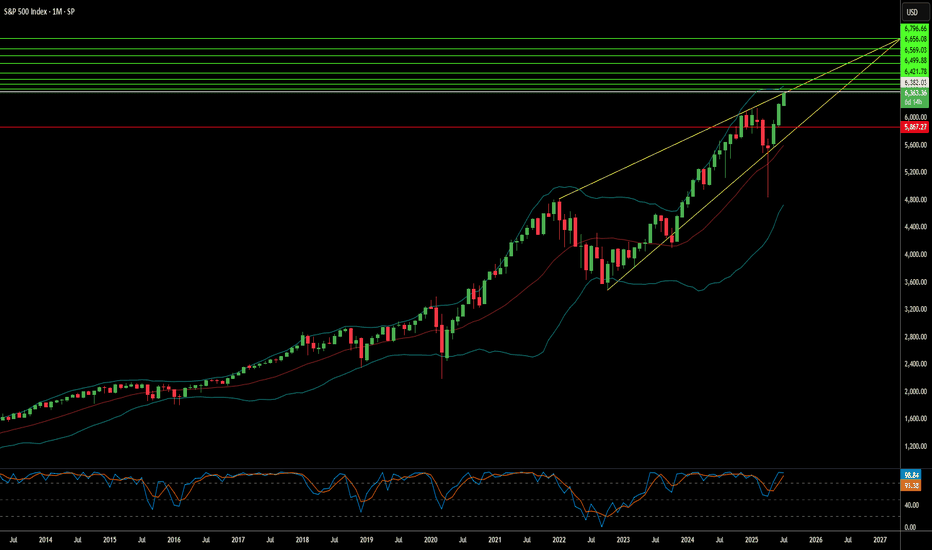
Can the S&P 500's Ascent Continue?The S&P 500 recently achieved unprecedented highs, reflecting a multifaceted market surge. This remarkable performance stems primarily from a robust corporate earnings season. A significant majority of S&P 500 companies surpassed earnings expectations, indicating strong underlying financial health. The Communication Services and Information Technology sectors, in particular, demonstrated impressive growth, reinforcing investor confidence in the broader market's strength.
Geopolitical and geostrategic developments have also played a crucial role in bolstering market sentiment. Recent "massive" trade agreements, notably with Japan and a framework deal with Indonesia, have introduced greater predictability and positive economic exchanges. These deals, characterized by reciprocal tariffs and substantial investment commitments, have eased global trade tensions and fostered a more stable international economic environment, directly contributing to market optimism. Ongoing progress in trade discussions with the European Union further supports this positive trend.
Furthermore, resilient macroeconomic indicators underscore the market's upward trajectory. Despite a recent dip in existing home sales, key data points like stable interest rates, decreasing unemployment claims, and a rising manufacturing PMI collectively suggest an enduring economic strength. While technology and high-tech sectors, driven by AI advancements and strong earnings from industry leaders like Alphabet, remain primary growth engines, some segments, such as auto-related chipmakers, face challenges.
The S&P 500's climb is a testament to the powerful confluence of strong corporate performance, favorable geopolitical shifts, and a resilient economic backdrop. While the immediate rally wasn't directly driven by recent cybersecurity events, scientific breakthroughs, or patent analyses, these factors remain critical for long-term market stability and innovation. Investors continue to monitor these evolving dynamics to gauge the sustainability of the current market momentum.
Marketvolatility
Temu's Price Magic: Shattered by Tariffs?PDD Holdings, the parent entity behind the popular e-commerce platform Temu, confronts a severe operational challenge following the recent imposition of stringent US tariffs targeting Chinese goods. These trade measures, particularly the dismantling of the "de minimis" rule for Chinese shipments, directly threaten the ultra-low-cost business model that fueled Temu's rapid expansion in the US market. The elimination of the previous $800 duty-free threshold for individual packages strikes at the core of Temu's logistical and pricing strategy.
The impact stems from newly enacted, exceptionally high tariffs on these formerly exempt low-value parcels. Reports indicate rates escalating to 90% of the item's value or a significant flat fee, effectively nullifying the cost advantages Temu leveraged by shipping directly from manufacturers in China. This fundamental shift disrupts the financial viability of Temu's model, which relied heavily on tariff-free access to deliver goods at minimal prices to American consumers.
Consequently, significant price increases for products sold on Temu appear almost inevitable as PDD Holdings grapples with these substantial new costs. While the company's official response is pending, economic pressures suggest consumers will likely absorb these charges, potentially eroding Temu's primary competitive advantage and slowing its growth momentum. PDD Holdings now faces the critical task of navigating this disrupted trade landscape and adapting its strategy to maintain its market position amidst heightened protectionism and geopolitical tension.
Flow Traders: A Deep Dive into a Volatility PlayFlow Traders has long been recognized as one of the leading market makers in Exchange Traded Products (ETPs), holding a dominant position in Europe and steadily expanding its global footprint. The firm’s success is driven by its technological prowess—its ultra-low latency trading systems and proprietary algorithms enable it to provide liquidity across thousands of listings. When compared with major competitors such as Virtu Financial, Citadel Securities, Jane Street, and Optiver, Flow Traders stands out for its high profit margins and robust returns during volatile periods. However, its earnings can swing dramatically: record profits during periods of market turbulence contrast with more compressed margins in quieter times.
Historically, Flow Traders followed a dividend policy with an intended payout ratio of at least 50% of net profits. In FY23, for example, the company paid a total dividend of €0.45 per share (an interim dividend of €0.30 per share plus a final dividend of €0.15 per share). However, in its recent 2Q24 results and AGM communications, Flow Traders announced a revised dividend policy that suspends regular dividend payments until further notice. The Board has made this decision to accelerate the expansion of its trading capital base—a move the management believes will deliver greater long-term value for shareholders through reinvestment in technology and market expansion rather than immediate income distribution.
Technologically, Flow Traders continues to push the boundaries by investing in co-located servers, low-latency networks, and even exploring cloud-based systems with microsecond-level synchronization. These initiatives ensure that the firm maintains a competitive edge, even as peers like Virtu and Citadel invest heavily in their own technological infrastructure. While Flow’s niche focus—especially in European ETF market making—provides a strong competitive moat, the firm is also expanding into fixed income and digital assets.
For valuation purposes, I used a blended approach incorporating a Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model and industry comparables, augmented by a scenario analysis that reflects the inherent cyclicality of its earnings. In my model, three scenarios were considered over a five-year period. Under the best-case scenario, where global market volatility surges and Flow capitalizes on its technological advantages to boost market share, the five-year target price could reach around €80 per share. In a base-case scenario, reflecting a more normalized yet steadily growing trading environment, the target price might be closer to €40 per share. In the worst-case scenario—if markets remain persistently calm and competitive pressures intensify—the target could drop to about €15 per share.
Given the current market environment, the probabilities are 30% for the best-case, 60% for the base-case, and 10% for the worst-case. Additionally, the discount rate in the DCF 6%, reflecting today’s economic landscape risk premium. With these assumptions, discounting the future target prices at 6% yields present values of approximately €60, €30, and €11 for the best, base, and worst scenarios respectively. Weighting these figures accordingly results in an expected intrinsic value of around €37 per share today.
