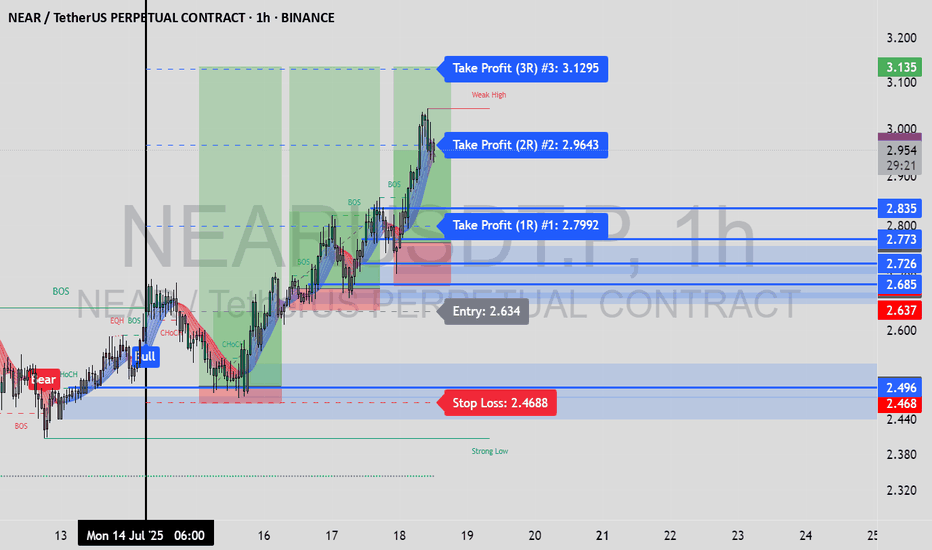
Mastering supply and demand zones - how to use it in trading?Supply and demand zones are key concepts in technical analysis used by traders to identify potential price reversal areas on a chart. They are based on the idea that prices move due to an imbalance between buyers (demand) and sellers (supply).
-------------------------
What will be discussed?
- What are supply and demand zones?
- How to detect supply and demand zones?
- Examples from supply and demand zones?
- How to trade using supply and demand zones?
-------------------------
What are supply and demand zones?
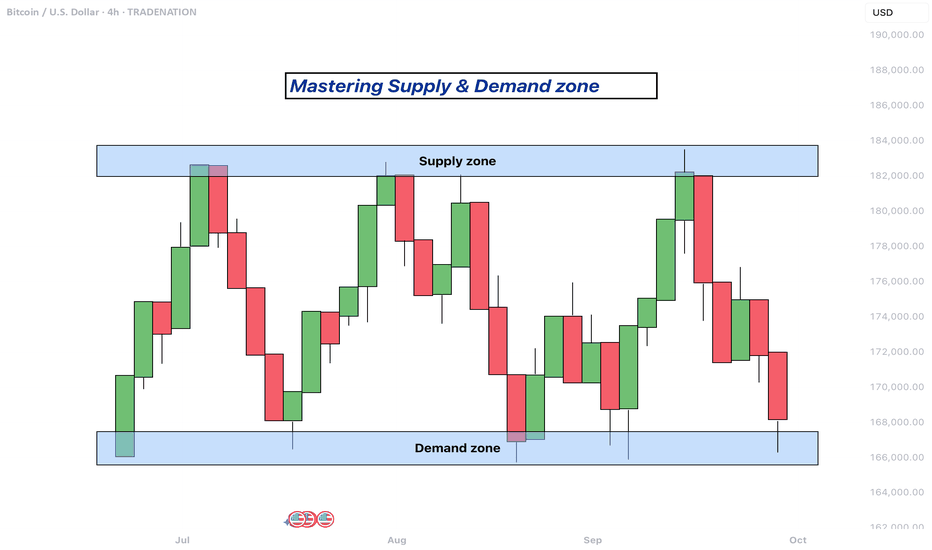
Supply and demand zones are areas on a price chart where the forces of buying and selling are strongly concentrated, causing significant movements in price. In simple terms, a supply zone is an area where selling pressure exceeds buying pressure, often leading to a drop in price. It usually forms when price moves upward into a region where sellers begin to outnumber buyers, pushing the price back down. On the other hand, a demand zone is a region where buying pressure exceeds selling pressure, typically resulting in a rise in price. This occurs when price moves downward into a region where buyers see value and begin to outnumber sellers, causing the price to increase again.
These zones reflect areas of imbalance in the market. In a supply zone, sellers are more eager to sell than buyers are to buy, often due to overbought conditions, news, or fundamental changes. In a demand zone, buyers are more eager to buy than sellers are to sell, often because the price has become attractive or undervalued. Traders look for these zones because they provide clues about where price may reverse or stall, offering potential entries or exits for trades.
-------------------------
How to detect supply and demand zones?
Identifying supply and demand zones involves analyzing price action on a chart, typically using candlestick patterns. A common way to detect a supply zone is to look for a sharp upward move followed by a sudden reversal or strong drop in price. The area where the price stalled before falling sharply is likely to be a supply zone. This zone includes the highest candle body or wick before the drop, and a few candles before it that mark where the selling pressure began.
To identify a demand zone, you would look for a sharp drop in price followed by a strong rally upward. The area where the price paused before rising significantly can be considered a demand zone. Like with supply zones, the demand zone includes the lowest candle before the price reversed and a few candles leading up to it.
These zones are not exact price levels but rather ranges. Price does not have to touch an exact line to react; it often moves within the general area. For more accuracy, traders often refine their zones by identifying them on higher time frames such as the 4-hour or daily chart, then adjusting them slightly on lower time frames like the 1-hour or 15-minute chart.
-------------------------
Examples from supply and demand zones:
-------------------------
How to trade using supply and demand zones?
Trading supply and demand zones involves anticipating how price is likely to behave when it returns to one of these key areas. A common method is to wait for price to enter a zone and then watch for confirmation that it is going to reverse. For example, if price rises into a supply zone, you might look for signs like a bearish candlestick pattern, a drop in volume, or a rejection wick to signal that sellers are stepping in again. This would be an opportunity to enter a short trade with the expectation that price will fall.
Conversely, if price falls into a demand zone, you would wait for bullish signals—such as a strong bullish candle, a double bottom pattern, or clear rejection of lower prices—to confirm that buyers are returning. This would be a potential setup for a long trade, expecting the price to move up from the zone.
Traders often place stop losses just beyond the zone to limit risk in case the level fails. For a supply zone, the stop loss would go just above the zone, while for a demand zone, it would go just below. Targets can be set at recent support or resistance levels, or by using risk-reward ratios like 1:2 or 1:3 depending on the trader’s strategy.
Patience and discipline are important when trading these zones. Not every zone will lead to a reversal, and false breakouts can occur. Therefore, combining supply and demand analysis with other tools such as trendlines, moving averages, or indicators can improve the chances of a successful trade.
In summary, supply and demand zones help traders understand where large buying or selling forces are likely to influence price. By learning to identify these zones and waiting for confirmation signals, traders can enter high-probability trades with clear risk and reward levels.
-------------------------
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Thanks for your support. If you enjoyed this analysis, make sure to follow me so you don't miss the next one. And if you found it helpful, feel free to drop a like and leave a comment, I’d love to hear your thoughts!
Community ideas
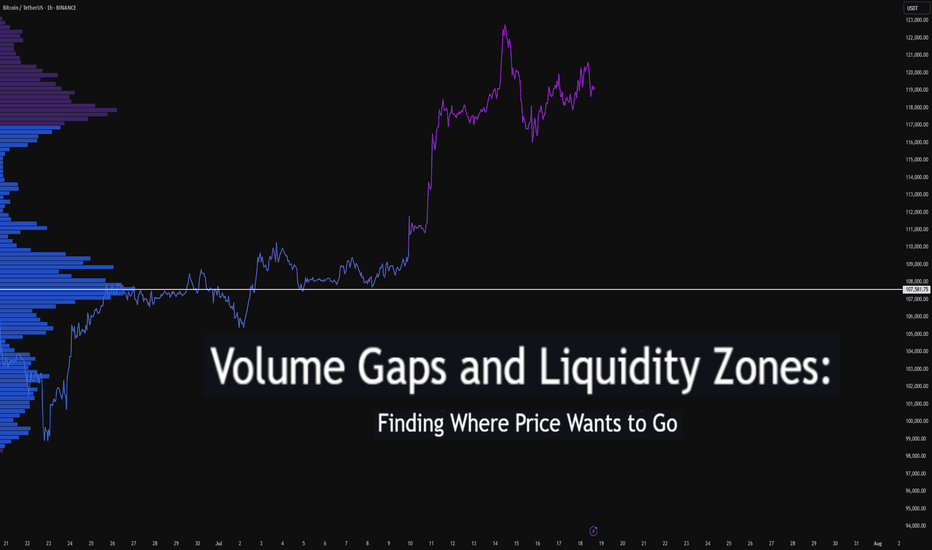
Volume Gaps and Liquidity Zones: Finding Where Price Wants to GoDifficulty: 🐳🐳🐳🐋🐋 (Intermediate+)
This article is best suited for traders familiar with volume profile, liquidity concepts, and price structure. It blends practical trading setups with deeper insights into how price seeks inefficiency and liquidity.
🔵 INTRODUCTION
Ever wonder why price suddenly accelerates toward a level — like it's being magnetized? It’s not magic. It’s liquidity . Markets move toward areas where orders are easiest to fill, and they often avoid areas with little interest.
In this article, you’ll learn how to identify volume gaps and liquidity zones using volume profiles and price action. These tools help you anticipate where price wants to go next — before it gets there.
🔵 WHAT ARE VOLUME GAPS?
A volume gap is a price region with unusually low traded volume . When price enters these areas, it often moves quickly — there’s less resistance.
Think of a volume gap as a thin patch of ice on a frozen lake. Once the market steps on it, it slides across rapidly.
Volume gaps usually show up on:
Volume Profile
Fixed Range Volume tools
Session or custom volume zones
They’re often created during impulsive moves or news events — when price skips levels without building interest.
🔵 WHAT ARE LIQUIDITY ZONES?
Liquidity zones are price areas where a large number of orders are likely to be sitting — stop losses, limit entries, or liquidation levels.
These zones often form around:
Swing highs and lows
Order blocks or fair value gaps
Consolidation breakouts
Psychological round numbers
When price approaches these areas, volume often spikes as those orders get filled — causing sharp rejections or breakouts.
🔵 WHY THIS MATTERS TO TRADERS
Markets are driven by liquidity.
Price doesn’t just move randomly — it hunts liquidity, clears inefficiencies, and fills orders.
Your edge: By combining volume gaps (low resistance) with liquidity zones (target areas), you can forecast where price wants to go .
Volume gap = acceleration path
Liquidity zone = destination / reversal point
🔵 HOW TO TRADE THIS CONCEPT
1️⃣ Identify Volume Gaps
Use a visible range volume profile or session volume. Look for tall bars (high interest) and valleys (low interest).
2️⃣ Mark Liquidity Zones
Use swing highs/lows, OBs, or EQH/EQL (equal highs/lows). These are magnet areas for price.
