NVDA📊 NVIDIA (NVDA) – Daily Chart Technical Analysis
Entry Point:
A long position is considered at $158, assuming the price holds above $157.78.
Resistance & Target:
The first target is set at $163, which is a clear resistance zone on the chart based on historical price reactions.
If momentum continues beyond that, higher targets could be considered in future analysis.
Stop Loss:
A tight stop-loss is placed just below key support at $157 to manage risk.
🔄 Weekly Bearish Scenario:
If the price closes below $157, this invalidates the bullish setup:
The first downside target would be $146, which is a previously established support zone.
A further drop could extend toward $115, especially if broader market weakness or sector rotation occurs.
📌 Key Technical Zones:
Support Zones: $157.78, $157.00 (critical for bullish continuation)
Resistance Zones: $158.12, $163.18
Multiple historical rejections and price consolidations are noted near these zones, highlighting their significance.
Summary:
As long as NVDA remains above $157.78, the outlook remains bullish targeting $163. However, a confirmed breakdown below $157 could shift the sentiment sharply bearish, targeting $146 and possibly $115.
NVDA trade ideas
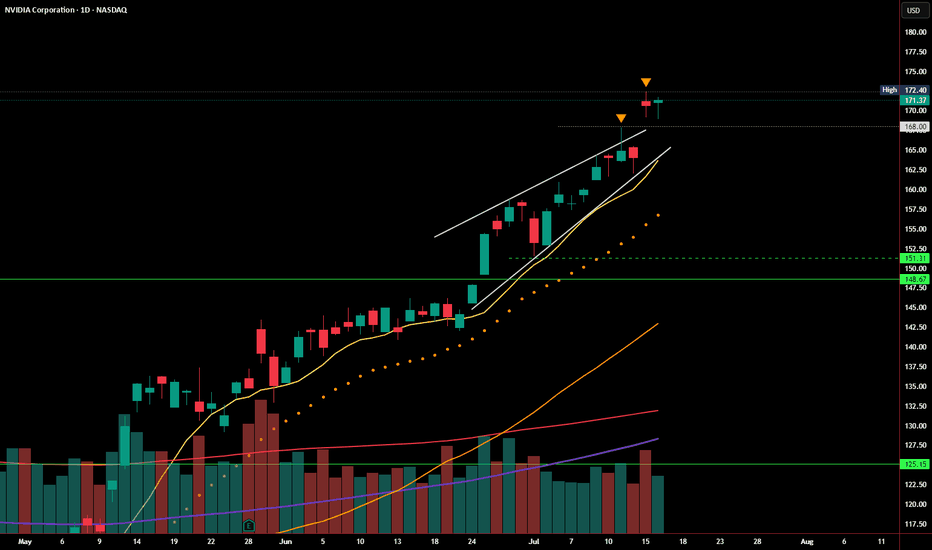
NVDA Follow-Up: Breakout Holding, But Still on Thin IceIn yesterday’s post, I highlighted the rising wedge pattern and noted that a breakout above $168 needed strong follow-through to confirm. Today, NVDA managed to hold above that level, closing at $171.37, just beneath the recent high of $172.40.
So far, the breakout attempt is intact — but not yet convincing.
🔹 Volume came in lighter, suggesting buyers aren’t fully committed
🔹 The candle printed a modest gain, but without expanding range or momentum
🔹 Price is still riding above the rising wedge, but hasn’t cleared resistance with authority
As long as NVDA stays above $168, bulls remain in control — but a daily close back below that level would re-enter the wedge and raise the risk of a false breakout, putting $151–148 back on the radar.
Until we see a strong breakout above $172.40 with volume, this remains a cautious breakout, not a confirmed one.
THRIVING IN CHAOSAs elections draws near, the result/outcome will definitely affect the financial market so WHY WILL NVIDIA GROW EVEN WITH THE WW3 LOOMING?
1.NVIDIA is the leaser in the artificial intelligence(AI) and data centre industries, largely due its cutting edge GPUS. These GPUs are essential for training large AI models like OpenAI's GBT series and other machine learning systems.
2.The company's AI- focused hardware, particularly the H100 GPUs ,is essential for training deep learning models ,autofocus vehicles and cloud based AI system
3.NVIDIA is branching into automotive AI and autofocus driving technology, partnering with companies like Mercedes and other automakers to provide the computing power needed for autonomous vehicles.
