GBPUSD. Weekly trading levels 14 - 18.04.2025During the week you can trade from these price levels. Finding the entry point into a transaction and its support is up to you, depending on your trading style and the development of the situation. Zones show preferred price ranges WHERE to look for an entry point into a trade.
If you expect any medium-term price movements, then most likely they will start from one of the zones.
Levels are valid for a week, the date is in the title. Next week I will adjust the levels based on new data and publish a new post.
! Please note that brokers have a difference in quotes, take this into account when trading.
The history of level development can be seen in my previous posts. They cannot be edited or deleted. Everything is fair. :)
----------------------------------------------
I don’t play guess the direction (that’s why there are no directional arrows), but zones (levels) are used for trading. We wait for the zone to approach, watch the reaction, and enter the trade.
Levels are drawn based on volumes and data from the CME. They are used as areas of interest for trading. Traded as classic support/resistance levels. We see the reaction to the rebound, we trade the rebound. We see a breakout and continue to trade on a rollback to the level. The worst option is if we revolve around the zone in a flat.
Do not reverse the market at every level; if there is a trend movement, consider it as an opportunity to continue the movement. Until the price has drawn a reversal pattern.
More information in my RU profile.
Don't forget to like Rocket and Subscribe!!! Feedback is very important to me!
Futurestrading
ZEC ANALYSIS🔮 #ZEC Analysis
🌟🚀 #ZEC is trading in an Ascending Triangle Pattern and here we can see that #ZEC testing the ascending trendline. Also there is an instant major support zone. We can see a pullback from its major support zone.
🔖 Current Price: $32
⏳ Target Price: $40
⁉️ What to do?
- We have marked crucial levels in the chart . We can trade according to the chart and make some profits. 🚀
#ZEC #Cryptocurrency #Breakout #DYOR
MNQ!/NQ1! Day Trade Plan for 04/11/2025MNQ!/NQ1! Day Trade Plan for 04/11/2025 (Just because 😏)
📈18670 18820
📉18220 18060
Thanks to all my followers! Truly appreciate the support!
Please like and share for more NQ levels Tues & Thurs 🤓📈📉🎯💰
*These levels are derived from comprehensive backtesting and research and a quantitative system demonstrating high accuracy. This statistical foundation suggests that price movements are likely to exceed initial estimates.*
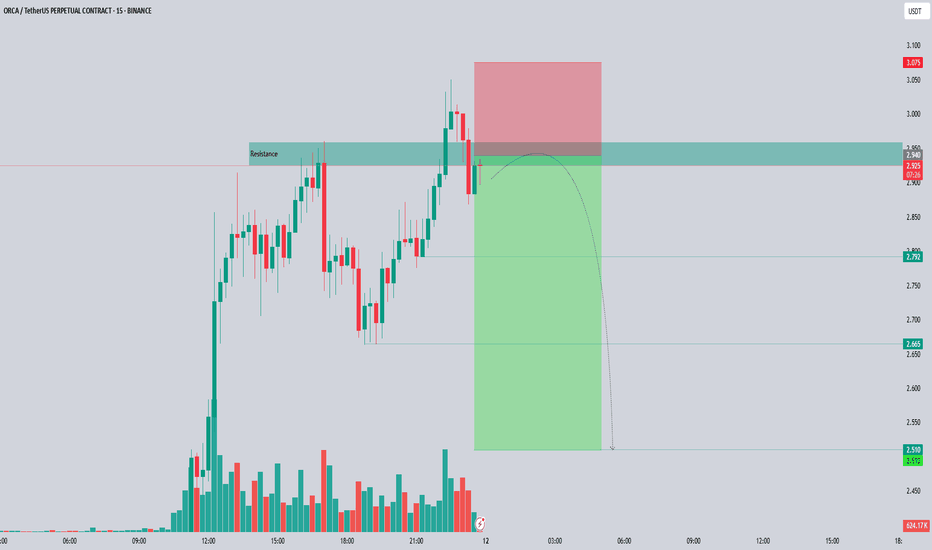
ORCA/USDT – Futures Setup: Potential Short OpportunityORCA is currently testing a resistance zone at 2.940 USDT, an area where selling pressure has historically emerged. Price action indicates a potential rejection, setting up a possible short trade targeting lower support levels.
📌 Futures Trading Levels:
Entry Zone: 2.920 - 2.940 – short positions could be considered upon confirmation of rejection.