3️⃣ Watch for Reactions
When price enters a gap, expect speed.
When it nears a liquidity zone, watch for:
Volume spike
Wick rejections
S/R flip or OB retest
🔵 EXAMPLE SCENARIO
A strong bearish move creates a volume gap between 103 000 – 96 000
Below 96 000 sits bullish order blocks — clear liquidity
Price enters the gap and slides fast toward 96 000
A wick forms as buyers step in, volume spikes — the reversal begins
That’s price filling inefficiency and tapping liquidity .
🔵 TIPS FOR ADVANCED TRADERS
Use higher timeframes (4H/1D) to define major gaps
Look for overlapping gaps across sessions (Asia → London → NY)
Align your trades with trend: gap-fills against trend are riskier
Add OB or VWAP as confirmation near liquidity zones
🔵 CONCLUSION
Understanding volume gaps and liquidity zones is like reading the market’s intention map . Instead of reacting, you start predicting. Instead of chasing, you’re waiting for price to come to your zone — with a plan.
Price always seeks balance and liquidity . Your job is to spot where those forces are hiding.
Have you ever traded a volume gap into liquidity? Share your setup below
From Liquidation to Withdrawal, It’s the MapDo you remember your first heavy loss? That exact moment when you realized trading isn’t just about patterns and candles?
This analysis is for you if you’re looking for a path to escape that liquidation pit and actually make your first real withdrawal.
No hype, no signals just a practical roadmap built on experience and mistakes.
Hello✌
Spend 3 minutes ⏰ reading this educational material.
🎯 Analytical Insight on Cardano:
BINANCE:ADAUSDT is testing a crucial daily support near the 0.38 Fibonacci retracement level, setting up for a potential 16% upside toward the key psychological and monthly resistance at $1. If this level holds, ADA could confirm bullish momentum and target higher levels soon. 📊🚀
Now , let's dive into the educational section,
🧭 It All Starts With the Tools
Before anything else, you need a compass and in trading, that compass is made of tools you can actually use on TradingView.
Here are some tools that serious traders never ignore, especially when analyzing crowd behavior and institutional traps:
Volume Profile (Fixed Range)
Shows you where money is actually concentrated, not just where price is. High-volume nodes often become breakout or breakdown zones in days ahead.
Liquidity Zones – Custom Indicators
Search for "liquidity" or "order block" in the Indicators section. There are tons of free community scripts that help you spot stop-loss clusters the exact places where the market loves to hunt.
Relative Volume (RVOL)
Tells you how strong the current market move is compared to its average volume. Is this a real breakout, or just noise? RVOL helps answer that.
Session Volume & Time-Based Boxes
Use drawing tools to box London, New York, or Asia sessions. This lets you track where real money enters. Time matters volume without time is meaningless.
Got the tools? Great. But now what? Let’s walk the path...
🚪 The Entry Point: First Liquidation
Almost every trader starts here: a signal, a rushed entry, a tight stop... then liquidation or a brutal margin call.
But that exact moment? It’s not your failure. It’s the beginning of your real journey.
Ask yourself:
Why did I take that trade?
What tool was available but ignored?
Was my position size reasonable or emotional?
Analyze this moment deeper than you analyze Bitcoin’s chart.
🔁 Repeat or Reroute?
This is the loop most traders never escape.
They stay stuck between losses because they don’t reflect, don’t learn, and don’t adjust.
What you should do instead:
Start a trade journal raw and honest.
Use TradingView as your lab, not just a chart. Practice, backtest, fail, and fix.
🧠 Turning Point: Where Your Mind Starts Trading
Once you stop chasing profit and start chasing clarity, things shift.
You begin spotting real triggers, real volume, and real market intent.
Here’s where tools become meaningful:
Use OBV to confirm volume alignment
Let RSI tell you about weakness before reversal
Follow EMA50/EMA200 to map trend structure
Not because someone told you to but because now you know why and when to use them.
🤑 The First Real Withdrawal Isn’t From Your Wallet
The first "withdrawal" isn’t a bank transfer.
It’s when you can walk away from the market without FOMO, without guilt, and without overtrading.
You now:
Accept risk, every single trade
Respect the market, not fear it
Have patience not because you're lazy, but because you understand timing
That’s the real payout.
📌 Final Thoughts
The path to becoming a trader starts with loss, grows with tools, and ends with discipline.
TradingView isn’t just for charts it’s your practice field.
Before chasing the next win, start by understanding your last mistake.
✨ Need a little love!
We pour love into every post your support keeps us inspired! 💛 Don’t be shy, we’d love to hear from you on comments. Big thanks , Mad Whale 🐋
📜Please make sure to do your own research before investing, and review the disclaimer provided at the end of each post.
In trading, the long way is the shortcut⚠️ The Shortcut Is an Illusion — And It Will Cost You
In trading, everyone wants to arrive without traveling.
They want the profits, the freedom, and the Instagram lifestyle — even if it’s fake.
What they don’t want is the process that actually gets you there.
So they chase shortcuts:
• Copy signals without understanding the reason behind them
• Over-leverage on “the perfect setup”
• Buy indicators they don’t know how to use
• Skip journaling and backtesting
• Trade real money without trading psychology
And then they wonder…
Why is my account bleeding?
Why does this feel like a cycle I can't break?
Because:
Every shortcut in trading is just a fast track to disaster.
You will lose. You will restart. And it will take even longer than if you just did it right the first time.
🤡 The TikTok Fantasy: “1-Minute Strategy That Will Make You Millions in 2025”
This is the new wave:
A 60-second video showing you a magical indicator combo.
No context. No testing. No risk management.
Just fake PnL screenshots and promises of millionaire status before next summer.
“This 1-minute scalping strategy made me $12,000 today!”
And people fall for it… because it’s easier to believe in shortcuts than to accept that real trading is boring, repetitive, and hard-earned.
If it fits in a TikTok video, it’s not a strategy. It’s clickbait.
________________________________________
❓ Looking for a System Without Knowing the Basics
Here’s the paradox:
Most people are desperate to find a “profitable strategy” — but they haven’t even mastered the basic math of trading.
• They don’t know how pip value is calculated
• They don’t understand how leverage works
• They confuse margin with risk
• They size positions emotionally, not based on their account
• They can’t define what 1% risk per trade actually means in dollars
But they’re out here, loading indicators, watching YouTube “hacks,” and flipping accounts with 1:500 leverage.
Imagine trying to perform surgery before learning anatomy.
That’s what trying to trade a strategy without knowing pip cost looks like.
________________________________________
🛠️ The Long Way Is the Fastest Way
You want the real shortcut?
Here it is:
• Learn price structure deeply
• Backtest like a scientist
• Journal like a professional
• Risk small while you're learning
• Stay on demo until your edge is proven
• Master basic math: leverage, margin, pip value, position sizing
This is the long way.
But it’s the only way that doesn’t end in regret.
________________________________________
⏳ Most Traders Waste 2–5 Years Looking for a Shortcut
And in the end?
They crawl back to the long path.
Broke, humbled, and wishing they had just started there from the beginning.
The shortcut is a scam.
The long way is the only path that leads to consistency.
You either take it now… or take it later — after your account pays the price.
________________________________________
✅ Final Thought
Don’t ask how fast you can get profitable.
Ask how solid you can build your foundation.
Because in trading:
❌ The shortcut costs you everything
✅ The long way gives you everything
And the longer you avoid it, the longer it takes.
WHY DO YOU KEEP ASKING ABOUT PRICE SO MUCH?WHY DO YOU KEEP ASKING ABOUT PRICE SO MUCH?
The problem lies in the wrong frame of reference when you first enter the market. Faulty input leads to flawed thinking, resulting in poor actions and bad outcomes.
I constantly receive questions like:
“Can I buy at this price yet?”
“Should I wait for a lower price?”
“Is this the bottom?”
“BTC is at 108k, is it still good to LONG?”
“It’s at 123k now, will it go to 180k?”
All of these revolve around PRICE, but in reality, price isn't what you should focus on. What's important is understanding market movements and trends.
Many of you DCA blindly at resistance, support, or based on on-chain data, thinking the price will reverse or bounce… but it doesn’t. So why?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Let me give you an analogy:
Imagine you're hiking the Alps.
You start early in the morning. When you're tired, you rest. When the scenery is beautiful, you stop and enjoy it. When you're thirsty or hungry, you take a break. Eventually, you reach the top (PEAK).
Did you ever ask your friend along the way:
"How many meters have we climbed?"
"How many meters left to the top?"
Of course not.
You just know you're ascending, and when you reach the peak, you’ll know.
Uptrend is like climbing up, downtrend is climbing down.
You don’t need to know your exact altitude — you just need to know whether you’re going up or down, and when you’re at the top, you’ll feel it.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The market is the same.
When it goes up, you know it’s going up.
When it goes down, you know it’s going down.
When it’s the peak, you’ll know.
When it’s the bottom, you’ll feel it.
There's no need to obsess over:
“Is this the top?”
“Is this the bottom?”
Why?
Because when you're fixated on the real-time price, without understanding market movement, you’re being led by price — not leading your trades.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In summary:
Stop letting price control your mind.
Focus on trends and market movement, and you’ll know where you are.
When climbing, you know you’re climbing. When peaking, you’ll know it’s time to pause. Simple as that.
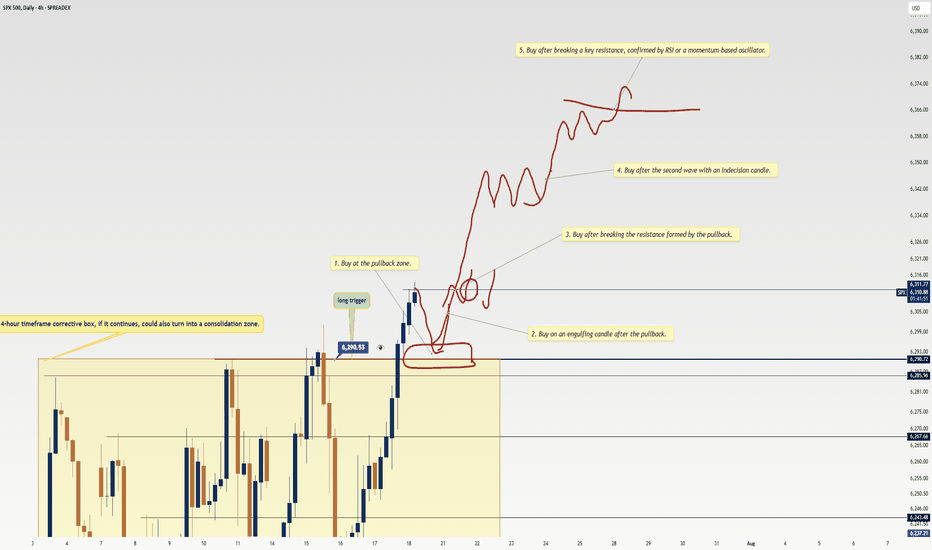
5 Proven Tricks to Trade Without FOMO After Missing Your TriggerYo traders! In this video, I’m breaking down what to do if you miss a trading trigger , so you can stay calm , avoid FOMO , and still catch the next move. We’re diving into five solid strategies to re-enter the market without losing your cool:
Buy on the pullback zone.