So, what does this mean for investors? At current trading levels in the mid-€20s, Flow Traders appears to be undervalued relative to its long-term potential. Although the firm is currently not paying dividends—opting instead to reinvest its profits to grow its trading capital—the strategic focus on reinvestment may unlock greater growth opportunities. In essence, Flow Traders represents an intriguing volatility play: it can generate outsized returns in turbulent times while offering a balanced risk/reward profile in more normalized markets.
Ultimately, Flow Traders’ strategic decision to suspend dividends underscores its commitment to long-term growth. Investors are essentially buying into the firm’s reinvestment strategy, which has historically delivered strong returns on trading capital. As market volatility and technological advancements continue to drive the industry, Flow Traders is well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and create shareholder value over the long run.
Speculation: With Trump’s tariffs continuing to rock global markets and trigger bouts of heightened volatility reminiscent of past trade wars, there’s reason to speculate that Flow Traders could find itself in a particularly advantageous position. As tariffs fuel uncertainty and market swings—further rattling investor confidence and prompting rapid shifts in liquidity—Flow Traders’ expertise in market making, especially in ETPs, could allow it to capture significant trading opportunities. The elevated volatility may widen bid-ask spreads and boost trading volumes, directly benefiting firms like Flow that thrive on rapid, high-frequency trades. While these are merely speculative thoughts, given the unpredictable nature of tariff-driven market disruptions, Flow’s focus on liquid, exchange-traded products might well make this turbulent period a silver lining for the company.
Could Silver's Price Soar to New Heights?In the realm of precious metals, silver has long captivated investors with its volatility and dual role as both an industrial staple and a safe-haven asset. Recent analyses suggest that the price of silver might skyrocket to unprecedented levels, potentially reaching $100 per ounce. This speculation isn't just idle talk; it's fueled by a complex interplay of market forces, geopolitical tensions, and industrial demand that could reshape the silver market landscape.
The historical performance of silver provides a backdrop for these predictions. After a notable surge in 2020 and a peak in May 2024, silver's price has been influenced by investor sentiment and fundamental market shifts. Keith Neumeyer of First Majestic Silver has been an outspoken advocate for silver's potential, citing historical cycles and current supply-demand dynamics as indicators of future price increases. His foresight, discussed across various platforms, underscores the metal's potential to break through traditional price ceilings.
Geopolitical risks add another layer of complexity to silver's valuation. The potential for an embargo due to escalating tensions between China and Taiwan could disrupt global supply chains, particularly in industries heavily reliant on silver like technology and manufacturing. Such disruptions might not only increase the price due to supply constraints but also elevate silver's status as a safe-haven investment during times of economic uncertainty. Moreover, the ongoing demand from sectors like renewable energy, electronics, and health applications continues to press against the available supply, setting the stage for a significant price rally if these trends intensify.
However, while the scenario of silver reaching $100 per ounce is enticing, it hinges on numerous variables aligning perfectly. Investors must consider not only the positive drivers but also factors like market manipulation, economic policies, and historical resistance levels that have previously capped silver's price growth. Thus, while the future of silver holds immense promise, it also demands a strategic approach from those looking to capitalize on its potential. This situation challenges investors to think critically about market dynamics, urging a blend of optimism with strategic caution.
Can the Yuan Dance to a New Tune?In the intricate ballet of global finance, the Chinese yuan performs a delicate maneuver. As Donald Trump's presidency introduces new variables with potential tariff hikes, the yuan faces depreciation pressures against a strengthening U.S. dollar. This dynamic challenges Beijing's economic strategists, who must balance the benefits of a weaker currency for exports against the risks of domestic economic instability and inflation.
The People's Bank of China (PBOC) is navigating this complex scenario with a focus on maintaining currency stability rather than aggressively stimulating growth through monetary policy easing. This cautious approach reflects a broader strategy to manage expectations and market reactions in an era where geopolitical shifts could dictate economic outcomes. The PBOC's recent moves, like suspending bond purchases and issuing warnings against speculative trades, illustrate a proactive stance in controlling the yuan's descent, aiming for an orderly adjustment rather than a chaotic fall.
This situation provokes thought on the resilience and adaptability of China's economic framework. How will Beijing reconcile its growth ambitions with the currency's stability, especially under the looming shadow of U.S. trade policies? The interplay between these two economic giants will shape their bilateral relations and influence global trade patterns, investment flows, and perhaps even the future of monetary policy worldwide. As we watch this economic dance unfold, one must ponder the implications for international markets and the strategic responses from other global players.
Can Political Tremors Rewrite Global Financial Markets?In the intricate dance of global finance, South Korea's recent political upheaval serves as a compelling microcosm of how geopolitical dynamics can instantaneously transform economic landscapes. The Kospi Index's dramatic 2% plunge following President Yoon Suk-yeol's fleeting martial law declaration reveals a profound truth: financial markets are not merely numerical abstractions, but living, breathing ecosystems acutely sensitive to political breath.
Beyond the immediate market turbulence lies a deeper narrative of institutional resilience and adaptive governance. The swift parliamentary intervention, coupled with the Bank of Korea's strategic liquidity injections, demonstrates a remarkable capacity to pivot and stabilize in moments of potential systemic risk. This episode transcends South Korea's borders, offering global investors a masterclass in crisis management and the delicate art of maintaining economic equilibrium amid political uncertainty.
The broader implications are both provocative and instructive. As heavyweight corporations like Samsung Electronics and Hyundai Motors experienced significant share price fluctuations, the event underscores an increasingly interconnected global financial system where local political tremors can rapidly cascade into international market movements. For forward-thinking investors and policymakers, this moment represents more than a crisis—it's an invitation to reimagine risk, resilience, and the complex interdependencies that define our modern economic reality.
Will Religious Tensions Reshape Europe's Financial Future?Europe stands at a critical crossroads where religious tensions are silently transforming its financial landscape, with the CAC 40 emerging as a crucial barometer of this unprecedented shift. What many market analysts initially dismissed as temporary social friction has evolved into a fundamental force reshaping investment strategies and corporate valuations. The extraordinary security measures deployed for the France-Israel football match – requiring 4,000 police officers – signals a new reality that transcends simple event management, pointing to deeper structural changes in how European markets must operate in an increasingly divided society.
The continent's financial centers are witnessing a profound transformation as religious tensions ripple through market fundamentals. In France, where Europe's largest Jewish and Muslim populations intersect, companies are frantically adapting their business models to navigate these uncharted waters. Traditional valuation metrics are proving inadequate as firms face rising security costs, shifting urban demographics, and evolving consumer behaviors driven by religious and cultural dynamics. This new paradigm forces investors to consider whether Europe's markets have entered an era where social cohesion rivals financial metrics in importance.
The emerging religious divisions in Europe represent more than a social challenge – they're reshaping the very foundation of market analysis. As witnessed in recent events across Amsterdam, Paris, and other major cities, what begins as cultural tension quickly translates into market volatility, altered consumer patterns, and revised risk assessments. Forward-thinking investors are now recognizing that success in European markets requires a sophisticated understanding of religious and cultural dynamics, marking a revolutionary shift in investment strategy. The CAC 40's journey through these turbulent waters may well predict how global markets will adapt to a world where religious tensions increasingly influence economic outcomes.