4.This company has has seen enormous growth in its data centre segment, which now contributes significantly to its revenue
6.The company has made strategic acquisitions, such as MELLANOX, which expanded its data centre and networking capabilities
AS TECHNOLOGY CONTINUE TO EVOLVE ,NVIDIA WILL BE THE CENTRE OF ATTENTION. LONG TERM BUY
There is a bullish structure that has been formed( w pattern) inside a bullish triangle showing a continuation bull movement/mometum coming . good luck on the longs
NVIDIA – Best Buy of the Decade (4T Record but now resistance)🚀🔥 NVIDIA – Best Buy of the Decade Post #6
💡📉 Great but why am I taking half profits Today?
Back in July 2021, I named NVIDIA "The Best Buy of the Decade. " Today, it just hit a mind-blowing milestone — becoming the first company to reach a $4 trillion market cap. But here's the thing... that happened right at major resistance.
From our initial call in 2021 , to the target at $143.85 drawn via parabola in 2023, to the April 2025 re-entry at $95, it’s all on the chart — and it's been a textbook ride so far.
At the current level of $163.89, we’re pressing into serious overhead resistance. This doesn’t mean the story is over — not even close. But it could mean we take a breather before the next leg higher.
🧭 Targets ahead remain unchanged:
🔹 First stop: $182.85
🔹 Long-term vision: $227.41
What started as a bold macro call in 2021 has now become a multi-year thesis with precision updates along the way. This is post #6 in the NVIDIA journey — and if you scroll back through the chart, each piece has built on the last with clarity and conviction.
🎯 NVIDIA is not just a tech stock — it’s the AI backbone. But every cycle has pauses, and this one looks ready for a short rest before we see the next breakout.
Stay sharp, follow the structure, and honor the parabola.
One Love,
The FX PROFESSOR 💙
Additional info, for those who like to dive deeper into NVDA:
🔍 Technical Breakdown Version
For the chartists and structure followers, here’s the breakdown:
📌 2021: Original call — "Best Buy of the Decade"
📌 2023: First parabola plotted, projecting toward $143.85 — target hit precisely
📌 April 2025: Market offered $95 re-entry — second parabola begins
📌 Now: Price sits at $163.89, testing resistance from both structure and Fibonacci
📌 Next levels:
- $182.85 → Key extension level
- $227.41 → Long-term target based on full parabolic arc
Current structure suggests a possible pause before continuation. No need for panic — parabola remains valid unless structure is broken. Volume still supportive, and price action is following projection beautifully.
🧠 AI Macro Narrative Version
The big picture? NVIDIA isn't just another semi stock — it’s the nervous system of the AI revolution.
From gaming → crypto → AI, NVIDIA has consistently been first to adapt, and now it’s the leader in AI hardware infrastructure. The $4 trillion milestone is more than symbolic — it represents capital reallocation toward AI as the next dominant sector.
🧠 Key macro takeaways:
AI demand is insatiable
Data centers need NVIDIA
Generative AI isn't slowing down
Institutions are still buying — not selling
The resistance we see now isn’t weakness — it’s the market pausing to digest before another acceleration. Just like every past cycle... we ride, retrace, reload, and resume.
Disclosure: I am happy to be part of the Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis. Awesome broker, where the trader really comes first! 🌟🤝📈
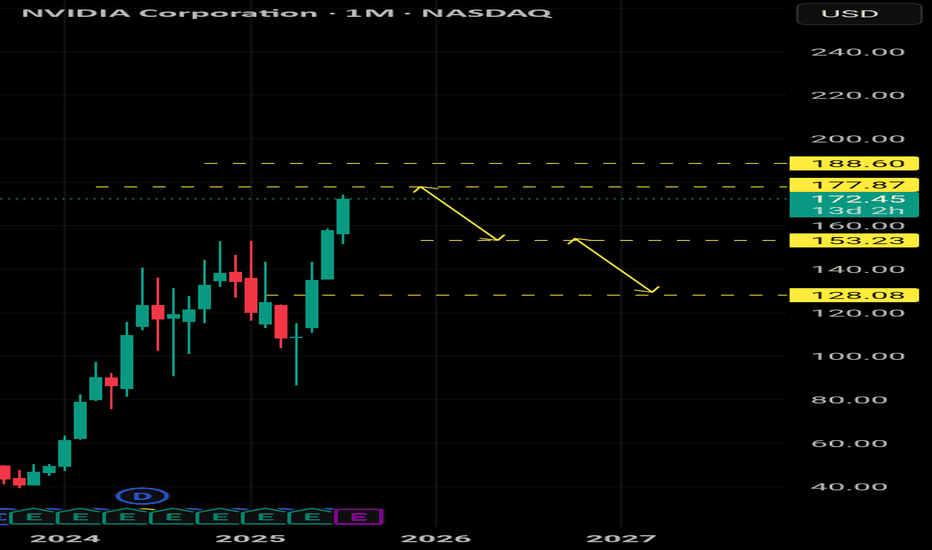
NVIDIA made history! First company with $4 trillion market cap!NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA) became today the first company in history to surpass a $4 trillion market value, as A.I. bulls extended the recent rally and pushed the price past the approximate $163.93 level needed to reach this market capitalization threshold.