Buy with an engulfing candle after a pullback.
Buy after breaking the resistance formed by the pullback.
Buy after the second wave with an indecision candle.
Buy after breaking a major resistance post-second wave, confirmed by RSI or momentum oscillators.
These tips are all about keeping your trades smart and your head in the game. For more on indecision candles, check out this lesson . Wanna master breakout trading? Here’s the breakout trading guide . Drop your thoughts in the comments, boost if you vibe with it, and let’s grow together! 😎
Advanced Order Types in ECN TradingAdvanced Order Types in ECN Trading
Electronic Communication Networks (ECN) have transformed the landscape of financial trading, offering direct market access and enhanced transparency. Central to ECN trading is the use of various order types, each tailored to specific strategies and risk management approaches. This article delves into advanced order types, providing traders with essential knowledge for navigating this dynamic trading environment.
Understanding ECN Trading
Electronic Communication Network (ECN) trading represents a pivotal development in financial markets, offering a pathway for traders to connect directly with each other without requiring intermediaries. This system functions through an electronic network that efficiently matches buy and sell trades, contributing to greater transparency and tighter spreads in the market.
In an ECN environment, traders can see the best available bid and ask prices, along with the market depth, which includes potential entries from various market participants. This visibility into the market's order book enables more informed decision-making as traders gain insights into potential market movements and liquidity.
A key advantage of ECNs is the anonymity they provide, enabling traders to execute transactions without exposing their strategy. This feature is particularly effective for large-volume traders who wish to avoid market impact.
ECN brokers, tend to offer lower costs compared to traditional market makers, as they typically charge a fixed commission per transaction rather than relying on the bid-ask spread. Such a cost structure can be advantageous for active traders and those employing high-frequency trading strategies.
Basic Market Order Types Explained
Forex and CFD trading involves several different order types, each serving unique strategies and goals. Among the most fundamental are market, limit and stop orders:
- Market: This type allows traders to buy or sell an asset at the current price. It's designed to offer immediate execution, making it ideal for traders who prioritise speed over control. They’re used when certainty of execution is more important than the execution price.
- Limit: Limit orders enable traders to specify the level at which they wish to buy or sell. A buy limit is set below the current price, while a sell limit is above. This type is used when traders seek to control the rate, accepting the risk of the entry not being filled if the market doesn’t reach their specified level.
- Stop: Stop orders act as a trigger for a trade. When the asset reaches the specified stop level, the stop becomes a market entry and executes a trade at the current price. It's a simple yet effective way to enter or exit the market at a predetermined point.
Advanced ECN Order Types
Advanced order types offer traders nuanced control over their transactions, catering to specific strategies and risk management needs. Here, we delve into three types: stop losses, trailing stops, and icebergs.
- Stop Loss: These are designed to limit a trader's loss on a position. A stop-loss order automatically sells (or buys, in the case of a short position) when the asset hits a predefined level. This tool is crucial in risk management, as it helps traders cap potential losses without the need to constantly monitor the charts.
- Trailing Stop: Trailing stop orders provide a dynamic way to manage risk. Instead of setting a fixed exit level like in a stop loss, a trailing stop moves with the current price at a set distance, potentially allowing traders to secure returns automatically as the market moves favourably, and adjusts to potentially protect against adverse moves.
- Iceberg: Named for the way only a small part of the total transaction is visible to the market, icebergs are used to buy or sell large quantities with small transactions. They prevent significant market impact, which could occur from a large trade and provide more discreet execution.
Stop Limit Orders Explained
In ECN trading, stop limit orders are an intricate yet powerful tool, blending the characteristics of stop and limit orders. A stop limit order type involves two prices: the stop price, which triggers the trade, and the limit price, at which the entry will be executed. It offers more control than a basic limit or stop order by specifying the exact range within which a trade should occur.
In a stop-limit buy order explained example, the stop price is set above the current price, and the limit price is set higher than the stop price. Once the stop level is reached, it becomes an order to buy at the limit price or better. It ensures that the trader does not pay more than a predetermined price.
The difference between a limit order and a stop order lies in their execution. A limit is executed at a specified value or better, but it doesn't guarantee execution. A stop, on the other hand, triggers at a specified price and then becomes a market entry executed at the current price. Stop limits merge these features, offering a targeted range for execution and combining the certainty of a stop order with the control of a limit order.
Conditional Orders
In ECN trading, conditional orders are sophisticated tools enabling traders to implement complex strategies. Here are the key types:
- One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO): An OCO links two orders; when one executes, the other is automatically cancelled. It's useful when setting up simultaneous profit and loss targets.
- One-Triggers-Another (OTA): An OTA activates a secondary instruction only after the primary order executes. They’re ideal for those planning successive actions based on initial trade execution.
- Ladder: This involves setting multiple orders at varying levels. As the market hits each level, a new order activates, allowing for gradual execution. They’re effective in managing entry and exit strategies in volatile assets.
- Order By Date (OBD): OBDs are time-based, executing on a specified date. It’s particularly useful for those looking to align their trades with specific events or timelines.
The Bottom Line
Mastering advanced order types in ECN trading may equip traders with the tools necessary for more effective strategy execution and risk management.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
AAPL Set for a Breakout? | Technical Checklist & Projections
▍Observation & Context
▪ AAPL has been moving sideways within a clearly defined range for the past three months .
▪ On July 07 , price tested the range resistance decisively, showing some interest in the upside.
→ Let's first explore the bullish breakout scenario.
▍What Makes a Good Breakout ?
Before we talk about targets, let’s define what a good breakout looks like:
▪ A strong bullish candle breaking through the resistance in one clean move .
▪ Followed by a retest of the broken resistance (now acting as support).
▪ After that, price should ideally:
1. Form a higher low , and
2. Reach the next resistance or target zone before pulling back.
▍Target Price – Method 1: Extension of the Range
🔹 Near-Term Target: 1.5–1.618x Fibonacci Extension
- A common zone where momentum often pauses.
- Aligns with the previous high from the last downtrend.
- Technically, to reverse a trend, price needs to take out the previous high. Even though the range has “cooled off” the pressure, we still respect that level.
🔹 Ultimate Target: 2x Range Extension
- Represents a 100% projection of the previous range.
- Commonly used in range breakout targets.
🔹 Dream Target: 2.618x Fibonacci Extension
- Aligns with the start of the last downtrend , adding significance to the level.
- Often marks the exhaustion point of strong trends.
▍Target Price – Method 2: Projection from Higher Low
Note: The new higher low is not yet confirmed at the time of writing. The levels below assume an upward breakout without dropping below 207.22 . However, the same logic can be applied once the higher low forms.
🔹 Near-Term Target: Same as Method 1
🔹 Ultimate Target: 100% Projection of Prior Swing
- Projecting the prior swing (from previous low to recent high) from the new higher low .
- This level also aligns with the 1.5–1.618x Fibonacci extension of that swing, increasing its significance.
🔹 Dream Target: Another 100% projection
- Rare, but happens when momentum is very strong .
- In such cases, price might skip any retracement and launch directly into a second leg , equal to the previous swing.
- Here, the level aligns perfectly with the start of the last downtrend , just like the 2.618x extension in Method 1.
▋Mental Notes
▪ No one knows for sure if the breakout will be real or fake. But when it happens, knowing what to look for and where price might go next gives us a clear plan of action .
▪ The market will always find ways to surprise. Stay open and follow the flow.
▋Not Financial Advice
The information contained in this article is not intended as, and should not be understood as financial advice. You should take independent financial advice from a professional who is aware of the facts and circumstances of your individual situation.
The Trader’s Journey: From Hope to MasteryLadies and gentlemen, fellow traders,
Whether you've just opened your first trading account or you’re already seeing consistent returns, I want to speak directly to your journey — The Trader’s Journey. It’s a path filled with hope, confusion, pain, breakthroughs, and ultimately, mastery.
Trading is not a get-rich-quick scheme — it’s a mirror. It shows you your discipline, your patience, your weaknesses, and your potential. Let me walk you through six powerful stages that every successful trader must face.
Stage 1: The Beginner
This is where the fire is lit.
You’ve just discovered trading — maybe you saw a video of someone making thousands in minutes, or a friend introduced you. You’re excited. You dream of quitting your job, making money in your sleep, living free. You don’t know much, but your heart is in it.
And that’s okay. Every trader starts here — driven by curiosity and ambition.
But beware: this is where most get trapped in illusion.
Stage 2: The Gambler
Without knowledge, the beginner becomes the gambler.
You enter trades without analysis. You chase signals from Telegram channels. You over-leverage, revenge trade, and your emotions run the show. You win once, lose three times, and still believe the next trade is “the one.”
At this stage, you’re not trading — you’re hoping. There’s no edge. Only chaos.
The gambler loses money, but gains the most valuable asset: humility.
Stage 3: The Sponge
Now that you’ve felt the pain of gambling, you decide to get serious. You become the sponge.
You buy courses. Watch endless YouTube videos. Download PDFs. Join mentorships. You’re learning — and learning — and learning.
But here’s the danger: information overload. You start to believe more knowledge equals better results. But unless that knowledge is applied, tested, and internalized, it’s just noise.
The sponge must eventually learn to filter, to focus, and to practice.
Stage 4: The Fighter
You’ve gained skills. Your chart looks cleaner. You can explain concepts now. You win some trades. You lose some. Sometimes you even feel like you’ve cracked it.
But you’re still fighting.
You jump from one strategy to another. You change your system after one bad week. You second-guess yourself. You're in the emotional trenches — and it’s exhausting.
But this stage is crucial. Because it’s here that most quit.
To move forward, the fighter must develop emotional control, patience, and a trading plan they can trust.
Stage 5: The Climber
Now, you're becoming a climber. You’ve found your edge. You follow your rules. You journal your trades. You’re no longer driven by thrill, but by execution. You’ve stopped chasing profits — now you chase process.
You start seeing consistent returns.
Risk management is no longer optional — it’s your oxygen. And trading is no longer about proving yourself — it’s about preserving and growing.
The climber is building the foundation of long-term wealth.
Stage 6: The Oracle
And finally, the oracle.
This trader has mastered not just the charts — but themselves. They understand that trading is 80% psychology and 20% execution. They know when not to trade. They know when to rest. Their results speak, but their ego is silent.
They don’t need to be right — they need to be disciplined.
They live by probabilities. They’ve seen every market condition. And they’ve turned trading into a business — not a hobby.
This is mastery. This is where the journey leads.
In Conclusion
My fellow traders — wherever you are in this journey, honor it. Don’t rush the process. Each stage has its purpose, and each stage will shape you.
You’ll lose trades. You’ll doubt yourself. You’ll feel like giving up.
But if you stay committed — not just to profits, but to growth — you will climb.
Remember: The market doesn’t reward perfection. It rewards consistency. It rewards discipline. It rewards self-awareness.
So I ask you:
🔥 Are you willing to fight through frustration?