Navigating High Volatility Periods in TradingMarket volatility is a critical aspect of trading, and during certain periods—particularly around significant news events—this volatility becomes more pronounced. The graphic titled *"The Cycle of Market Volatility"* effectively captures the stages involved in how markets react and stabilize after major news events. These events, such as red folder news releases, economic reports, and elections, are pivotal moments that traders need to approach with both caution and strategy.
The Cycle of Market Volatility
1. News Events Occur
High-impact news, known as *red folder news*, includes economic data releases such as the Non-Farm Payroll (NFP), central bank interest rate decisions, inflation reports, and major political developments like elections. These events are known for triggering swift market movements and increased volatility.
2. Market Reaction
Once the news breaks, markets tend to react swiftly. Prices may shoot up or down as traders digest the new information and position themselves accordingly. The initial reaction is often driven by the big institutional players, and retail traders are frequently caught up in the momentum.
3. Media Amplification
After the initial market response, the media plays a significant role in amplifying the event. Analysts, news outlets, and social media start discussing the potential ramifications, which often leads to further market movement. Speculation and public sentiment can magnify the volatility.
4. Trader Response
As traders react to both the news and the media coverage, there can be an increase in trading volumes. Some traders might attempt to capitalize on the price swings, while others might exit their positions to avoid losses. Emotions like fear and greed tend to dominate in this phase, making it essential for traders to stick to their strategies.
5. Market Stabilization
Eventually, after the initial surge in price movement and emotional trading subsides, the market begins to stabilize. Once the news has been fully priced in and the dust settles, the markets may find equilibrium, and normal trading conditions resume—until the next major event.
Trading During High Volatility: Pros and Cons
Trading during high volatility events such as red folder news releases and elections can be both rewarding and dangerous. Let's explore some of the **pros and cons** of trading during these periods:
Pros
Large Profit Opportunities
Volatility creates sharp price movements, and for traders who can accurately predict market direction, these swings can translate into significant profits in a short period. For example, interest rate announcements or jobs data releases can cause currencies to move hundreds of pips in minutes.
Increased Liquidity
High-impact events often bring more participants into the market, leading to increased liquidity. This means trades can be executed more quickly, and spreads (the difference between bid and ask prices) may narrow, offering better trading conditions for short-term traders.
Clear Trends
Often after a red folder event, markets establish clearer trends. Whether it’s a sharp bullish or bearish move, traders may find it easier to follow the trend and capitalize on the momentum rather than dealing with the choppier markets typically seen in low-volatility periods.
Cons
Whipsaw Risk
One of the biggest dangers of trading during high volatility is the potential for whipsaw movements. The market may initially react one way, only to reverse sharply after further analysis or new information comes to light. This can lead to traders being stopped out or suffering losses as prices swing unpredictably.
Wider Spreads
While liquidity can increase, the initial reaction to major news can cause spreads to widen dramatically. This can eat into potential profits and make it difficult for traders to enter or exit positions at favorable prices.
Emotional Trading
News events tend to stir up emotions in traders—especially fear and greed. These emotions can cloud judgment, causing traders to deviate from their trading plans, make impulsive decisions, or over-leverage themselves in pursuit of quick gains.
Gaps in the Market
High-impact news can cause gaps in the market, where price jumps from one level to another without trading in between. This can be hazardous for traders who are in open positions, as stop-loss orders may not be filled at the expected price, leading to larger losses than anticipated.
Key Red Folder Events and How to Approach Them
Central Bank Interest Rate Decisions
Perhaps the most influential news events, interest rate decisions by central banks like the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank can cause massive volatility in Forex markets. Traders need to watch not just the decision itself but also the accompanying statements and guidance for future monetary policy.
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP)
Released monthly, the U.S. NFP report often leads to sharp movements in the USD and related currency pairs. The NFP provides insights into the health of the U.S. economy and is closely watched by traders around the world.
Elections and Political Events
Elections, referendums, and major geopolitical developments (such as US elections last week) can cause sustained volatility in markets. Traders should be particularly cautious around these events as outcomes can be highly unpredictable, and market reactions may be extreme.
Inflation Reports
Inflation data can significantly impact market expectations for interest rates, which in turn influences currency values. Central banks tend to adjust their monetary policy based on inflation trends, making these reports crucial for traders.
How to Trade Volatile Events Safely
Have a Clear Plan
Don’t enter trades during volatile periods without a well-thought-out strategy. Make sure to set clear stop-loss and take-profit levels and be prepared for sudden market reversals.
Consider Waiting for the Dust to Settle
Instead of trading the immediate market reaction, some traders prefer to wait until the news has been fully digested. By waiting for clearer trends to form after the event, traders can reduce their risk of getting caught in whipsaw price movements.
Practice Proper Risk Management
With greater volatility comes greater risk, so it’s crucial to limit your exposure. Reduce your position sizes and avoid over-leveraging during these times. Risk management is vital to surviving and thriving in high-volatility environments.
Stay Informed
Understanding the context behind major news events is critical. Following economic calendars, staying updated on geopolitical developments, and listening to expert analysis can help traders navigate high-volatility markets more effectively.
Conclusion
Trading during high volatility periods can present both opportunities and risks. While the potential for quick profits is tempting, the unpredictability of the markets during these times requires discipline, a solid strategy, and strong risk management. Understanding the *Cycle of Market Volatility* can help traders better anticipate how markets react to red folder news and major events, allowing them to make more informed trading decisions.
Is the S&P 500's Bull Run a Mirage?The S&P 500's recent all-time high has ignited a frenzy of optimism among investors. However, as the market reaches unprecedented heights, questions arise about the sustainability of this bull run and the potential risks lurking beneath the surface.
While the allure of soaring stock prices is undeniable, investing in a market at its peak carries inherent risks. The concentration of returns within a few dominant stocks (such as Nvidia, Alphabet, and Amazon), coupled with the potential for geopolitical shocks and economic downturns, introduces significant uncertainty. The dot-com bubble serves as a stark reminder of the market's cyclical nature and the perils of overvaluation.
To navigate this complex landscape, investors must adopt a balanced approach. Diversification, coupled with a keen understanding of economic indicators, geopolitical events, and corporate news, is essential for making informed decisions. By recognizing the potential pitfalls and taking proactive measures to mitigate risk, investors can position themselves for long-term success in the ever-evolving market.
The S&P 500's future remains uncertain, but by approaching the bull market with a critical eye and a strategic mindset, investors can navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities that lie ahead.
ZILUSD Forecast: Bullish Momentum & Targets for Q4 2024, Q1 2025ZILUSD currently finds robust support at $0.0136, suggesting favorable conditions for a potential uptrend. The recent retesting and observed volume indicate a promising setup for a bounce. Concurrently, the ETHBTC pairing shows notable growth, poised to potentially flip the 0.6 level, signaling a likely rally in altcoins. Moreover, with ETH's ETF approval nearing, the market anticipates heightened volatility and upward movements in Q4 2024. Historically, such periods have exhibited significant price rises and increased market activity during bull runs. Notably, preparations for market exit around March or November 2025 are advisable as bull runs typically conclude during these times.