The long-term trend on the 1D time-frame couldn't look more bullish. Coming off a 1D Golden Cross less than 2 weeks ago, the price has turned the 1D MA50 (blue trend-line) into Support and sits at +88.13% from the April 07 2025 Low.
This is the exact set-up that the market had when it was coming off the 2022 Inflation Crisis bottom (October 13 2022). As you can see, both fractals started with a -44% decline, bottomed and when they recovered by +88.13%, there were just past a 1D Golden Cross. In fact that Golden Cross (January 24 2023) was the last one before the current.
NVIDIA entered a Channel Up (green) on its recovery and for as long as the 1D MA50 was supporting, it peaked on the 2.618 Fibonacci extension before it pulled back below it.
If history repeats this pattern, we are looking at a potential peak around $390, which may indeed seem incredibly high at the moment, but as we pointed out on previous analyses, the market is in the early stages of the A.I. Bubble, similar to the Internet Bubble of the 1990s.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
Nvidia Market Capitalisation Reaches $4 TrillionNvidia Market Capitalisation Reaches $4 Trillion
Yesterday, Nvidia’s (NVDA) share price surpassed $162 for the first time in history. As a result, the company’s market capitalisation briefly exceeded $4 trillion during intraday trading (according to CNBC), making Nvidia the first publicly listed company to reach this milestone.
The rise in NVDA’s share price is being driven by both bullish sentiment across the broader equity market—which appears optimistic ahead of the upcoming Q2 earnings season—and evidence of sustained demand for Nvidia’s products, as artificial intelligence technologies continue to gain widespread adoption.
Noteworthy developments include:
→ Nvidia may begin producing a specialised AI chip for the Chinese market this autumn, potentially circumventing current export restrictions;
→ Perplexity, a company backed by Nvidia, is launching an AI-powered browser aimed at competing with Google Chrome.
Technical Analysis of NVDA Chart
In our previous analysis of NVDA’s price action, we:
→ Drew an ascending channel;
→ Highlighted bullish conviction in overcoming the $145–150 resistance zone.
The channel remains valid, with the current price trading near its upper boundary. However, the RSI indicator is showing signs of bearish divergence, suggesting that the stock may be vulnerable to a near-term correction—potentially towards the median line of the existing upward channel.
At the same time, a major shift in the prevailing bullish trend appears unlikely. The $145–150 range may serve as a key support zone for NVDA in the foreseeable future.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
NVIDIA ($NVDA) Elliott Wave Outlook: Larger Pullback on the HoriNvidia (NVDA) continues its remarkable ascent, consistently reaching new all-time highs and reinforcing a robust bullish outlook. The ongoing rally, which began from a significant low on April 7, 2025, remains structured as an impulsive wave pattern, indicative of strong upward momentum. However, despite the potential for further short-term gains, the cycle appears mature. This suggests a larger-degree pullback could be imminent. Investors should exercise caution when considering chasing this rally in shorter time frames, as the risk of a corrective move grows.
In the short term, the cycle initiated from the June 2 low is progressing as a lower-degree impulse. From this low, wave ((i)) peaked at $144, followed by a corrective pullback in wave ((ii)) that concluded at $137.88. The stock then surged in wave ((iii)) to $159.42. The subsequent wave ((iv)) correction unfolded as a double-three structure, with wave (w) ending at $151.49, wave (x) at $154.98, and wave (y) completing at $151.10, finalizing wave ((iv)). Currently, Nvidia is advancing in wave ((v)), exhibiting a five-wave subdivision. Within this, wave (i) of ((v)) reached $160.98, with a minor pullback in wave (ii) concluding at $157.34. As long as the pivotal low at $142.01 holds, any near-term pullbacks are likely to attract buyers in a 3, 7, or 11-swing pattern, supporting further upside potential. This technical setup underscores Nvidia’s strength but highlights the need for prudent risk management.