🔥 Are you willing to outlast the noise?
🔥 Are you willing to master yourself before mastering the market?
Because if you are… then one day, you won’t just be another trader.
You’ll be a professional. An oracle.
Thank you — and trade well.
Need a trading strategy to avoid FOMO
Hello, traders.
If you "Follow", you can always get new information quickly.
Have a nice day today.
-------------------------------------
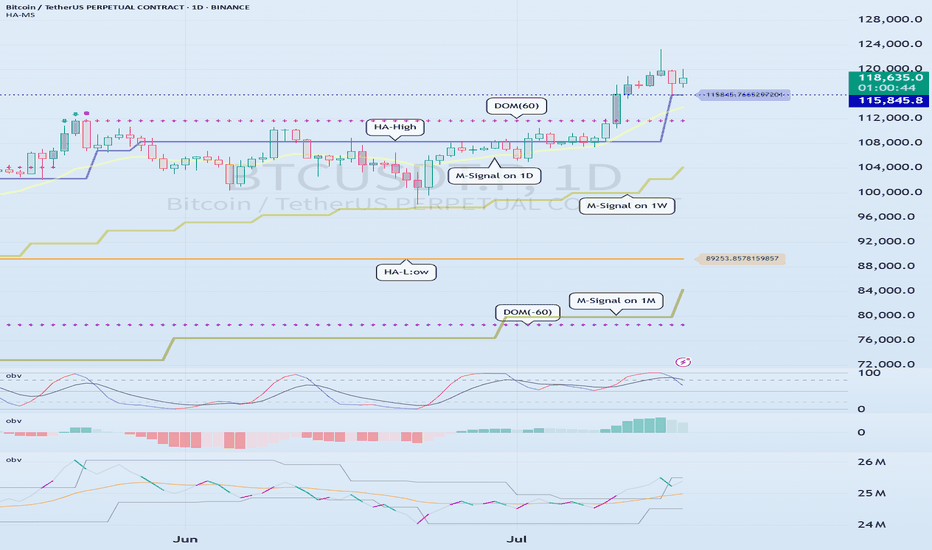
1D chart is the standard chart for all time frame charts.
In other words, if you trade according to the trend of the 1D chart, you can make profits while minimizing losses.
This can also be seen from the fact that most indicators are created based on the 1D chart.
In that sense, the M-Signal indicators of the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts are suitable indicators for confirming trends.
If the price is maintained above the M-Signal indicator of the 1M chart, it is highly likely that the upward trend will continue in the medium to long term, so it is recommended to take note of this advantage especially when trading spot.
The M-Signal indicator on the 1W, 1D chart shows the medium-term and short-term trends.
The M-Signal indicator uses the MACD indicator formula, but it can be seen as a price moving average.
You can trade with just the price moving average, but it is difficult to select support and resistance points, and it is not very useful in actual trading because it cannot cope with volatility.
However, it is a useful indicator when analyzing charts or checking general trends.
Therefore, what we can know with the M-Signal indicator (price moving average) is the interrelationship between the M-Signal indicators.
You can predict the trend by checking how far apart and close the M-Signal indicators are, and then checking the direction.
-
If you have confirmed the trend with the M-Signal indicator, you need support and resistance points for actual trading.
Support and resistance points should be drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts.
The order of the roles of support and resistance points is 1M > 1W > 1D charts.
However, the strength of the role of support and resistance points can be seen depending on how long the horizontal line is.
Usually, in order to perform the role of support and resistance points, at least 3 candles or more form a horizontal line.
Therefore, caution is required when trading when the number of candles is less than 3.
The indicators created considering this point are the HA-Low and HA-High indicators.
The HA-Low and HA-High indicators are indicators created for trading on the Heikin-Ashi chart and indicate when the Heikin-Ashi candle turns upward or downward.
Therefore, the creation of the HA-Low indicator means that there is a high possibility of an upward turn.
In other words, if it is supported by the HA-Low indicator, it is a time to buy.
However, if it falls from the HA-Low indicator, there is a possibility of a stepwise decline, so you should also consider a countermeasure for this.
The fact that the HA-High indicator was created means that there is a high possibility of a downward turn.
In other words, if there is resistance from the HA-High indicator, it is a time to sell.
However, if it rises from the HA-High indicator, there is a possibility of a stepwise upward turn, so you should also consider a countermeasure for this.
This is where a dilemma arises.
What I mean is that the fact that the HA-High indicator was created means that there is a high possibility of a downward turn, so you know that there is a high possibility of a downward turn, but if it receives support and rises, you think that you can make a large profit through a stepwise upward turn, so you fall into a dilemma.
This is caused by greed that arises from falling into FOMO due to price volatility.
The actual purchase time should have been when it showed support near the HA-Low indicator, but when it showed a downward turn, it ended up suffering a large loss due to the psychology of wanting to buy, which became the trigger for leaving the investment.
Therefore, if you failed to buy at the purchase time, you should also know how to wait until the purchase time comes.
-
It seems that you can trade depending on whether the HA-Low and HA-High indicators are supported, but the task of checking whether it is supported is quite difficult and tiring.
Therefore, to complement the shortcomings of the HA-Low and HA-High indicators, the DOM(60) and DOM(-60) indicators were added.
The DOM(-60) indicator indicates the end of the low point.
Therefore, if it shows support in the DOM(-60) ~ HA-Low section, it is the purchase time.
If it falls below the DOM(-60) indicator, it means that a stepwise downtrend is likely to begin.
The DOM(60) indicator indicates the end of the high point.
Therefore, if it is supported and rises in the HA-High ~ DOM(60) section, it means that a stepwise uptrend is likely to begin.
If it is resisted and falls in the HA-High ~ DOM(60) section, it is likely that a downtrend will begin.
With this, the basic trading strategy is complete.
This is the basic trading strategy of buying when it rises in the DOM(-60) ~ HA-Low section and selling when it falls in the HA-High ~ DOM(60) section.
For this, the trading method must adopt a split trading method.
Although not necessarily, if it falls in the DOM(-60) ~ HA-Low section, it will show a sharp decline, and if it rises in the HA-High ~ DOM(60) section, it will show a sharp rise.
Due to this volatility, psychological turmoil causes people to start trading based on the price, which increases their distrust in the investment market and eventually leads them to leave the investment market.
-
When looking at the movement of the 1D chart, it can be seen that it is not possible to proceed with trading at the moment because it is already showing a stepwise upward trend.
However, since there is a SHORT position in futures trading, trading is possible at any time.
In any case, it is difficult to select a time to buy because the 1D chart shows a stepwise upward trend.
However, looking at the time frame chart below the 1D chart can help you select a time to buy.
The basic trading strategy is always the same.
Buy when it rises in the DOM(-60) ~ HA-Low section and sell when it falls in the HA-High ~ DOM(60) section.
Currently, since the 1D chart is continuing a stepwise upward trend, the main position is to eventually proceed with a long position.
Therefore, if possible, you should focus on finding the right time to buy.
However, if it falls below the HA-High indicator of the 1D chart, the possibility of a downtrend increases, so at that time, you should focus on finding the right time to sell.
In other words, since the HA-High indicator of the current 1D chart is generated at the 115845.8 point, you should think of different response methods depending on whether the price is above or below the 115845.8 point.
Therefore, when trading futures, increase the investment ratio when trading with the main position (a position that matches the trend of the 1D chart), and decrease the investment ratio when trading with the secondary position (a position that is different from the trend of the 1D chart) and respond quickly and quickly.
When trading in the spot market, you have no choice but to trade in the direction of the 1D chart trend, so you should buy and then sell in installments whenever it shows signs of turning downward to secure profits.
In other words, buy near the HA-Low indicator on the 30m chart, and if the price rises and the HA-High indicator is created, sell in installments near that area.
-
You should determine your trading strategy, trading method, and profit realization method by considering these interrelationships, and then trade mechanically accordingly.
If you trade only with fragmentary movements, you will likely end up suffering losses.
This is because you do not cut your losses.
-
Thank you for reading to the end.
I hope you have a successful trade.
--------------------------------------------------
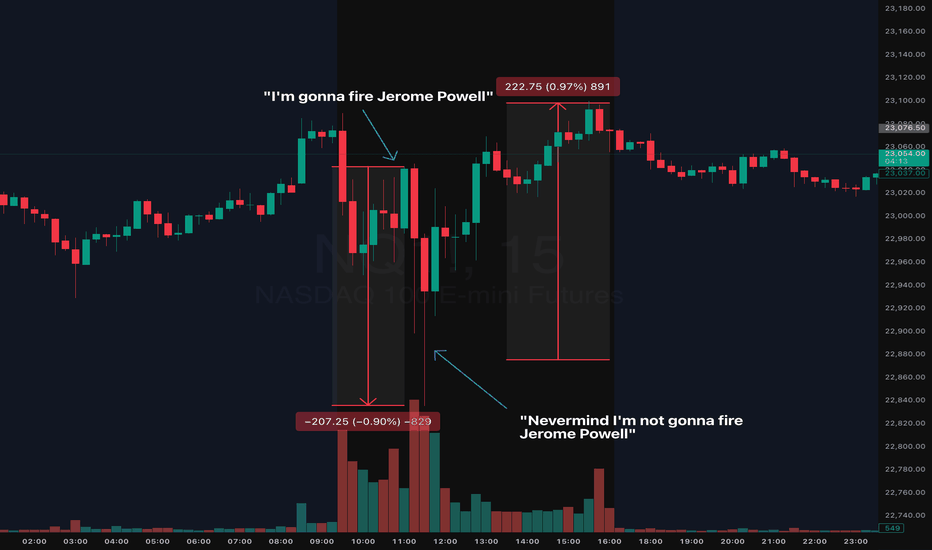
2025 Trading Final Boss: Daily Market Manipulation, The New NormMarking this point in history because we'll likely forget and move on.
During the early hours of the July 16th NYC session, we saw indices quickly flush ( CME_MINI:NQ1! CME_MINI:ES1! ) nearly 1% on the news that Trump will fire Jerome Powell. The dip was bought almost instantly.
Shortly after the dip was bought (roughly 0.50% recovery), guess what? Trump announced, he is "not considering firing Jerome Powell". The dip then recovered and achieved a complete V to finish the day somewhat green. Make what you want of it but always use a stop loss in these tough conditions.