In historical contexts, ZILUSD has shown resilience and substantial targets during bull runs, with a minimum target projection of around $0.5 in Q4 2024. Breaking the $0.5 resistance could propel prices towards a maximum target of $1.5 by Q1 2025. Since its listing in January 2018 amidst a bear market, ZILUSD underwent significant downtrends until March 2020, followed by a notable uptrend till May 2021's bull run. Subsequently, a downturn from May 2021 to December 2022 led to a consolidation phase until March 2024, marked by recent upward movements.
Retesting support at $0.0135 suggests a potential for a substantial uptrend towards Q1 2025 amidst the approaching altcoin season, expecting similar market volatility. Monitoring resistance zones and patterns is essential to maintain active trading strategies. Consider exiting long positions around March or November 2025, aligning with historical market cycles.
For more detailed analysis and future trading ideas, follow us on TradingView. Share this idea with your friends and family to maximize profits. Please like, comment, and engage with our posts for more insights. Thanks!
Crypto Market Insights: Bitcoin.D and Bitcoin Price PredictionUnderstanding Bitcoin Dominance:
Bitcoin dominance is crucial for understanding the broader crypto market, identifying potential growth projects, and making informed decisions to balance your crypto portfolio. BTC.D is approaching a significant resistance level of 57.42, which we expect to hit by October or November. Following this, a potential downtrend in BTC.D is anticipated.
Bitcoin Key Levels and Market Reactions:
Bitcoin has a strong support level at $53,400. If this support breaks, we might see BTC dominance around 57.42. Historically, when BTC dominance rises, Bitcoin's price tends to fall, and vice versa. The resistance zone at 57.42 has not been hit yet, but it is expected to by September. We foresee Bitcoin's price hovering between 52K and 48K, leading to a significant movement. A bullish market is likely to start after November, with increased volatility expected in Q4 2024.
Bitcoin Bull Market Projections:
Based on historical data and calculations, Bitcoin's bull run targets a minimum of $253,623. If Bitcoin flips this resistance by February 2025, we could see a maximum target of $275,780. Past bull runs in 2013, 2017, and 2021 saw unexpected price pumps, and similar volatility is expected this time. It's crucial to keep trades active while monitoring resistance zones, with a strategic exit from long positions by March or November 2025.
As we anticipate these market movements, staying informed and prepared is key. By understanding and acting on these insights, you can navigate the crypto market more effectively. Remember, each bull market brings its own set of opportunities and challenges.
For more in-depth analysis and to stay updated with our latest trading ideas, follow us on TradingView. Gain valuable insights and make informed trading decisions with our expert analysis.
Overall Sentiment for US Economy from January to May 2024The period from January to May 2024 has been marked by significant bearish sentiment due to multiple geopolitical events. The escalation of conflicts in Ukraine, increased US-China trade tensions, disruptions in the Red Sea, and heightened hostilities in the Middle East have collectively contributed to market instability. These events led to increased energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and heightened global volatility, which pressured the US Dollar Index.
The overall bearish impact on the dollar was driven primarily by inflationary pressures from higher oil prices and increased geopolitical risks, reducing demand for the dollar as a safe haven. Large institutions had to adjust their portfolios and manage risks strategically to navigate the volatile environment.
UVXY crosses over mean anchored VWAP LONGUVXY which leverages the VIX as a measure of volatility / greed/ fear has finally crossed
over the mean anchored VWAP. This is a sign of bullish momentum and perhaps a signal that
traders should hedge or consider their positions in terms of hard risk management. Those
who traded this move up today made 10% or better in the trade. Those who bought call options
expiring tomorrow made 10X and those with call options for next Friday made 5X overnight.
Tomorrow is another day. Likely the market will rise from the correction and UXVY will fade
a bit. No matter, its value for insurance and hedging is reinforced on days like the past day.
I am maintaining a full position aside the call options closed at the afternoon bell which
expire on Friday and had time decay to contend with. My first target is 7.75 then comes
8.05 and 8.45. I will take off 20% at each target and keep the others for insurance for
a true market crash or black swan event to buffer losses while stops get hit.
Options Blueprint Series Strangles vs. StraddlesIntroduction
In the realm of options trading, the choice of strategy significantly impacts the trader's ability to navigate market uncertainties. Among the plethora of strategies, the Strangle holds a unique position, offering flexibility in unclear market conditions without the upfront costs associated with more conventional approaches like the Straddle. This article delves into the intricacies of the Strangle strategy, emphasizing its application in the volatile world of Gold Futures trading. For traders seeking a foundation in the Straddle strategy, refer to our earlier discussion in "Options Blueprint Series: Straddle Your Way Through The Unknown" -
In-Depth Look at the Strangle Strategy
The Strangle strategy involves purchasing a call option and a put option with the same expiration date but different strike prices. Typically, the call strike price is higher than the current market price, while the put strike price is lower. This approach is designed for situations where a significant price movement is anticipated, but the direction of the movement is uncertain. It's particularly effective in markets prone to sudden swings, making it a valuable strategy for Gold Futures traders who face volatile market conditions.
Advantages of the Strangle strategy include its lower upfront cost compared to the Straddle strategy, as options are bought out-of-the-money (OTM). This aspect makes it a more accessible strategy for traders with budget constraints. The potential for unlimited profits, should the market make a strong move in either direction, further adds to its appeal.
However, the risks include the total loss of the premium paid if the market does not move significantly and both options expire worthless. Therefore, timing and market analysis are critical when implementing a Strangle in the gold market.
Example: Consider a scenario where Gold Futures are trading at $1,800 per ounce. Anticipating volatility, a trader might purchase a call option with a strike price of $1,820 and a put option with a strike price of $1,780. If gold prices swing widely enough in either direction, the strategy could yield substantial profits.
Strangle vs. Straddle: Understanding the Key Differences
The Strangle and Straddle strategies are both designed to capitalize on market volatility, yet they differ significantly in execution and ideal market conditions. While the Straddle strategy involves buying a call and put option at the same strike price, the Strangle strategy opts for different strike prices. This fundamental difference impacts their cost, risk, and potential return.
Cost Implications: The Strangle strategy is generally less expensive than the Straddle due to the use of out-of-the-money options. This lower initial investment makes the Strangle appealing to traders with tighter budget constraints or those looking to manage risk more conservatively.
Risk Exposure and Profit Potential: Although both strategies offer unlimited profit potential, the Strangle requires a more significant price move to reach profitability due to its out-of-the-money positions. Consequently, the risk of total premium loss is higher with Strangles if the anticipated volatility does not materialize to a sufficient degree.
Market Conditions: Straddles are best suited for markets where significant price movement is expected but without clear directional bias. Strangles, given their lower cost, might be preferred in situations where substantial volatility is anticipated but with a slightly lower conviction level, allowing for larger market moves before profitability.
In the context of Gold Futures and Micro Gold Futures, traders might lean towards a Strangle strategy when expecting major market events or economic releases that could induce significant gold price fluctuations. The choice between a Strangle and a Straddle often comes down to the trader's market outlook, risk tolerance, and cost considerations.
Application to Gold Futures and Micro Gold Futures
Implementing a Strangle in the Gold Futures market requires a keen understanding of underlying market conditions and volatility. Given the precious metal's sensitivity to global economic indicators, political instability, and changes in demand, traders can leverage the Strangle strategy to capitalize on expected price swings without committing to a directional bet. When applying a Strangle to Gold Futures, selecting the appropriate strike prices becomes crucial. The goal is to position the OTM options in a way that balances the potential for significant price movements with the cost of premiums paid. This balance is critical in scenarios like central bank announcements or inflation reports, where gold prices can experience sharp movements, offering the potential for Strangle strategies to flourish.