Nvidia - Blow off top?Time to book some AI stock profits, I have exited ARM and today I am taking profits on Nvidia. We entered at the golden pocket, up over 88% since the recent lows. I am now scaling out of my position, starting with 50% of my total. I will use a trailing stop loss for the rest.
We have hit a 4 trillion dollar market cap, more than the entire UK stock market combined. Am I bearish on Nvidia? Of course not, but the market is getting greedy and I like to book profits.
I love the company, but I expect huge volatility going forward.
Not financial advice, do what's best for you.
Nvidia - New all time highs!Nvidia - NASDAQ:NVDA - breaks out now:
(click chart above to see the in depth analysis👆🏻)
Within two and a half months, Nvidia rallied more than +70%. Following this recent bullish strength, a retest of the previous highs was totally expected. But this does not seem to be the end at all. There is a much higher chance that we will see new all time highs soon.
Levels to watch: $150
Keep your long term vision🙏🙏
Philip (BasicTrading)
NVDA - NVIDIA's 3-Drive Pattern target if it plays outThis is the weekly chart of NVDA.
We can clearly see a 3-Drives pattern forming.
If this pattern plays out, the centerline would be my target. Of course, it's still too early to short.
But I’ve got my hunting hat on and I'm watching for signals on the daily chart.
One would be a break of the slanted trendline—but there are a couple of other conditions that need to align as well.
Always ask yourself: What if?
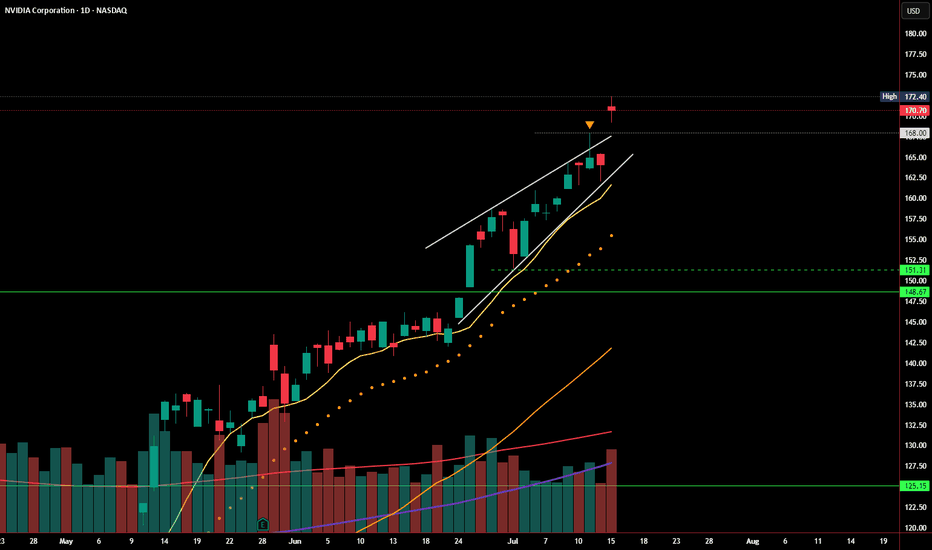
NVDA Update: Breakout Fading or Wedge Still in Play?In my last post, I highlighted the rising wedge pattern forming at the top of NVDA’s strong rally. Price briefly pushed above the upper wedge resistance and tagged $172.40, but today’s session printed a bearish close at $170.70 — just above the breakout level, but with no real follow-through.
Volume came in higher, but price action failed to extend the breakout, suggesting this could be a stall or even a false breakout in progress. RSI remains overbought, and momentum may be slowing despite the recent push.
If price slips back below $168, we could see the original wedge breakdown scenario come back into play. Watch for support around:
🔹 $151.31–148.67
🔹 Below that: $125 zone
For bulls, continuation above $172.40 with strong volume would invalidate this pattern and confirm breakout strength. Until then, caution is warranted.