Welcome to 2025 Trading Final Boss
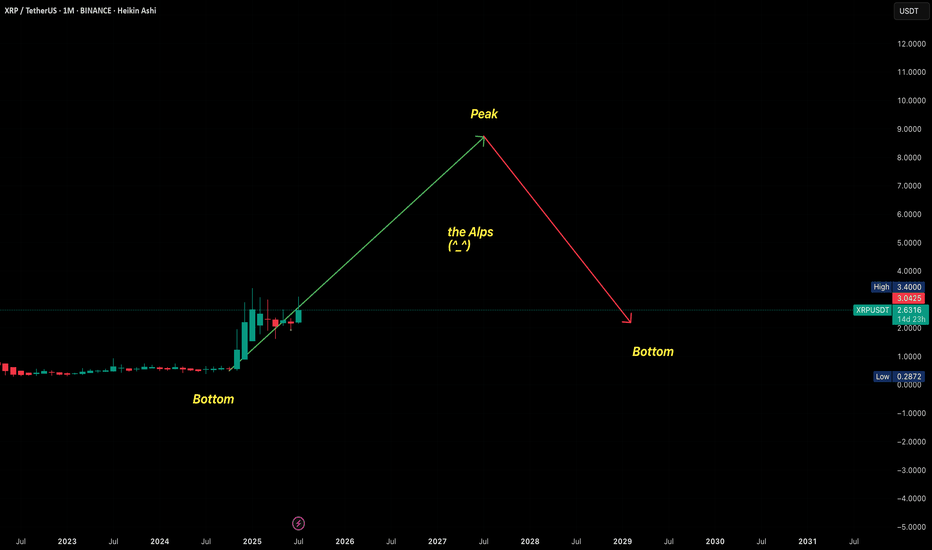
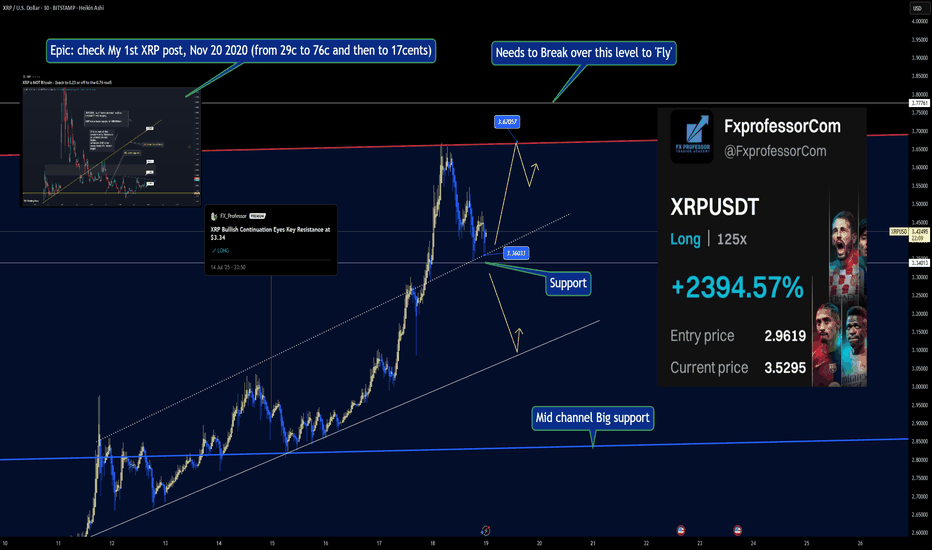
Will XRP Go to $10? Educational + Epic History Post(apologies for bad audio quality, i messed up with the microphones)
💭📈 Will XRP Go to $10? Let's Look at the History 📚⚡
Will XRP go to $10? That’s the question you ask me.
Before we chase moonshots , let’s take a step back and look at what XRP has already done — and what the structure is telling us.
🔁 In November 2020, I shared my very first XRP idea:Epic posts, click on 'play' and think!!!
🚀 From $0.29 to $0.76
📉 Then a fast drop to $0.17
That cycle played out within days — wild, but entirely technica l. Levels held, and the market did what it always does: reward patience and punish hype. 📉📈
Fast-forward to Today:
My current XRP position is up +2394% on a 125x long, with price now testing a critical resistance at $3.67. Half profit has already been secured.
✅ Entry: $2.9619
✅ Price: $3.5295
⛳ Target: A confirmed breakout over $3.67 is the reason i am keeping this half trade left
The real move only starts after that level breaks. (3.67 breakout is 50% likely, yes)
So… Can XRP Reach $10?
The answer lies in:
📌 Structure
📌 Volume
📌 Patience
Only a clean breakout over the channel opens the door to exploring new territory — $5, $7, and potentially $10.
Until then, it's all about playing the levels. Mid-channel support, wedge breakouts, and respecting price action — this isn’t hopium. It’s precision.
This post is educational — not just about XRP, but about how we trade intelligently. The big picture is great, but the small details get you there.
Keep learning. Keep building. XRP might fly… but the question is, are we able to know when to enter and when to take profit? When to increase our positions and when to cash some profits? Or when to go short? This video offers you the answers 🎯
One Love,
The FX PROFESSOR 💙
Disclosure: I am happy to be part of the Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis. Awesome broker, where the trader really comes first! 🌟🤝📈
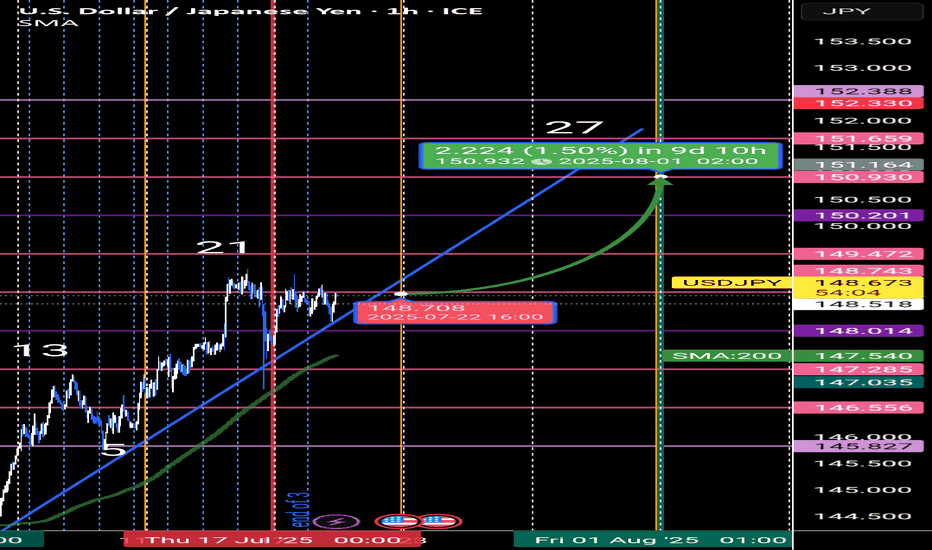
USD/JPY FORCAST🟦 Time Structure Analysis – USD/JPY | The 3-6-9 Temporal Cycle
📌 Price can lie. But time never does.
While many traders rely on price action or Elliott Wave counts, I take a different route — I trade time. Why?
Because time sets the rhythm, and the rhythm defines everything.
🔄 The 3-6-9 Time Cycle
Every complete market movement follows a hidden structure based on natural timing laws
In the current month, July 2 was the entry gate. That’s where I anchor the beginning of the new cycle.
⏳ Why Time Wins Over Price
Indicators lag
Price patterns repaint
But time never repaints.
Once the temporal cycle is locked in, it dictates future market rhythm.
You can identify where the market must move next — not by guessing the price level, but by counting time bars from a known pivot.
---
⚡ Strategy in Practice
In my system, I use:
✅ Cycle Lines starting from key reversal points
✅ Fixed monthly gates as temporal anchors
✅ Bar counting based on 3-6-9 geometry
✅ Fractal validation from higher timeframes
This gives me a predictive edge based on time pressure, not price patterns.
🎯 “The market doesn’t move because of buyers and sellers...
It moves because of time.”
Time is the structure. Price is just the effect.
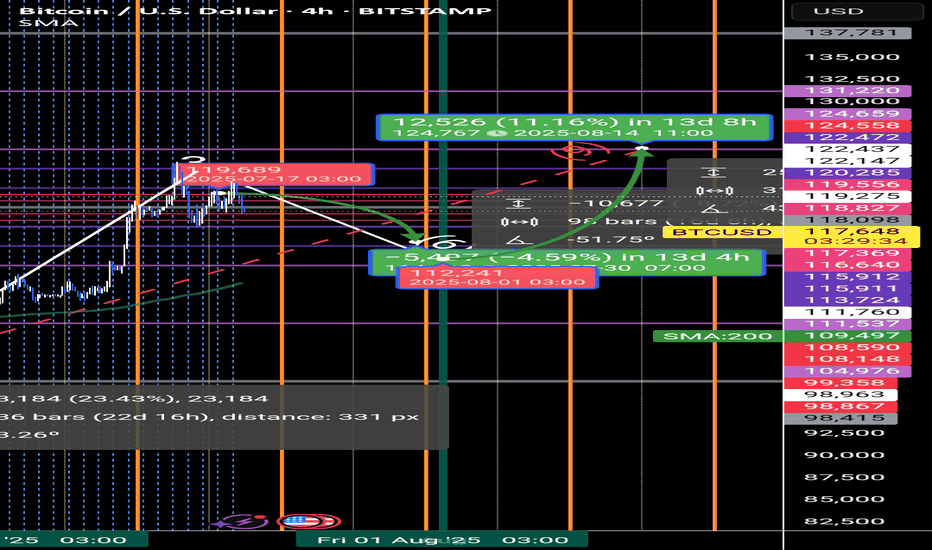
Bitcoin Forecast 🔁 I use a unique time-based cycle method built around the universal law of 3-6-9:
3 = Impulse wave
6 = Correction
9 = Cycle end
we are at the higher time frame cycle 9
each cycle of the 3, 6 ,9
contain a smaller one 3 ,6 , 9
This isn’t just about charts — the number 9 governs all natural cycles:
Pregnancy, learning, lunar cycles, economic growth, etc.
---
🗓️ These are the key monthly turning points I track every year:
> Jan 8 – Feb 7 – Mar 6 – Apr 5 – May 5 – Jun 4 – Jul 2 – Aug 1 – Aug 31 – Oct 30 – Nov 29 – Dec 6
📍 This month, July 2nd was a critical time pivot. From there, Bitcoin entered a new time cycle.
📌 Time Is More Powerful Than Price
Most traders focus on price action, waves, or indicators…
But the reality? Time is the real market driver.
⏳ Entry signals based on time outperform those based on price.
Why? Because price is a reaction — time is the cause.
What Moves the Crypto Market?Hello, Traders!
If you’ve spent any time staring at crypto charts, you’ve probably asked: “Why is this happening?” And the truth is… there’s never one simple answer.
Crypto markets are complex, global, 24/7 systems. The forces behind a price move can be technical, fundamental, psychological or all at once. So let’s unpack what really moves this market.
1. Supply and Demand — The Fundamentals Behind the Volatility
At its core, crypto prices are governed by supply and demand. If more people want to buy than sell, the price goes up and vice versa. But it’s not that simple.
Take Bitcoin. It has a fixed max supply of 21 million, and most of those coins are already mined. But available liquidity on exchanges is much smaller and this is where things get interesting. During bull markets, demand surges while liquid supply dries up. That creates parabolic moves. Then you have supply unlocks, token vesting schedules, and inflationary emissions all of which affect how much of a coin is flowing into the market.
Example: When Lido enabled ETH withdrawals in 2023, it shifted the ETH supply dynamics, some saw it as bearish (more unlocked supply), others bullish (greater staking confidence).