Long Straddle Trade-Example
Underlying Asset: Gold Futures or Micro Gold Futures (Symbol: GC1! or MGC1!)
Strategy Components:
Buy Put Option: Strike Price 2275
Buy Call Option: Strike Price 2050
Net Premium Paid: 11.5 points = $1,150 ($115 with Micros)
Micro Contracts: Using MGC1! (Micro Gold Futures) reduces the exposure by 10 times
Maximum Profit: Unlimited
Maximum Loss: Net Premium paid
Risk Management
Effective risk management is paramount when employing options strategies like the Strangle, especially within the volatile realms of Gold Futures and Micro Gold Futures trading. Traders should be acutely aware of the expiration dates and the time decay (theta) of options, which can erode the potential profitability of a Strangle strategy as the expiration date approaches without significant price movement in the underlying asset. To mitigate such risks, it's common to set clear criteria for adjusting or exiting the positions. This could involve rolling out the options to a further expiration date or closing the position to limit losses once certain thresholds are met.
Additionally, the use of stop-loss orders or protective puts/calls as part of a broader trading plan can provide a safety net against unforeseen market reversals. Such techniques ensure that losses are capped at a predetermined level, allowing traders to preserve capital for future opportunities.
Conclusion
The Strangle and Straddle strategies each offer unique advantages for traders navigating the Gold Futures market's uncertainties. By understanding the distinct characteristics and application scenarios of each, traders can make informed decisions tailored to their market outlook and risk tolerance. While the Strangle strategy offers a cost-effective means to leverage expected volatility, it also necessitates a disciplined approach to risk management and an acute understanding of market dynamics.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Options Blueprint Series: Straddle Your Way Through The UnknownIntroduction
Options trading offers a dynamic avenue for investors to navigate the financial markets, and among the myriad of strategies available, the Straddle strategy stands out for its unique ability to capitalize on market volatility without necessitating a directional bet. This article, part of our Options Blueprint Series, zooms in on utilizing Options on S&P 500 Futures (ES) to employ the Straddle strategy. The S&P 500 index, embodying a broad spectrum of the market, presents a fertile ground for options traders to implement this strategy, especially in times of uncertainty or ahead of major market-moving events.
Understanding S&P 500 Futures Options
Options on S&P 500 Futures offer traders and investors a versatile tool for hedging, speculating, and portfolio management. These options grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying S&P 500 Futures at a predetermined price before the option expires. Trading on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), these instruments encapsulate the market sentiment towards the future direction of the U.S. economy and stock market. Their popularity stems from the leverage they offer, alongside the efficiency and liquidity provided by the CME, making them an effective instrument for executing sophisticated strategies like the Straddle.
The Core of the Straddle Strategy
The Straddle strategy in options trading is a powerful method to exploit volatility. It involves simultaneously buying a call and put option on the same underlying asset, with identical strike prices and expiration dates. This non-directional strategy is designed to profit from significant price movements in either direction. For S&P 500 Futures options, this means traders can position themselves to benefit from market swings without trading the trends. The beauty of the Straddle lies in its simplicity and the direct way it captures volatility, making it a commonly used strategy in times of economic reports, earnings announcements, or geopolitical events that can trigger substantial market movements.
Executing the Straddle Strategy on S&P 500 Futures Options
Implementing a Straddle with S&P 500 Futures options involves a calculated approach. The first step is selecting the right expiration date and strike price, typically at-the-money (ATM) or near-the-market values of the ES options, to ensure a balanced exposure to price movements. Timing is crucial; initiating a Straddle ahead of anticipated volatility spikes can be more cost-effective, as option premiums tend to rise with increased uncertainty. Utilizing TradingView's comprehensive analysis tools, traders can gauge market sentiment, identify potential volatility catalysts, and choose the optimal entry points. Managing the trade requires vigilance, as the key to maximizing profits with a Straddle lies in the ability to respond adeptly to market shifts, possibly adjusting positions to mitigate risks or capture emerging opportunities.
Market Analysis for Straddle Execution
For a successful Straddle execution on S&P 500 Futures options, thorough market analysis is indispensable. Volatility, the lifeblood of the Straddle strategy, can be assessed using various technical indicators available on TradingView, such as the Average True Range (ATR) or the CME Group Volatility Index (CVOL). Economic indicators and scheduled events also play a crucial role. Traders should closely monitor the economic calendar for upcoming reports or news that could sway the market, adjusting their strategies accordingly. By analyzing past market reactions to similar events, traders can better predict potential price movements, enhancing their Straddle trade's effectiveness.
Implied Volatility and CVOL
Understanding Implied Volatility (IV) when trading Straddles is essential. IV reflects the market's expectation of a security's price fluctuation and significantly influences option premiums.
Since the S&P 500 Futures is a CME product, examining CVOL could provide an advantage to the trader as CVOL is a comprehensive measure of 30-day expected volatility from tradable options on futures which can help to understand if options are underpriced of overpriced at the time of the trade.
Strategic Risk Management for Straddle Trades
Risk management is paramount in options trading, especially with strategies like the Straddle that involve multiple option positions. Setting predefined exit criteria can help traders lock in profits or cut losses, ensuring that one side of the Straddle does not negate the other's gains. It's also vital to consider the time decay (theta) of options, as it can erode the value of positions as expiration approaches. Utilizing stop-loss orders or adjusting the Straddle to a more defensive setup, like transforming it into an Iron Condor, are ways to manage risk. Moreover, traders must keep an eye on liquidity to ensure they can adjust or exit their positions without significant slippage.
Case Study: Navigating Market Uncertainty with a Straddle on ES Options
Let's examine a hypothetical scenario where a trader employs a Straddle strategy on S&P 500 Futures options ahead of a potential major expected movement as the S&P 500 gaps up significantly after making a new all-time high which may lead to an unsustainable market condition. The trader selects ATM options with a 50-day expiration, expecting a sharp price movement in either direction.
Key S&P 500 Contract Specs
Tick Size (Minimum Price Fluctuation): 0.25 index points, equivalent to $12.50 per contract.
Trading Hours: Nearly 24-hour trading, starting from Sunday evening to Friday afternoon (Chicago times) with a 1-hour break each day.
Cash Settlement: No physical delivery of goods; contracts are settled in cash based on the index value.
Margin Requirements: Traders must post an initial margin and a maintenance margin, set by the exchange as a recommendation, to hold a position. These margins can vary based on market volatility and changes in the index value. Currently: $11,800 per contact.
Trading Venue: S&P 500 Futures are traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
Access and Participation: Available to individual and institutional investors through futures brokerage accounts.
Leverage and Risk: Futures offer leverage, meaning traders can control large contract values with a relatively small amount of capital, which also increases risk.
Long Straddle Trade-Example
Underlying Asset: E-mini S&P 500 Futures (Symbol: ES1!)