Stop-Loss: 3.075 – placed above resistance to limit risk exposure.
Take-Profit Targets:
First TP: 2.79
Second TP: 2.665
Third TP: 2.51
This structure aligns with futures trading principles while maintaining risk management. Let me know if you’d like further refinements! 🚀📊
MNQ!/NQ1! Day Trade Plan for 04/10/2025MNQ!/NQ1! Day Trade Plan for 04/10/2025
📈19130
📉18530
Thanks to all my followers! Truly appreciate the support!
Please like and share for more NQ levels Tues & Thurs 🤓📈📉🎯💰
*These levels are derived from comprehensive backtesting and research and a quantitative system demonstrating high accuracy. This statistical foundation suggests that price movements are likely to exceed initial estimates.*
BTC ANALYSIS📊 #BTC Analysis
✅There is a formation of Falling Wedge Pattern on 12 hr chart and currently trading around its major support zone🧐
Pattern signals potential bullish movement incoming after a breakout
👀Current Price: $78,150
🚀 Target Price: $84,900
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #BTC price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#BTC #Cryptocurrency #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
MNQ!/NQ1! Day Trade Plan for 04/08/2025MNQ!/NQ1! Day Trade Plan for 04/08/2025
📈18365
📉17755
Thanks to all my followers! Truly appreciate the support!
Please like and share for more NQ levels Tues & Thurs 🤓📈📉🎯💰
*These levels are derived from comprehensive backtesting and research and a quantitative system demonstrating high accuracy. This statistical foundation suggests that price movements are likely to exceed initial estimates.*
ETH ANALYSIS🔮 #ETH Analysis :: Support & Resistance Trading
💲💲 #ETH is trading between support and resistance area. If #ETH sustains above major support area then we will a bullish move and if not then we will see more bearish move in #ETH then could expect a pullback.
💸Current Price -- $1564
⁉️ What to do?
- We have marked crucial levels in the chart . We can trade according to the chart and make some profits. 🚀💸
#ETH #Cryptocurrency #DYOR
Nasdaq Enters Correction Territory Do we go Deeper
Monthly analysis done on the NQ with the ambition to connect with current price activity and gauge a deeper technical understanding on if this is just the start of a bigger correction for the year ahead . Tools used in this video Standard Fib , TR Pocket , CVWAP/ PVWAP Incorporating PVWAP and CVWAP into trading strategies allows for a more nuanced understanding of market dynamics used to assess trading performance and market trends.
Date and price range and trend line .
Some research below regarding the previous correction that I reference the technicals to in the video .
In November 2021, the Nasdaq reached record highs
However, concerns over rising inflation, potential interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve, and supply chain disruptions led to increased market volatility. These factors contributed to a correction in the Nasdaq, with the index experiencing notable declines as investors reassessed valuations, particularly in high-growth technology stocks.
VS Today
March 2025 Correction:
As of March 2025, the Nasdaq Composite has faced another significant correction. On March 10, 2025, the index plummeted by 4%, shedding 728 points, marking its third-worst point loss ever, with only earlier losses during the COVID-19 pandemic surpassing this.
This downturn has been attributed to several factors:
Economic Policies: President Trump's announcement of increased tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China has unsettled markets, raising fears of a potential recession
Inflation Concerns: Investors are closely monitoring upcoming consumer-price index (CPI) reports to gauge inflation trends, as higher-than-expected inflation could hinder the Federal Reserve's ability to lower interest rates, exacerbating stock market declines
Sector-Specific Declines: Major technology companies, including Tesla, have experienced significant stock price declines, contributing to the overall downturn in the Nasdaq
Comparison of the Two Corrections:
Catalysts: The November 2021 correction was primarily driven by concerns over rising inflation and potential interest rate hikes. In contrast, the March 2025 correction has been influenced by geopolitical factors, including new tariff announcements, and ongoing inflation concerns.
Magnitude: While both corrections were significant, the March 2025 correction has been more severe in terms of single-day point losses. The 4% drop on March 10, 2025, resulted in a loss of 728 points, marking it as one of the most substantial declines in the index's history.
Investor Sentiment: Both periods saw increased market volatility and a shift towards risk aversion. However, the recent correction has been accompanied by heightened fears of a potential recession, partly due to inconsistent government messaging regarding economic prospects.
In summary, while both corrections were driven by concerns over inflation and economic policies, the March 2025 correction has been more pronounced, with additional factors such as new tariffs and recession fears playing a significant role.