2. Sentiment and Psychology: Fear & Greed Still Rule
If you want to understand the crypto market, start by studying people. Emotions drive decision-making, and crypto is still largely a retail-dominated space. Bull runs often start with doubt, accelerate with FOMO, and end in euphoria. Bear markets move from panic to despair to apathy. The crypto psychology chart rarely lies, but it always feels different in real time.
The classic “psychological numbers in trading”, like $10K, $20K, $100K BTC, often act as invisible walls of resistance or support. Why? Because traders anchor to these round levels.
👉 We’ve covered this phenomenon in detail in a dedicated post “The Power of Round Numbers in Trading.” Highly recommend checking it out if you want to understand how these zones shape market psychology and price action.
3. On-Chain Activity and Network Utility
Fundamentals matter. But in crypto, fundamentals are on-chain. The transparency of blockchain networks provides valuable insights into fundamental usage and investor behavior, which often foreshadow price trends. On-chain metrics such as active addresses, transaction volumes, and wallet holdings offer insight into the health and sentiment of the crypto ecosystem:
Network Usage (Active Addresses & Transactions): A growing number of active addresses or transactions might indicate rising network demand and adoption. Empirical studies have found that BTC’s price strongly correlates with its on-chain activity – increases in the number of wallets, active addresses, and transaction counts tend to accompany price appreciation.
Exchange Inflows/Outflows: Tracking the movement of Bitcoin or Ether in and out of exchanges provides clues to investor intent. Large outflows from exchanges are often bullish signals – coins withdrawn to private wallets imply holders are opting to HODL rather than trade or sell, tightening the available supply on the market. For example, in late March 2025, as Bitcoin neared $90,000, exchange outflows hit a 7-month high (~11,574 BTC withdrawn in one day) mainly by whale holders, indicating strong confidence.
Mining Activity and Miner Behavior: In Proof-of-Work coins like Bitcoin, miners are forced sellers (regularly selling block rewards to cover costs), so their behavior can impact price. Periods of miner capitulation, when mining becomes unprofitable and many miners shut off or sell holdings, have historically aligned with market bottoms.
For example, in August 2024, Bitcoin experienced a miner “capitulation event”: daily miner outflows spiked to ~19,000 BTC (the highest in months) as the price dipped to around $ 49,000, suggesting that miners had dumped inventory as profit margins evaporated. Shortly after, the network hash rate quickly recovered to new highs, indicating that miners’ confidence was returning, even as the price was low.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the crypto market’s price movements are driven by a complex interplay of factors… Market sentiment and psychology can override fundamentals in the short run, leading to euphoric rallies or panicked crashes. On-chain metrics provide the ground truth of user adoption and big-holder behavior, often signaling trend changes before they happen. Halvings and tokenomics remind us that the code underlying these assets directly affects their value by controlling supply. And finally, specific catalysts and news events encapsulate how all these forces can converge in real time.
For enthusiasts, understanding “what moves the crypto market” is crucial for navigating its volatility. Crypto will likely remain a fast-evolving space, but its price movements are not random. They are the sum of these identifiable factors, all of which savvy market participants weigh in their quest to predict the next move in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and beyond.
What do you think? 👇🏻
Fibonacci Retracement: The Hidden Key to Better EntriesIf you’ve ever wondered how professional traders predict where price might pull back before continuing... the secret lies in Fibonacci Retracement.
In this post, you’ll learn:
What Fibonacci retracement is
Why it works
How to use it on your charts (step-by-step)
Pro tips to increase accuracy in the market
🧠 What Is Fibonacci Retracement?:
Fibonacci Retracement is a technical analysis tool that helps traders identify potential support or resistance zones where price is likely to pause or reverse during a pullback.
It’s based on a mathematical sequence called the Fibonacci Sequence, found everywhere in nature — from galaxies to sunflowers — and yes, even in the markets.
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting with 0 and 1. The sequence typically begins with 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, and so on. This pattern can be expressed as a formula: F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2), where F(n) is the nth Fibonacci number.
The key Fibonacci levels traders use are:
23.6%
38.2%
50%
61.8%
78.6%
These levels represent percentages of a previous price move, and they give us reference points for where price might pull back before resuming its trend and where we can anticipate price to move before showing support or resistance to the trend you are following.
💡Breakdown of Each Fib Level:
💎 0.236 (23.6%) – Shallow Pullback
What it indicates:
Weak retracement, often signals strong trend momentum.
Buyers/sellers are aggressively holding the trend.
Best action:
Aggressive entry zone for continuation traders.
Look for momentum signals (break of minor structure, bullish/bearish candles). Stay out of the market until you see more confirmation.
💎 0.382 (38.2%) – First Strong Area of Interest
What it indicates:
Healthy pullback in a trending market.
Seen as a key area for trend followers to step in.
Best action:
Look for entry confirmation: bullish/bearish engulfing, pin bars, Elliott Waves, or break/retest setups.
Ideal for setting up trend continuation trades.
Stop Loss 0.618 Level
💎 0.500 (50.0%) – Neutral Ground
What it indicates:
Often marks the midpoint of a significant price move.
Market is undecided, can go either way.
Best action:
Wait for additional confirmation before entering.
Combine with support/resistance or a confluence zone.
Useful for re-entry on strong trends with good risk/reward.
Stop Loss 1.1 Fib Levels
💎 0.618 (61.8%) – The “Golden Ratio”
What it indicates:
Deep pullback, often seen as the last line of defense before trend reversal.
High-probability area for big players to enter or add to positions.
Best action:
Look for strong reversal patterns (double bottoms/tops, engulfing candles).
Excellent area for entering swing trades with tight risk and high reward.
Use confluence (structure zones, moving averages, psychological levels, Elliott Waves).
Wait for close above or below depending on the momentum of the market.
Stop Loss 1.1 Fib Level
💎 0.786 (78.6%) – Deep Correction Zone
What it indicates:
Very deep retracement. Often a final “trap” zone before price reverses.
Risk of trend failure is higher.
Best action:
Only trade if there's strong reversal evidence.
Use smaller position size or avoid unless other confluences are aligned.
Can act as an entry for counter-trend trades in weaker markets.
Stop Loss around 1.1 and 1.2 Fib Levels
⏱️Best Timeframe to Use Fibs for Day Traders and Swing Traders:
Day trading:
Day traders, focused on capturing short-term price movements and making quick decisions within a single day, typically utilize shorter timeframes for Fibonacci retracement analysis, such as 15-minute through hourly charts.
They may also use tighter Fibonacci levels (like 23.6%, 38.2%, and 50%) to identify more frequent signals and exploit short-term fluctuations.
Combining Fibonacci levels with other indicators such as moving averages, RSI, or MACD, and focusing on shorter timeframes (e.g., 5-minute or 15-minute charts) can enhance signal confirmation for day traders.
However, relying on very short timeframes for Fibonacci can lead to less reliable retracement levels due to increased volatility and potential for false signals.
Swing trading:
Swing traders aim to capture intermediate trends, which necessitates giving trades more room to fluctuate over several days or weeks.
They typically prefer utilizing broader Fibonacci levels (like 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%) to identify significant retracement points for entering and exiting trades.
Swing traders often focus on 4-hour and daily charts for their analysis, and may even consult weekly charts for a broader market perspective.
🎯 Why Does Fibonacci Work?:
Fibonacci levels work because of:
Mass psychology – many traders use them
Natural rhythm – markets move in waves, not straight lines
Institutional footprint – smart money often scales in around key retracement zones
It's not magic — it's structure, and it's surprisingly reliable when used correctly.
🛠 How to Draw Fibonacci Retracement (Step-by-Step):
Let’s say you want to trade XAU/USD (Gold), and price just had a strong bullish run.
✏️ Follow These Steps:
Identify the swing low (start of move)
Identify the swing high (end of move)
Use your Fibonacci tool to draw from low to high (for a bullish move)
The tool will automatically mark levels like 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, etc.
These levels act as pullback zones, and your job is to look for entry confirmation around them.
🔁 For bearish moves, draw from high to low. (I will show a bearish example later)
Now let’s throw some examples and pictures into play to get a better understanding.
📈 XAU/USD BULLISH Example:
1.First we Identify the direction of the market:
2.Now we set our fibs by looking for confirmations to get possible entry point:
Lets zoom in a bit:
Now that we have a break of the trendline we wait for confirmation and look for confluence:
Now we set our fibs from the last low to the last high:
This will act as our entry point for the trade.
3. Now we can look for our stop loss and take profit levels:
Stop Loss:
For the stop loss I like to use the fib levels 1.1 and 1.2 when I make an entry based upon the 0.618 level. These levels to me typically indicate that the trade idea is invalid once crossed because it will usually violate the prior confirmations
Take Profit:
For the take profit I like to use the Fib levels 0.236, 0, -0.27, and -0.618. This is based upon your personal risk tolerance and overall analysis. You can use 0.236 and 0 level as areas to take partial profits.
Re-Entry Point Using Elliott Waves as Confluence Example:
This is an example of how I used Elliott Waves to enter the trade again from the prior entry point. If you don’t know what Elliott Waves are I will link my other educational post so you can read up on it and have a better understanding my explanation to follow.
After seeing all of our prior confirmations I am now confident that our trend is still strongly bullish so I will mark my Waves and look for an entry point.
As we can see price dipped into the 0.38-0.5 Fib level and rejected it nicely which is also in confluence with the Elliott Wave Theory for the creation of wave 5 which is the last impulse leg before correction.
🔻 In a downtrend:
Same steps, but reverse the direction — draw from high to low and look to short the pullback.
XAU/USD Example:
As you can see the same basic principles applied for bearish movement as well.
⚠️ Pro Tips for Accuracy:
✅ Always use Fib in confluence with:
Market structure (higher highs/lows or lower highs/lows)
Key support/resistance zones
Volume or momentum indicators
Candle Patterns
Elliott Waves, etc.
❌ Don’t trade Fib levels blindly — they are zones, not guarantees.
📊 Use higher timeframes for cleaner levels (4H, Daily)
💡 Final Thought
Fibonacci retracement doesn’t predict the future — it reveals probability zones where price is likely to react.
When combined with structure and confirmation, it becomes one of the most reliable tools for new and experienced traders alike.
🔥 Drop a comment if this helped — or if you want a Part 2 where I break down Fibonacci Extensions and how to use them for take-profit targets.
💬 Tag or share with a beginner who needs to see this!