Strategy Components:
Buy Put Option: Strike Price 5200
Buy Call Option: Strike Price 5200
Net Premium Paid: 195 points = $9,750
Micro Contracts: Using MES1! (Micro E-mini Futures) reduces the exposure by 10 times
Maximum Profit: Unlimited
Maximum Loss: Net Premium paid
Conclusion
The Straddle strategy, when applied to S&P 500 Futures options, offers traders a potent tool to potentially profit from market volatility without taking a directional stance. By understanding the nuances of the S&P 500 Futures options market, meticulously planning their Straddle setups, and employing rigorous risk management practices, traders can navigate the complexities of the options landscape with confidence. Continuous learning and practice, particularly in simulated trading environments, are essential for refining strategy execution and enhancing trade outcomes.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Options Blueprint Series: Protective Puts for Market DefenseIntroduction to Protective Puts: Safeguarding Your Investments with Options
In the ever-fluctuating world of finance, protective puts emerge as a strategy for investors aiming to shield their portfolios from unexpected downturns. This options blueprint series delves into the intricacies of protective puts, presenting them as a pivotal component in the arsenal of market defense mechanisms.
Understanding Gold Futures
Before we navigate the strategic utilization of protective puts, it's essential to grasp the fundamentals of Gold Futures traded on the COMEX exchange. Gold Futures are contracts to buy or sell a specific amount of gold at a predetermined price on a set future date. These contracts are standardized in terms of quality, quantity, and delivery time, making them a popular tool for risk management.
Contract Specifications:
Contract Size: One Gold Futures contract represents 100 troy ounces of gold.
Point Value: Each point move in the gold price equates to a $100 change per contract.
Margin Requirements: Initial and maintenance margin requirements vary (currently $8,300 per contract), providing leverage to traders but also increasing risk.
Trading Hours: Gold Futures trading hours extend beyond the traditional market hours (currently 23 hours of trading per day), offering flexibility to traders across the globe.
In addition to standard Gold Futures, investors and traders can also consider Micro Gold Futures as a more granular tool for their trading and hedging strategies. Micro Gold Futures represent 10 troy ounces of gold, offering a tenth of the size of a standard Gold Futures contract. This smaller contract size allows for greater precision in position sizing, making it easier for individual investors to tailor their investment strategies to their specific risk tolerance and market outlook. Micro Gold Futures follow the same trading hours and quality standards as their standard counterparts, providing the same level of liquidity and access but with added flexibility.
These specifications underscore the liquidity and accessibility of both Gold Futures and Micro Gold Futures, making them attractive instruments for a diverse range of trading strategies, including protective puts. The addition of Micro Gold Futures to your trading arsenal can offer more precise control over your investment exposure, enhancing your ability to implement protective measures like puts effectively.
Implementing Protective Puts with Gold Futures
The protective put strategy entails purchasing a put option for an asset you own, in this case, Gold Futures. This approach effectively sets a floor on the potential losses should gold prices plummet, while still allowing for unlimited gains if gold prices soar.
This graph illustrates the payoff of a put strategy. Combining such outcome with a Long Gold Futures Positions would present a loss limitation below the put option's strike price, reflecting the insured nature of the investment against significant downturns. Conversely, the graph indicates the potential for unlimited gains, minus the cost of the put premium, as gold prices rise.
Why Use Protective Puts?
The allure of protective puts lies in their ability to provide a safety net for investors, particularly in the volatile realm of Gold Futures trading. This strategy is akin to purchasing insurance for your portfolio; it's about preparedness, not prediction. In an unpredictable market, protective puts are a testament to the adage, "Hope for the best, but prepare for the worst."
Cost of Protection
The cost of purchasing a put option, known as the premium, is the price paid for downside protection. While this cost can impact overall returns, the premium is often viewed as a reasonable fee for the insurance it provides against significant losses. Savvy investors consider this cost an investment in portfolio stability and risk management.
How Protective Puts Work
Understanding the mechanics of protective puts is crucial for effectively employing this strategy in the context of Gold Futures trading. This section demystifies the process, guiding investors on how to leverage protective puts for market defense.
The Mechanics of Protective Puts
Purchasing the Put Option: The first step involves buying a put option for the Gold Futures contracts you own. This put option grants you the right, but not the obligation, to sell your futures contracts at a specific strike price up to the option's expiration date.
Choosing the Strike Price: The strike price should reflect the level of protection you desire. A strike price set below the current market price of the Gold Futures offers a balance between cost (premium) and the degree of protection.
Determining the Premium: The cost of the put option, or premium, varies based on several factors, including the strike price, the duration until expiration, and the volatility of the gold market. This premium is the maximum risk the investor faces, as it represents the cost of protection.
Scenario Outcomes:
If Gold Prices Fall: Should the market price of Gold Futures drop below the strike price of the put option, the investor can exercise the option, selling the futures contracts at the protected strike price, thereby minimizing losses.
If Gold Prices Rise: In the event that gold prices increase, the protective put option may expire worthless, but the investor benefits from the rise in the value of their Gold Futures contracts, less the cost of the premium.
Implementing Protective Puts in Your Portfolio
To effectively implement protective puts in your investment strategy, consider the following steps:
Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Determine the level of downside protection you need based on your risk appetite and investment goals.
Select the Appropriate Put Options: Choose put options with strike prices and expiration dates that align with your desired level of protection and market outlook.
Monitor the Market: Stay informed about market conditions and adjust your protective put strategy as necessary to align with changing market dynamics and investment objectives.
Scenario Analysis: Protective Puts in Action
Let's explore how protective puts would work out in the current Gold Futures market scenario.
In a bullish market, where Gold Futures prices are rising, the protective put option may expire worthless, but the investor benefits from the increase in the value of their Gold Futures contracts. The cost of the put option (the premium) is the only loss, considered an insurance expense against downside risk.
In a bearish market, Gold Futures prices decline. If the price falls below the strike price of the put option, the investor can exercise the option to sell the futures at the strike price, thus minimizing losses.
In a market where Gold Futures prices remain relatively stable, the protective put option may expire worthless. The investor retains ownership of the futures contracts, which have not significantly changed in value, losing only the premium paid for the put option.
Considerations and Best Practices
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh the cost of the put option premiums against the potential benefits of downside protection. Protective puts are an investment in peace of mind and should be evaluated as part of a broader risk management strategy.
Diversification: While protective puts offer specific risk mitigation for Gold Futures, consider diversification across different asset classes such as WTI Oil Futures, Yield Futures, etc. and strategies as a comprehensive approach to portfolio risk management.
Conclusion
Protective puts are a powerful tool for investors in Gold Futures, offering a methodical approach to safeguarding investments against adverse market movements. By thoughtfully implementing protective puts, investors can achieve a balanced portfolio, characterized by reduced risk and preserved potential for growth. As we move forward in our Options Blueprint Series, the importance of a disciplined approach to risk management and strategic planning cannot be overstated in the pursuit of investment success.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
MCDOWELL-N: Riding the Upward Wave! Analyzing for Potential GainHello traders,
Following the positive response to last week's study on AARTIIND , let's delve into another promising stock: NSE:MCDOWELL_N (United Spirits).
📈 Uptrend Observation: MCDOWELL-N has been exhibiting a consistent upward trajectory, bouncing off demand zones and charting higher.
⚖️ Strategic Entry Points: Anticipating potential upward movements, especially as it tests the demand zone below the CMP (Current Market Price).