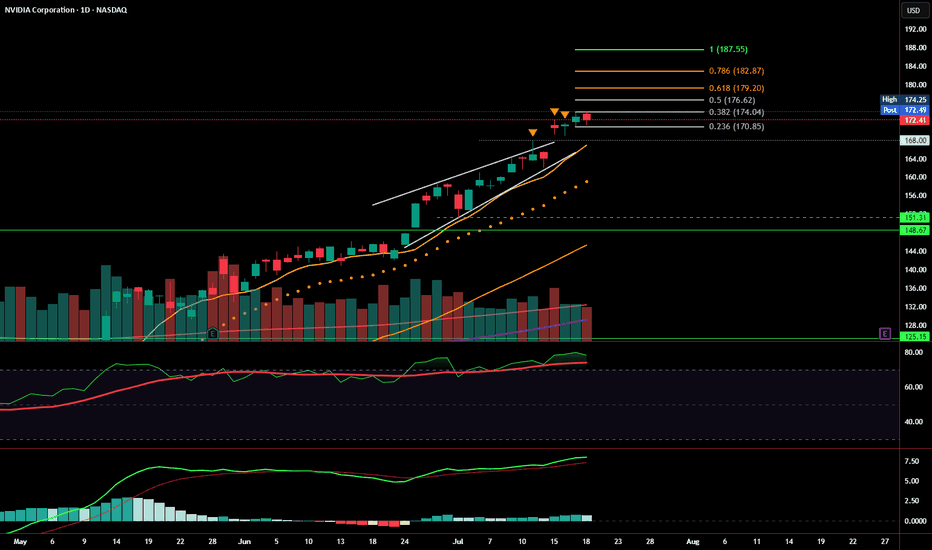
Weekly Close: Still Bullish, But Momentum Is SlowingNVDA closed the week at $172.41, just under short-term resistance and holding well above the prior rising wedge structure. Price action remains technically bullish, with a healthy consolidation forming just below the 0.382 Fibonacci retracement at $174.04.
That said, momentum is beginning to cool, and the next few sessions will be key.
📊 Current Read: Mildly Bullish
Price is holding above key support levels: 9 EMA, $170.85, and prior wedge resistance
No breakdowns — structure remains intact
However, volume is fading, and MACD is flattening, suggesting possible buyer fatigue
RSI remains elevated, not yet signaling reversal, but approaching caution territory
A confirmed breakout above $174.25 sets the stage for Fibonacci targets at:
🔸 $176.62, $179.20, $182.87, and $187.55
A close below $170.85 , and especially $168, would invalidate the current bullish structure and shift bias to bearish — targeting the $151.31–148.67 support zone.
Summary:
📈 Bias: Bullish - but cautious.
Price is consolidating near highs with no signs of breakdown yet. Continuation likely if bulls step in early next week.
NVDA: Ready for a Gamma Squeeze or Cooling Off? for July 10NVDA: Ready for a Gamma Squeeze or Cooling Off? Here's the Setup You Need 🎯
Options Sentiment (GEX Analysis):
NVDA is trading around $163.35 and sitting just above the Gamma Wall at $162.50, which also marks the highest positive NET GEX zone—a key resistance created by dealer positioning. Above that, the second CALL Wall is stacked near $165, with further resistance layering in toward $170 and $172.50.
Below, there’s a liquidity pocket around $157.50 (HVL zone), and deeper PUT support doesn’t come in until $152.50–$151.00.
* GEX: Bullish leaning (CALLS 2.6% domination, GEX bar fully green)
* IVR: Low at 5.9, and IVx Avg 38 → Options are relatively cheap.
* Sentiment: Leaning bullish with potential for a gamma squeeze if momentum builds above $165.
🟢 Strategy Suggestion:
Consider 160C or 165C weekly calls (with tight spreads) if NVDA holds above $162.50 and breaks through $165 with volume. A gamma squeeze toward $170 is on the table.
Risk-managed PUTs (e.g., 158P) only if price flushes back below $160 support with momentum.
1-Hour Chart Technical Outlook:
NVDA has broken out of the previous range, flipping internal structure bullish. The CHoCH and BOS confirm trend change earlier this week, and the price is now consolidating just under a resistance zone (purple box) near $164.
Support below is layered at:
* $160 (broken resistance, now key support)
* $158.05 (previous structure low)
* $152.00–151.00 (demand zone + GEX support alignment)
Resistance:
* $164.41 (current high)
* $167.50, $170, $172.50 (GEX option walls)
Structure is showing a rising wedge/channel pattern; however, we’re still trending strong with clean higher lows.