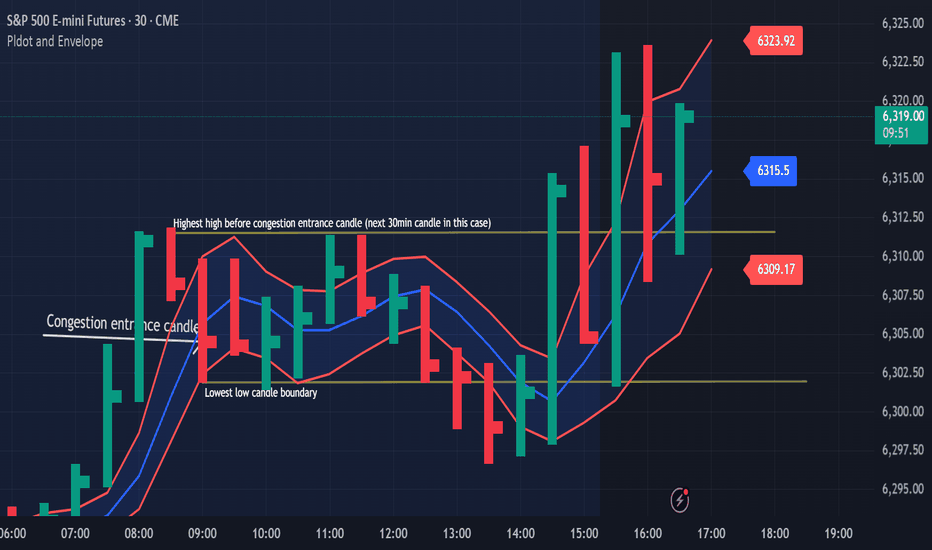
Congestion Action vs Congestion Exit – Mastering the TransitionWhen markets go quiet and churn sideways, it’s easy to get lost in the noise. But inside that congestion lies opportunity — if you understand the difference between "Congestion Action" and "Congestion Exit." Here’s how to apply Drummond Geometry to trade these phases with precision:
🔹 Congestion Action
Congestion action is when the market is not ready to trend — it's swinging back and forth within a defined range, between a strong block level and a well-established dotted line. Think of it as a "resting zone" before the next directional move.
📏 Original Confines: Highest high and lowest low after a congestion entrance as shown on the chart
🚧 Expanded Confines: Price temporarily breaks out of the range but doesn’t establish a trend (3 closes on the came side of the PLdot (blue line)).
🧲 This is where scalpers and range traders thrive. Look for setups near envelope confines and use nearby energy fields.
✅ Trade Plan: Play the range — buy support, sell resistance — until proven otherwise.
🔸 Congestion Exit
This is when the market transitions from ranging to trending — a trend run begins from within the congestion zone.
🚀 First bar of a new trend closes outside the congestion confines (either the block level (highest high on the chart) or the dotted line (the low on the chart)).
📊 The next bar must confirm with a trend run close — if not, it’s a failed breakout. You can see on the chart that price tried to trend lower but the trend was not confirmed!
⚡ Patterns to watch:
Energy pushing in the direction of the exit (PL Dot push, c-wave continuation).
6-1 lines against the breakout direction disappear.(Not visible in this version)
Resistance/support against the exit breaks.
✅ Trade Plan: Enter on breakout confirmation, not just the breakout bar. Measure energy and watch the follow-through.
🧭 Tip:
Don't get faked out. If price re-enters congestion after a breakout, re-draw the boundaries — the old congestion is no longer valid.
🔥 Bottom Line:
Congestion Action is where the market breathes. Congestion Exit is where it moves. Mastering the handoff between the two gives you a decisive edge.
wall Street has set camp on Satoshi's backyard...Bitcoin didn’t just wake up and choose violence. It chose velocity.
As BTC blasts through the six-figure ceiling and fiddles $120k with laser precision, everyone’s pointing to “the halving” like it’s some magical switch. But let's be real, Bitcoin bull runs don’t run on fairy dust and hope. They run on liquidity, macro dislocations, structural demand shifts, and a pinch of regulatory chaos.
Here’s the nerdy breakdown of what’s really driving the Bitcoin Rocketship (and why this one’s different):
1. The Halving Effect (Not Just the Halving)
Yes, the April 2024 halving slashed miner rewards from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC. But this time, the reflexivity is louder. Miners now have to sell less, and buyers (especially ETFs) have to beg for more.
Miners = Reduced Sell Pressure.
ETFs = Constant Buy Pressure.
That’s a one-way order book squeeze. Simple math, but powerful dynamics.
2. ETF Flows: The "Spot" That Launched a Thousand Rallies
When the SEC finally gave the green light to Bitcoin spot ETFs, TradFi didn’t walk in—they stormed in.
Think BlackRock, Fidelity, and friends becoming daily buyers. It's not retail FOMO anymore, it's Wall Street with billions in dry powder doing dollar-cost averaging with institutional consistency.
🧠 Nerd Note: The top 5 U.S. spot ETFs alone are now hoarding more BTC than MicroStrategy.
3. Dollar Liquidity is Leaking Again
Despite Fed jawboning, real rates are still under pressure and global liquidity is quietly creeping back. Look at the TGA drawdowns, reverse repo usage, and China’s stealth QE.
Bitcoin, being the apex predator of liquidity, smells it from a mile away.
“In a world flooded with fiat, Bitcoin doesn’t float. It flies.”
4. Sovereigns Are Quietly Watching
El Salvador lit the match. Now, Argentina, Turkey, and even Gulf countries are tiptoeing toward a Bitcoin pivot, hedging USD exposure without broadcasting it to CNN.
Central banks don’t need to love BTC to stack it. They just need to fear the dollar system enough.
5. Scarcity Narrative Goes 3D
With 99% of BTC supply already mined and over 70% HODLed for over 6 months, every new buyer is bidding for a smaller slice of the pie. ETFs and institutions are trying to drink from a faucet that only drips.
This is not a market with elastic supply. This is financial physics with a scarcity twist.
6. Market Microstructure is Fragile AF
Order books are thin. Real liquidity is fragmented. And the sell-side has PTSD from getting blown out at $70k.
This creates a “skateboard-on-a-freeway” scenario, when a few billion in inflows hit, prices don’t just rise. They gap.
Nerdy Bonus: The Memecoin Effect (No, Really)
The memecoin mania on Solana, Base, and Ethereum has been injecting dopamine into degens—and their profits are increasingly flowing into the OG digital gold.
It’s the 2021 cycle all over again, just with more liquidity bridges and fewer inhibitions.
Nerdy Insight: The Bull Run Has Layers
What’s driving BTC to $120,000 isn’t a single headline. It’s a stacked convergence of macro, structure, psychology, and coded scarcity.
Bitcoin isn’t “going up” just because of hope or halving hype. It’s going up because it’s the cleanest asset in a dirty system, and now both retail and institutions agree.
Still shorting? That’s not “fading the crowd.” That’s fighting thermodynamics.
Stay nerdy, stay sharp.
put together by : @currencynerd as Pako Phutietsile
The only key levels you need - DITCH THE INDICATORS- Previous day high/Low
- Weekly high/low
- Session high/low
- Closing Price
In this specific example on OANDA:AUDUSD we have a day 3 Tuesday breakout fail reversal setup on the backside of a previous weeks expansion.
Fridays closing price was plotted going into Monday day 2 on the backside of a new week. Once the initial high low was set on day 2 below the previous weeks high and closing price we than look for short opportunities going into day 3 Tuesday.
In this case day 2 Ny session high acted as the reversal point staying below Friday closing price below the high of the previous week. The Asia/London session printed a beautiful high/low range reversing at near the midpoint of the previous days range (50% retrace.)
A great opportunity for a projected range expansion presented with confluence at a previous days low giving a solid set and forget trade with little to no stress or heat. This parabolic opportunity took place in the NY session below Fridays closing price to a previous weeks LOD level.
- Mondays High (Stop)
- NY session High, Fridays Close (Entry)
- Wed Low, Range expansion (Target)
KEY NOTES:
It is very important to keep your trading simple. As a newer trader I filled my chart with as many indicators as possible trying to find a "signal" because I lacked the patience for the market to give me a setup over multiple days. Now as a more experienced trader I sit back on higher time frames (1H/15M) TO WAIT FOR THE DAILY LEVELS TO PRINT. Avoiding trading inside a range on a low time frame. Lower time frames are only to decrease risk and increase position accuracy already derived from higher time frames. It is key to understand when higher time frame traders are triggered into a market and to understand there are only two main plays from key levels. Keep it simple, find the scalable setups, AND PUT THE SIZE ON WITH CONFIDENCE.
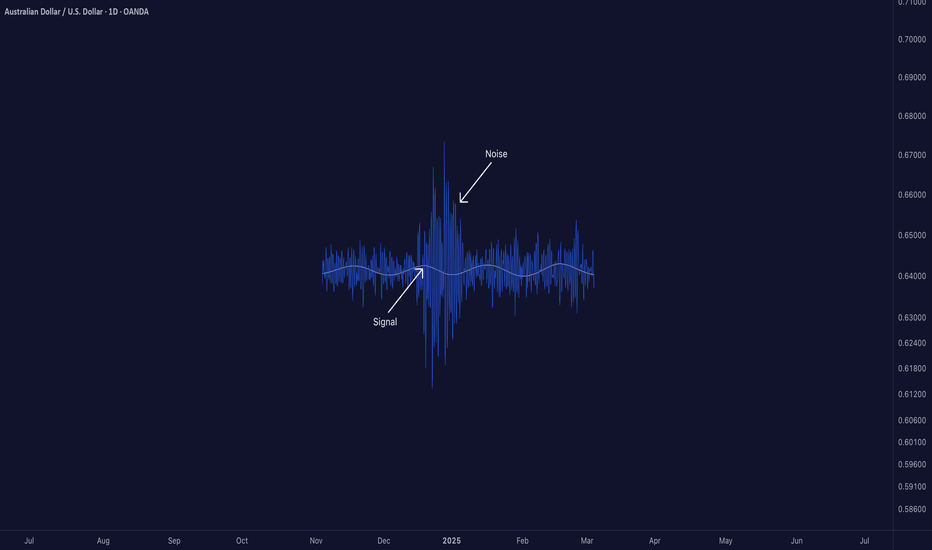
Signal-to-Noise Ratio: The Most Misunderstood Truth in Trading█ Signal-to-Noise Ratio: The Most Misunderstood Truth in Quant Trading
Most traders obsess over indicators, signals, models, and strategies.
But few ask the one question that defines whether any of it actually works:
❝ How strong is the signal — compared to the noise? ❞
Welcome to the concept of Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) — the invisible force behind why some strategies succeed and most fail.
█ What Is Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)?
⚪ In simple terms:
Signal = the real, meaningful, repeatable part of a price move
Noise = random fluctuations, market chaos, irrelevant variation
SNR = Signal Strength / Noise Level
If your signal is weak and noise is high, your edge gets buried.
If your signal is strong and noise is low, you can extract alpha with confidence.
In trading, SNR is like trying to hear a whisper in a hurricane. The whisper is your alpha. The hurricane is the market.
█ Why SNR Matters (More Than Sharpe, More Than Accuracy)
Most strategies die not because they’re logically flawed — but because they’re trying to extract signal in a low SNR environment.
Financial markets are dominated by noise.
The real edge (if it exists) is usually tiny and fleeting.
Even strong-looking backtests can be false positives created by fitting noise.
Every quant failure story you’ve ever heard — overfitting, false discoveries, bad AI models — starts with misunderstanding the signal-to-noise ratio.
█ SNR in the Age of AI
Machine learning struggles in markets because:
Most market data has very low SNR
The signal changes over time (nonstationarity)
AI is powerful enough to learn anything — including pure noise
This means unless you’re careful, your AI will confidently “discover” patterns that have no predictive value whatsoever.