SOL ANALYSIS🔮 #SOL Analysis 🚀🚀
💲💲 #SOL is trading in a Ascending Broadening Wedge Pattern and there is a breakdown of the pattern. And we can expect more bearish move towards it's support zone and the a reversal
💸Current Price -- $119.10
⁉️ What to do?
- We have marked crucial levels in the chart . We can trade according to the chart and make some profits. 🚀💸
#SOL #Cryptocurrency #DYOR
LTC ANALYSIS (support & resistance)🔮 #LTC Analysis 🚀🚀
💲💲 #LTC is trading between support and resistance area. There is a potential rejection again from its resistance zone and pullback from its major support area. If #LTC sustains above major support area then we will a bullish move till its major resistance area
💸Current Price -- $82.20
⁉️ What to do?
- We have marked crucial levels in the chart . We can trade according to the chart and make some profits. 🚀💸
#LTC #Cryptocurrency #DYOR
COTI ANALYSIS 📊 #COTI Analysis
✅There is a formation of Descending Channel Pattern in weekly time frame in #COTI.
Also there is a perfect breakout and retest. Now we can expect a bullish move from major support zone. If not the we will see more bearish move and then a reversal in #COTI.
👀Current Price: $0.06390
🎯 Target Price : $0.08660
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #COTI price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#COTI #Cryptocurrency #Breakout #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
IP ANALYSIS🔮 #IP Analysis 💰💰
🌟🚀 As we can see that #IP is trading in a symmetrical triangle and there was a breakdown of the pattern. Last time there was a bullish move from the same support level. We can expect again a bullish momentum from its major support level🚀🚀
🔖 Current Price: $4.190
⏳ Target Price: $5.500
#IP #Cryptocurrency #DYOR
BTC ANALYSIS 🔮 #BTC Analysis 🚀🚀
💲💲 #BTC is trading between support and resistance area. There is a potential rejection again from its resistance zone and pullback from its major support area. If #BTC breaks resistance zone $88500 then there will a chance of bullish movement
💸Current Price -- $84470
⁉️ What to do?
- We have marked crucial levels in the chart . We can trade according to the chart and make some profits. 🚀💸
#BTC #Cryptocurrency #DYOR
ATOM ANALYSIS📊 #ATOM Analysis
✅There is a formation of Falling Wedge Pattern on daily chart with a good breakout and currently retests from the major resistance zone and again trading around its major resistance zone 🧐
Pattern signals potential bullish movement incoming after a successful breakout of resistance zone
👀Current Price: $4.800
🚀 Target Price: $6.300
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #ATOM price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#ATOM #Cryptocurrency #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
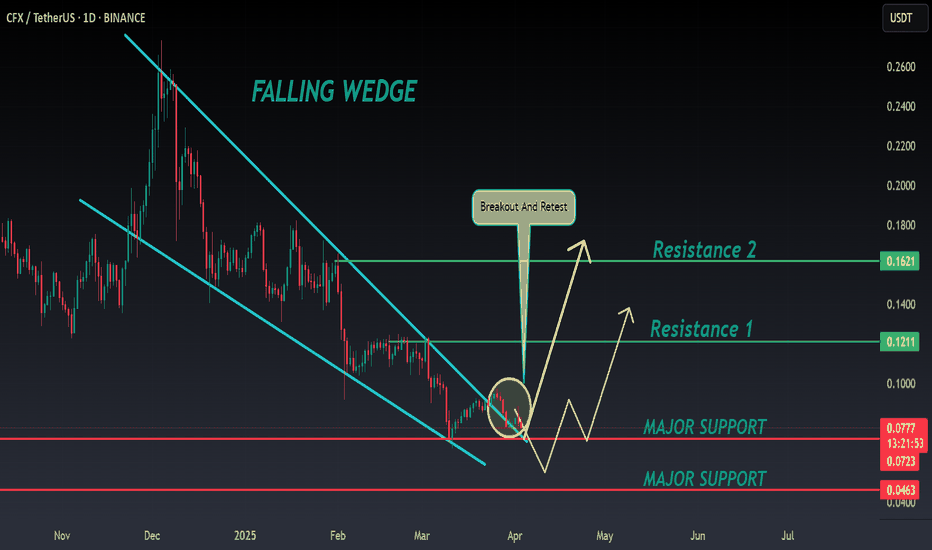
CFX ANALYSIS📊 #CFX Analysis
✅There is a formation of Falling Wedge Pattern on daily chart with a good breakout and currently retests from the major resistance zone🧐
Pattern signals potential bullish movement incoming after a successful retest
👀Current Price: $0.0775
🚀 Target Price: $0.1210
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #CFX price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#CFX #Cryptocurrency #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
RENDER ANALYSIS📊 #RENDER Analysis
✅There is a formation of Falling Wedge Pattern on daily chart with a good breakout and currently retests from the major resistance zone🧐
Pattern signals potential bullish movement incoming after a breakout of major resistance zone
👀Current Price: $3.455
🚀 Target Price: $4.4-6.0
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #RENDER price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#RENDER #Cryptocurrency #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
EOS ANALYSIS📊 #EOS Analysis
✅There is a formation of Falling Wedge Pattern on daily chart with a good breakout and currently retesting the major resistance zone🧐
Pattern signals potential bullish movement incoming after a breakout of major resistance zone
👀Current Price: $0.6235
🚀 Target Price: $0.9200
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #EOS price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#EOS #Cryptocurrency #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
Liberation, Altercation or Doom? ES Futures weekly planCME_MINI:ES1!