🟢 Long Trade Setup (Bullish Continuation):
* Entry: Above $164.50 with breakout confirmation
* Target: $167.50 → $170
* Stop: Below $160 (or tighter below $162.50 based on risk appetite)
🔴 Short Trade Setup (Reversal Scenario):
* Entry: Breakdown below $160 with rejection from $163–$164
* Target: $158 → $152 zone
* Stop: Above $165
My Thoughts:
NVDA is sitting in a key decision zone. As long as it holds above $162.50, bulls have the edge to push this higher into the next GEX walls. Watch for confirmation on $164.50 breakout for continuation. If it fakes out and drops below $160, that would likely trigger a downside flush to $158 or lower.
This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always do your own research and trade responsibly.
NVDA Testing Gamma Ceiling — Eyes on 162.5 🔩 Options Sentiment & GEX Analysis
NVDA is pressing into a critical Gamma Wall at 162.5, which aligns with the highest positive NET GEX and second-tier Call Wall concentration. Dealers are likely short calls here, meaning a breakout could trigger gamma-induced hedging, fueling a squeeze.
* Call Walls: 162.5 → 165 → 167.5 → 170
* Put Walls: 157.5 → 155 → 152
* GEX Skew: Strong bullish exposure into 162.5, suggesting a resistance zone but also potential fuel if breached.
* IVR: 6.6 — Implied Volatility remains cheap, ideal for directional plays.
* IVx Avg: 38.6 — still elevated, giving edge to debit spreads.
* Put/Call Ratio: 0.2% Puts – overly call-heavy positioning adds risk of dealer chasing if breakout occurs.
🧠 GEX-Based Option Trade Ideas
📈 Bullish Gamma Squeeze Play
* Setup: Buy 160/165 Call debit spread (Jul 19 or Jul 26 expiry).
* Trigger: Break & close above 161 with volume.
* Target: 165 → 167.5
* Why: Breaching Gamma Wall at 162.5 opens room to next Call Walls. Dealer hedging could force rapid upside.
📉 Bearish Fade Setup
* Setup: Buy 160/155 Put debit spread
* Trigger: Failure to reclaim 161–162.5 zone with clear rejection pattern.
* Target: 157.5 → 155
* Why: Rejection at GEX ceiling could unwind recent rally, especially if broader market rolls over.
🧭 1-Hour Technical Chart Overview
NVDA is consolidating tightly under its Gamma resistance within a clear ascending channel.
🔍 Structure & SMC Highlights
* Series of Breaks of Structure (BOS) confirms bullish trend.
* CHoCH zones have been retested and flipped bullish around 157.5.
* Current price is compressing under a key supply zone at 160.98–162.5, with rising trendline providing support.
* A clean bullish reaction from the 157.5 order block shows buyer interest is intact.
🔨 Levels to Watch
* Key Resistance: 161 → 162.5 (GEX ceiling, prior swing highs)
* Support Zone: 157.5 → 155 (prior CHoCH and OB zone)
* Trendline: Acting as dynamic support from June lows
📌 Trading Plan (1H Price Action Focus)
Long Setup
* Trigger: Break above 161 with bullish candle close and volume
* Entry: 161.20–161.50
* Stop: Below 159.80 (last demand zone wick)
* Target: 165 first, then 167.5
* Bias: Trend continuation + gamma squeeze
Short Setup
* Trigger: Rejection at 162.5 with bearish engulfing or shooting star
* Entry: 161.80–162.50
* Stop: Above 163
* Target: 157.5 → 155
* Bias: Fade extended rally into gamma wall
🧠 Summary
NVDA is perched just under a powerful options-driven ceiling. Whether this turns into a breakout squeeze or a sharp rejection depends on how price reacts to the 161–162.5 zone. Traders should prepare for both scenarios with defined-risk debit spreads and lean into price confirmation before committing.
This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always do your own research and manage risk carefully.
NVIDIA (NVDA)-Trade PlanNVDA, After an explosive run powered by GenAI infrastructure and bullish earnings, the chart is setting up for either a bullish continuation or a healthy pullback.
With volatility tightening and volume compressing, this is a great moment to prepare for either breakout or breakdown scenarios.