Smart quants don’t just train models. They fight for SNR — every input, feature, and label is scrutinized through this lens.
█ How to Measure It (Sharpe, t-stat, IC)
You can estimate a strategy’s SNR with:
Sharpe Ratio: Signal = mean return, Noise = volatility
t-Statistic: Measures how confident you are that signal ≠ 0
Information Coefficient (IC): Correlation between forecast and realized return
👉 A high Sharpe or t-stat suggests strong signal vs noise
👉 A low value means your “edge” might just be noise in disguise
█ Real-World SNR: Why It's So Low in Markets
The average daily return of SPX is ~0.03%
The daily standard deviation is ~1%
That's signal-to-noise of 1:30 — and that's for the entire market, not a niche alpha.
Now imagine what it looks like for your scalping strategy, your RSI tweak, or your AI momentum model.
This is why most trading signals don’t survive live markets — the noise is just too loud.
█ How to Build Strategies With Higher SNR
To survive as a trader, you must engineer around low SNR. Here's how:
1. Combine signals
One weak signal = low SNR
100 uncorrelated weak signals = high aggregate SNR
2. Filter noise before acting
Use volatility filters, regime detection, thresholds
Trade only when signal strength exceeds noise level
3. Test over longer horizons
Short-term = more noise
Long-term = signal has more time to emerge
4. Avoid excessive optimization
Every parameter you tweak risks modeling noise
Simpler systems = less overfit = better SNR integrity
5. Validate rigorously
Walk-forward, OOS testing, bootstrapping — treat your model like it’s guilty until proven innocent
█ Low SNR = High Uncertainty
In low-SNR environments:
Alpha takes years to confirm (t-stat grows slowly)
Backtests are unreliable (lucky noise often looks like skill)
Drawdowns happen randomly (even good strategies get wrecked short-term)
This is why experience, skepticism, and humility matter more than flashy charts.
If your signal isn’t strong enough to consistently rise above noise, it doesn’t matter how elegant it looks.
█ Overfitting Is What Happens When You Fit the Noise
If you’ve read Why Your Backtest Lies , you already know the dangers of overfitting — when a strategy is tuned too perfectly to historical data and fails the moment it meets reality.
⚪ Here’s the deeper truth:
Overfitting is the natural consequence of working in a low signal-to-noise environment.
When markets are 95% noise and you optimize until everything looks perfect?
You're not discovering a signal. You're just fitting past randomness — noise that will never repeat the same way again.
❝ The more you optimize in a low-SNR environment, the more confident you become in something that isn’t real. ❞
This is why so many “flawless” backtests collapse in live trading. Because they never captured signal — they captured noise.
█ Final Word
Quant trading isn’t about who can code the most indicators or build the deepest neural nets.
It’s about who truly understands this:
❝ In a world full of noise, only the most disciplined signal survives. ❞
Before you build your next model, launch your next strategy, or chase your next setup…
Ask this:
❝ Am I trading signal — or am I trading noise? ❞
If you don’t know the answer, you're probably doing the latter.
-----------------
Disclaimer
The content provided in my scripts, indicators, ideas, algorithms, and systems is for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or a solicitation to buy or sell any financial instruments. I will not accept liability for any loss or damage, including without limitation any loss of profit, which may arise directly or indirectly from the use of or reliance on such information.
All investments involve risk, and the past performance of a security, industry, sector, market, financial product, trading strategy, backtest, or individual's trading does not guarantee future results or returns. Investors are fully responsible for any investment decisions they make. Such decisions should be based solely on an evaluation of their financial circumstances, investment objectives, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs.
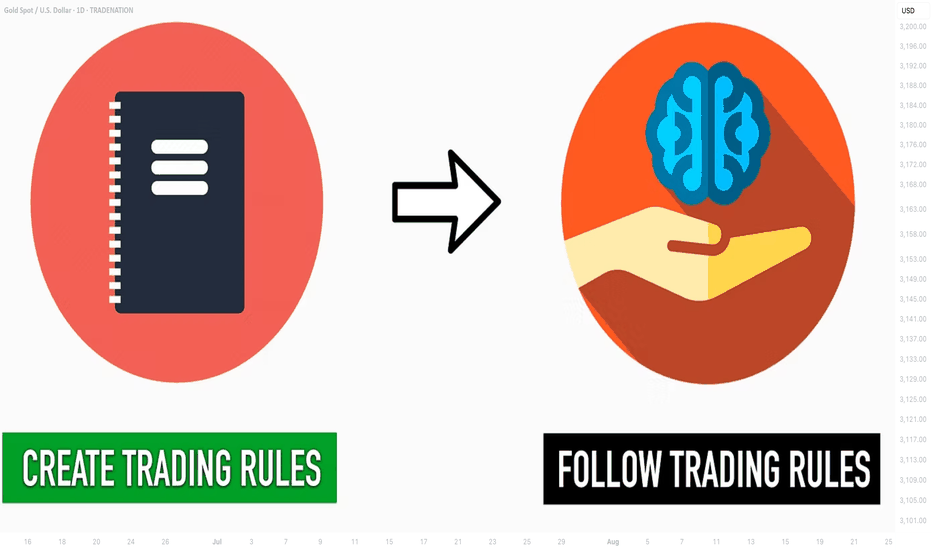
Learn 2 Essential Elements of Forex Gold Trading
In the today's post, we will discuss how Forex Gold trading is structured, and I will share with you its 2 key milestones.
Trading with its nuances and complexities can be explained as the interconnections of two processes: trading rules creation and trading rules following.
1️⃣ With the trading rules, you define what you will trade and how exactly, classifying your entry and exist conditions, risk and trade management rules. Such a set of consistent trading rules compose a trading strategy.
For example, you can have a following trading plan:
you trade only gold, you analyze the market with technical analysis,
you buy from a key support and sell from a key resistance on a daily, your entry confirmation is a formation of a reversal candlestick pattern.
You set stop loss above the high/low of the pattern, and your target is the closest support/resistance level.
Here is how the trading setup would look like.
In the charts above, all the conditions for the trade are met, and the market nicely reached the take profit.
2️⃣ Trading strategy development is a very simple process. You can find hundreds of different ones on the internet and start using one immediately.
The main obstacle comes, however, with Following Trading Rules.
Following the rules is our second key milestone. It defines your ability to stay disciplined and to stick to your trading plan.
It implies the control of emotions, patience and avoidance of rationalization.
Once you open a trade, following your rules, challenges are just beginning. Imagine how happy you would feel yourself, seeing how nicely gold is moving to your target after position opening.
And how your mood would change, once the price quickly returns to your entry.
Watching how your profits evaporate and how the initially winning position turns into a losing one, emotions will constantly intervene.
In such situations, many traders break their rules , they start adjusting tp or stop loss or just close the trading, not being able to keep holding.
The ability to follow your system is a very hard skill to acquire. It requires many years of practicing. So if you believe that a good trading strategy is what you need to make money, please, realize the fact that even the best trading strategy in the world will lose without consistency and discipline.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Portfolio Destruction In Bull Markets = Greed Without Strategy When the market is bullish, everyone thinks whatever they buy will make a profit.
But does a rising price really mean you’re winning? Or are you just chasing an illusion?
What kills most traders is greedy trading without a clear plan even when the market is green!
Hello✌
Spend 3 minutes ⏰ reading this educational material.
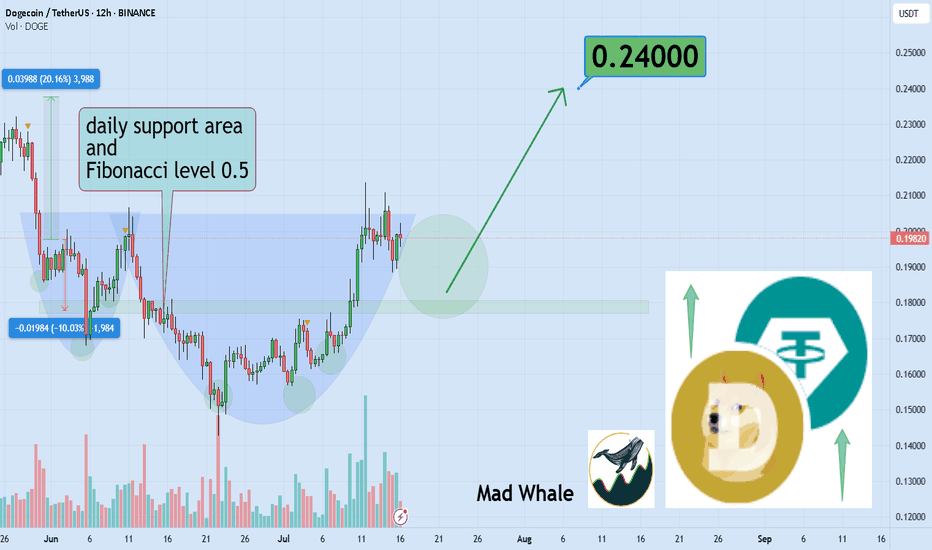
🎯 Analytical Insight on Dogecoin :
🚀 After breaking out of its daily downtrend channel, BINANCE:DOGEUSDT is now testing a strong support zone near the 0.5 Fibonacci level. This setup suggests the potential for a further 20% upside, with the main target around 0.24.
Now, let's dive into the educational section,
🧨 When the market is green fear should grow
In bearish markets people are cautious But in bull runs everyone fears missing out
This phase is exactly what pumpers love Why Because they know people are ready to chase every green candle
Are you actually profiting or just running after profits
If you do not have a strategy if your exit points are not clear if you do not know when to take profits
You are giving the game away to others
🕳️ Illusion of control traders’ silent enemy
When a few trades go well you think you have got the market figured out But actually the market has you
This sense of control mixed with greed leads to heavy risking skipping stop losses or riding fake pumps to the end
What is the solution Only strategy No influencer hype no social media noise no candle colors.
📊 Smart use of TradingView’s tools:
Many traders decide with emotions not data
But with a few simple TradingView tools you can base your decisions on data not feelings
One of the most practical indicators to spot overbought conditions or excessive greed is the RSI
When RSI goes above seventy it means the market is in a hype phase That is when many blindly jump in
A simple method Add RSI to your favorite crypto chart and check if a pump happened in the overbought zone
Another tool Volume Profile shows you the price levels with the highest trading volume
When price hits an area with very low volume behind it be cautious This could be a fake top
A golden tip Use TradingView Alerts
Instead of constantly staring at charts set alerts for when RSI passes seventy five or price reaches a suspicious zone Then get notified instantly
This way you let data guide you not momentary excitement
And this is exactly where you separate yourself from an unplanned greedy trader
💡 Summary and advice
Trading without strategy whether in bull or bear markets puts your capital at risk sooner or later
You can’t remove greed but you can control it
TradingView tools exist for exactly this reason to help you think before you act
Profit comes from planning not from chasing the next pump
✨ Need a little love!
We pour love into every post your support keeps us inspired! 💛 Don’t be shy, we’d love to hear from you on comments. Big thanks , Mad Whale 🐋
📜Please make sure to do your own research before investing, and review the disclaimer provided at the end of each post.