Quick Update
The upcoming week is poised to be critical for financial markets as President Donald Trump's so-called "Liberation Day" on April 2 approaches. On this date, the administration plans to implement new tariffs aimed at reducing the U.S. trade deficit by imposing reciprocal duties on imports from various countries.
As April 2 looms, the full impact of these tariffs remains uncertain, leaving markets and investors in a state of heightened anticipation.
We may get clarity on the tariff situation on April 2, 2025.
Universal tariff announcement of categories of imports may clarify US administration’s maximum tariff escalation approach.
A phased out and unclear tariff approach may keep markets in limbo.
Economic Calendar
Keep an eye on the data docket, NFP and other key releases are due this week.
Tuesday, Apri 1, 2025 : ISM Manufacturing PMI, JOLTS Job Openings
Wednesday April 2, 2025 : ADP Employment Change, Factory Orders MoM
Thursday April 3, 2025 : Balance of Trade, Imports, Exports, ISM Services PMI, Initial Jobless Claims
Friday, April 4, 2025 : Non-Farm Payrolls, Unemployment rate, Average Hourly Earnings MoM,Average Hourly Earnings YoY, Fed Chair Powell Speech
Key Levels to Watch:
Yearly Open 2025 : 6001.25
Key Resistance : 5850- 5860
LVN : 5770 -5760
Neutral Zone : 5705-5720
Key LIS Mid Range 2024 : 5626.50
2024-YTD mCVAL : 5381
2022 CVAH : 5349.75
August 5th, 2024 Low : 5306.75
Scenario 1: Bold but Strategic Tariffs (Effective Use of Tariff to reduce trade deficit and raise revenue) : In this scenario, we may see relief rally in ES futures, price reclaiming 2024 mid-range with a move higher towards key resistance level.
Scenario 2: Maximum pressure, maximum tariff (All out trade war) : In this scenario, we anticipate a sell-off with major support levels, such as 2024- YTD mCVAL, 2022 CVAH and August 5th, 2024 low as immediate downside targets.
Scenario 3: Further delays in Tariff policy (A negotiating tool, with looming uncertainty) : In this scenario, sellers remain in control and uncertainty persists, while we anticipate that rallies may be sold, market price action may remain choppy and range bound.
ZEC ANALYSIS📊 #ZEC Analysis
✅There is a formation of Falling Wedge Pattern on daily chart with a good breakout and currently retesting the major resistance zone🧐
Pattern signals potential bullish movement incoming after a breakout of major resistance zone
👀Current Price: $37.80
🚀 Target Price: $50.00
⚡️What to do ?
👀Keep an eye on #ZEC price action and volume. We can trade according to the chart and make some profits⚡️⚡️
#ZEC #Cryptocurrency #TechnicalAnalysis #DYOR
FET ANALYSIS🔆 #FET Analysis : Breakdown
📊As we can see that #FET is following ascending channel on 4hr time frame. There is a breakdown in #FET and if it sustain this breakdown then we would see a dump first then a pump.
⁉️ What to do?
- Keep your eyes on the chart, observe trading volume and stay accustom to market moves.🚀💸
#FET #Cryptocurrency #ChartPattern #DYOR