🎯 Trade Plan – Tiered Long Setup
📌 Entry Zones (Tiered Buying):
🔹 $150
🔸 $140
🔻 $120
📈 Profit Targets:
TP1: $160
TP2: $175
TP3: $200+ – Long-term continuation play if AI macro momentum persists
📌 DISCLAIMER: This idea is for educational purposes only. Always use proper risk management and assess your own strategy
NVDA at a Make-or-Break Zone – Trade Setups Ahead 🔍 Options GEX Insights (Gamma Exposure):
* GEX Map Observation:
* NVDA is currently trading near 158, slightly under the major Gamma Wall at 160.98.
* This level marks the highest positive net GEX – strong resistance due to heavy call positioning.
* Above that, additional call walls stack at 162.5 → 165 → 167.5, creating a squeeze zone if price breaks out.
* Below, support levels sit at 155 (2nd PUT wall) and 152.5 (3rd PUT wall).
* Volatility & Options Sentiment:
* IVR: 8.8, IVx: 40.8 – low implied volatility rank = cheap options.
* Put Positioning: Only 1.4% = call-heavy environment, skewed bullish.
* Positive GEX (+) across expiries shows dealers will hedge upward if we move beyond 161.
🟢 Bullish Scenario (Breakout/Squeeze Setup):
* Break over 160.98 could ignite a gamma squeeze toward 165–167.5 range.
* Ideal for low delta CALL verticals or debit spreads targeting the 165 zone.
* Weekly options are cheap due to low IV.
🔴 Bearish Rejection Scenario:
* If price stays pinned under 160 and loses 155, dealers start to de-hedge – momentum toward 152/150.
* Consider put spreads or a cautious fade if it breaks structure.
📌 GEX Summary Suggestion:
If NVDA stays under 160, price may remain pinned or retrace. But above 161 opens the gamma doors to 165+. Cheap IV = opportunity.
📊 1-Hour Price Action Technicals:
* Market Structure:
* Previous BOS toward the upside has stalled inside a consolidation box under 160.
* Multiple CHoCH zones form below current price, hinting at exhaustion.
* Price is stuck within a wedge, coiling beneath resistance = compression phase.
* Support & Resistance Zones:
* Resistance: 159.34 → 160.98 (Gamma Wall and price supply).
* Support: 155.34, then 151.10.
* Bullish OB remains untested around 151 area if price flushes.
* Volume & Trend:
* Volume declining during chop = balance phase.
* RSI & MACD show slight bearish divergence, favoring caution near top of range.
⚙️ Trade Thoughts:
* Scalp Setup:
* Above 160.98 = scalp long toward 162.5/165, tight stop at 159.3.
* Below 155 = scalp short toward 152 zone.
* Swing Setup:
* Long only on strong breakout close above 161 with volume.
* Short swing possible under 155 if CHoCH confirms trend flip.
Conclusion:
NVDA sits at the pivot point of either breaking out toward 165+ or rejecting and retracing toward 152. GEX and price both hint at a coiled move ahead. Stay nimble, follow the volume.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
NVDA ShortNVDA is currently exhibiting short-term bearish order flow on the 15-minute chart, with price making lower highs and lower lows following a clear CHoCH (Change of Character) to the downside. The current leg suggests continued weakness as price retraces toward the highlighted bullish order block around the 156.20–157.00 range, aligning closely with the 50% equilibrium level of the last bullish impulse.
This area represents a high-probability demand zone where we anticipate a potential bullish reaction. A confirmation entry (e.g., bullish BOS or lower timeframe CHoCH within the OB) will be required to validate a long setup from this zone. Should confirmation present itself, upside targets can be trailed back toward recent highs near 159.00–160.00.
Risk Management Note:
Always wait for confirmation before entering against the prevailing short-term trend. Use a well-defined stop-loss below the order block and calculate your position size based on your overall risk tolerance (typically 0.5–1% of account equity per trade). Avoid overleveraging, and remember that patience and discipline are key to capital preservation.
How To Spot The Breakout In 3 Steps Or More..In this video we dive into how to spot the breakout
but here is a catch we are using the Stochastic RSI
to spot these breakouts.
Also this spotting of these breakouts is happening
together with the Rocket booster
strategy.
Watch this video to learn more.
Disclaimer:Trading is risky please learn risk management and profit
taking strategies.Also feel free to use a simulation trading account
before you trade with real money.