💹 Derivative Trading: Derivative traders, consider the 1100CE option for liquidity. Monitor spot prices and buy the premium at opportune moments.
📅 February Forecast: With heightened volatility expected in February due to budget considerations, a watchful eye on market dynamics is crucial.
🧐 Trade Caution: Remember, my analysis is a guide, not a directive. Conduct thorough research before making any trading decisions.
📌 TradingView Wisdom: As TradingView says, "Look first, then leap."
🙏 Thank You: Grateful for your support! See you in the next post.
Best regards,
Alpha Trading Station
Quiet Before the Volatility Storm: WTI Crude Oil Options PlaysStay tuned!
Beyond this exploration of WTI Crude Oil options plays, we're excited to bring you a series of educational ideas dedicated to all types of options strategies. More insights coming soon!
Introduction to Market Volatility
In the realm of commodity trading, WTI Crude Oil stands out for its susceptibility to rapid price changes, making market volatility a focal point for traders. This volatility, essentially the rate at which the price of oil increases or decreases for a given set of returns, is a crucial concept for anyone involved in the oil market. It affects not only the risk and return profile of direct investments in crude oil but also plays a pivotal role in the pricing of derivatives and options tied to this commodity.
Volatility in the crude oil market can be attributed to a myriad of factors, ranging from geopolitical developments and supply-demand imbalances to economic indicators and natural disasters. For options traders, understanding the nuances of volatility is paramount, as it directly influences option pricing models through metrics such as Vega, which indicates the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the volatility of the underlying asset.
By delving into both historical and implied volatility, traders can gain insights into past market movements and future expectations, respectively. Historical volatility provides a retrospective view of price fluctuation intensity over a specific period, offering a statistical measure of market risk. Implied volatility, on the other hand, reflects the market's forecast of a likely range of movement in crude oil prices, derived from the price of options.
Incorporating volatility analysis into trading strategies enables options traders to make more informed decisions, particularly when considering positions in WTI Crude Oil options. Whether aiming to capitalize on anticipated market movements or to hedge against potential price drops, volatility remains a critical element of successful trading in the oil market.
News as a Catalyst for Volatility
The crude oil market, with its global significance, is incredibly sensitive to news, where even rumors can precipitate fluctuations in prices. Recent events have starkly demonstrated this phenomenon, showcasing how geopolitical tensions, OPEC+ decisions, and inventory data can serve as major catalysts for volatility in WTI Crude Oil markets.
1. Geopolitical Tensions: Middle East Conflicts
Geopolitical events, especially in oil-rich regions like the Middle East, have a pronounced impact on oil prices. For instance, conflicts or tensions in this area can lead to fears of supply disruptions, prompting immediate spikes in oil prices due to the region's significant contribution to global oil supply. Such events underscore the market's vulnerability to geopolitical instability and the swift reaction of oil prices to news suggesting potential supply threats.
2. OPEC+ Production Decisions
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, known as OPEC+, play a pivotal role in global oil markets through their production decisions. An announcement by OPEC+ to cut production usually leads to an increase in oil prices, as the market anticipates a tighter supply. Conversely, decisions to increase production can cause prices to drop. These actions directly influence market sentiment and volatility, illustrating the significant impact of OPEC+ policies on global oil markets.
3. Inventory Data Releases
Weekly inventory data from major consumers like the United States can lead to immediate reactions in the oil market. An unexpected increase in crude oil inventories often leads to a decrease in prices, reflecting concerns over demand or oversupply. Conversely, a significant draw in inventories can lead to price spikes, as it may indicate higher demand or supply constraints. These inventory reports are closely watched by market participants as indicators of supply-demand balance, affecting trading strategies and market volatility.
Each of these events has the potential to cause significant movements in WTI Crude Oil prices, affecting the strategies of traders and investors alike. By closely monitoring these developments, market participants can better anticipate volatility and adjust their positions accordingly, highlighting the importance of staying informed on current events and their potential impact on the market.
Technical Analysis Tools: Bollinger Bands and the 14-Day ADX
A sophisticated approach to navigating the fluctuating markets of WTI Crude Oil could involve the combined use of Bollinger Bands and the 14-day Average Directional Index (ADX). While Bollinger Bands measure market volatility and provide visual cues about the market's overbought or oversold conditions, the ADX offers a unique perspective on market momentum and trend strength.
The 14-Day ADX is pivotal in assessing the strength of a trend. A rising ADX indicates a strengthening trend, whether bullish or bearish, while a declining ADX suggests a weakening trend or the onset of a range-bound market. For options traders, particularly those interested in the long strangle strategy, the ADX provides valuable information. A low or declining ADX signals a weak or non-existent trend.
Bollinger Bands® serve as a dynamic guide to understanding market volatility. In this case an idea could be to apply Bollinger Bands® to the 14-Day ADX values instead of the WTI Crude Oil Futures prices. When combined, a pierce of the lower Bollinger Bands®, may suggest an opportune moment to establish a long strangle position in anticipation of a forthcoming breakout while options prices may be underpriced.
This combined approach allows traders to fine tune their entry and exit points. By waiting for the ADX to signal a nascent trend and Bollinger Bands to indicate a period of low volatility, traders can position themselves advantageously before significant market movements.
Strategizing with Bollinger Bands and ADX: In the dance of market analysis, the interplay between the ADX and Bollinger Bands choreographs a strategy of precision. Traders can look for moments when the market is quiet and options are underpriced. This dual-focus approach maximizes the potential of entering a long strangle options trade at the most opportune time, aiming for potential gains from subsequent volatility spikes in the WTI Crude Oil market.
Strategies for Trading WTI Crude Oil Options
In the volatile landscape of WTI Crude Oil trading, strategic agility is paramount. One strategy that stands out for its ability to harness volatility is the long strangle. This strategy is especially relevant in periods of low implied volatility (IV), providing traders with a unique opportunity to capitalize on potential market shifts without committing to a specific direction of the move.
Understanding the Long Strangle
The long strangle options strategy involves purchasing both a call option and a put option on the same underlying asset, WTI Crude Oil in this case, with the same expiration date but at different strike prices. The call option has a higher strike price than the current underlying price, while the put option has a lower strike price. This setup positions the trader to profit from significant price movements in either direction.
The beauty of the long strangle lies in its flexibility and the limited risk exposure it offers. The total risk is confined to the premiums paid for the options, making it a controlled way to speculate on expected volatility. This strategy is particularly appealing when the IV of options is low, implying that the market expects calm but the trader anticipates turbulence ahead.
Risk Management and the Importance of Timing
Risk management is a critical component of successfully implementing the long strangle strategy. The key to minimizing risk while maximizing potential reward is timing. Entering the trade when IV is low—and, consequently, the cost of options is relatively cheaper—allows for greater profitability if the anticipated volatility materializes and the price of the underlying asset moves significantly.
The Implications of a Limited Risk Strategy
A limited risk strategy like the long strangle ensures that traders know their maximum potential loss upfront—the total amount of premiums paid. This predefined risk exposure is particularly advantageous in the unpredictable oil market, where sudden price swings can otherwise lead to substantial losses.
Moreover, the limited risk nature of the long strangle allows traders to maintain a balanced portfolio, allocating a portion of their capital to speculative trades without jeopardizing their entire investment. It's a strategic approach that leverages the inherent volatility of WTI Crude Oil, potentially turning market uncertainties into opportunities.
Case Studies: Real-world Applications of the Long Strangle in WTI Crude Oil Trading
In the ever-volatile world of WTI Crude Oil trading, several events have starkly highlighted the efficacy of the long strangle strategy. These case studies exemplify how sudden market movements, driven by unforeseen news or geopolitical developments, can provide significant opportunities for prepared traders. Here, we explore instances where shifts in volatility facilitated lucrative trades, underscoring the potential of strategic options plays.
Case Study 1 : Geopolitical Escalation in the Middle East
Event Overview: An unexpected escalation in geopolitical tensions in the Middle East led to concerns over potential supply disruptions. Given the region's pivotal role in global oil production, any threat to its stability can significantly impact crude oil prices.
Trading Strategy: Anticipating increased volatility, traders employing the long strangle strategy before the escalation could imply significant gains. As prices surged in response to the tensions, the value of a strangle would have potentially increased.
Case Study 2 : Surprise OPEC+ Production Cut Announcement
Event Overview: In a move that caught markets off-guard, OPEC+ announced a substantial cut in oil production. The decision aimed at stabilizing prices instead triggered a sharp increase in volatility as traders scrambled to adjust their positions.
Trading Strategy: Traders with long strangle positions in place could have capitalized on the sudden price jump.
Case Study 3 : Major Hurricane Disrupts Gulf Oil Production
Event Overview: A major hurricane hit the Gulf Coast, disrupting oil production and refining operations. The immediate threat to supply lines led to a spike in oil prices, reflecting the market's rapid response to supply-side shocks.
Trading Strategy: The long strangle strategy could be invaluable for traders who had positioned themselves ahead of the hurricane season. The abrupt increase in crude oil prices following the hurricane highlighted the strategy's advantage in situations where directional market movements are expected but their exact nature is uncertain.
Conclusion
These case studies illustrate the practical application of the long strangle strategy in navigating the tumultuous waters of WTI Crude Oil trading. By strategically entering positions during periods of low implied volatility, traders can set themselves up for success, leveraging market movements to their advantage while maintaining a controlled risk profile. The key takeaway is the importance of vigilance and readiness to act on sudden market changes, employing comprehensive risk management practices to safeguard investments while exploring speculative opportunities.
The essence of trading in such a dynamic market lies not just in predicting future movements but in preparing for them through well-thought-out strategies and an acute understanding of market indicators and global events. The long strangle options strategy, with its limited risk and potential for significant returns, exemplifies this approach, offering a compelling method for traders aiming to capitalize on the inherent volatility of WTI Crude Oil.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Discover the Trading Month-End Rebalancing Model🔍 Introduction:
Unlock the secrets of profit potential with the Trading Month-End Rebalancing Model. In our vast experience, we acknowledge that profiting from these models can be challenging, but there are exceptional opportunities during the month-end fix. During periods of heightened volatility and significant divergences in global assets, these models can hold substantial value.
📈 Key Insights:
1️⃣ Delving into the Intricacies: Our team meticulously examines the market intricacies, uncovering the nuances of the Trading Month-End Rebalancing Model.
2️⃣ A Golden Opportunity: While sustained profitability may have its limitations, the end of each month presents a golden opportunity. Astute traders can capitalize on market fluctuations during this crucial period, securing profitable outcomes.
3️⃣ Magnified Significance: During times of elevated volatility and notable disparities in global assets, the significance of these models is amplified. Seizing these rare occasions can prove exceptionally valuable, enabling traders to navigate turbulent waters and reap the rewards of their foresight.
💡 Tradingview Educational Tips:
1️⃣ Competitive Edge: Gain an edge in the trading arena by leveraging the Trading Month-End Rebalancing Model.
2️⃣ Stay Vigilant: Keep a watchful eye on the market and remain alert to potential opportunities.
3️⃣ Maximize Potential: Utilize the invaluable insights provided by our cutting-edge model to maximize your trading potential.
🚀 Embrace Success:
Success awaits those brave enough to embrace it. With the Trading Month-End Rebalancing Model as your ally, you have the tools to navigate the market and unlock your trading potential. Start your journey to success today!
Learn The Market Volatility | The Double-Edged Sword
Have you ever wondered why the certain trading instruments are very rapid while some our extremely slow and boring?
In this educational article, we will discuss the market volatility, how is it measured and how can it be applied for making smart trading and investing decisions.
📚 First, let's start with the definition. Market volatility is a degree of a fluctuation of the price of a financial instrument over a certain period of time.
High volatility reflects quick and significant rises and falls on the market, while low volatility implies that the price moves slowly and steadily.
High volatility makes it harder for the traders and investors to predict the future direction of the market, but also may bring substantial gains.
On the other hand, a low volatility market is much easier to predict, but the potential returns are more modest.
The chart on the left is the perfect example of a volatile market.
While the chart on the right is a low volatility market.
📰 The main causes of volatility are economic and geopolitical events.
Political and economic instability, wars and natural disasters can affect the behavior of the market participants, causing the chaotic, irrational market movements.
On the other hand, the absence of the news and the relative stability are the main sources of a low volatility.
Here is the example, how the Covid pandemic affected GBPUSD pair.
The market was falling in a very rapid face in untypical manner, being driven by the panic and fear.
But how the newbie trader can measure the volatility of the market?
The main stream way is to apply ATR indicator, but, working with hundreds of struggling traders from different parts of the globe, I realized that for them such a method is complicated.
📏 The simplest way to assess the volatility of the market is to analyze the price action and candlesticks.
The main element of the volatile market is occasional appearance of large candlestick bars - the ones that have at least 4 times bigger range than the average candles.
Sudden price moves up and down are one more indicator of high volatility. They signify important shifts in the supply and demand of a particular asset.
Take a look at a price action and candlesticks on Bitcoin.
The market moves in zigzags, forming high momentum bullish and bearish candles. These are the indicators of high volatility.
🛑 For traders who just started their trading journey, high volatility is the red flag.
Acting rapidly, such instruments require constant monitoring and attention. Moreover, such markets require a high level of experience in stop loss placement because one single high momentum candle can easily hit the stop loss and then return to entry level.
Alternatively, trading a low volatility market can be extremely boring because most of the time it barely moves.
The best solution is to look for the market where the volatility is average, where the market moves but on a reasonable scale.
Volatility assessment plays a critical role in your success in trading. Know in advance, the degree of a volatility that you can tolerate and the one that you should avoid.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
VIX Uptrend ImplicationVIX (implied volatility) has reversed with market indicating increased volatility expected.
This may be viewed as a canary in the coal mine, with increasing likelihood of a more substantive market correction.
The measurement further supports risk of correction as economic environment cannot sustain extreme QE in face of rising inflation and the risk of inflation being "locked in."
Market Volatility The vix indicates how volatile the market currently is. Right now, the VIX is sitting at 14.40. A neutral market is indicated by a vix being at 17. Since the vix is sitting on the low end, we should continue to see the market stay relatively safe. However, with all the ongoing issues of a slowing global growth, trade, and poor economic data, it would be best to keep your risk appetite low until things smooth over. The VIX is currently trading below the 50 EMA and 200 EMA.