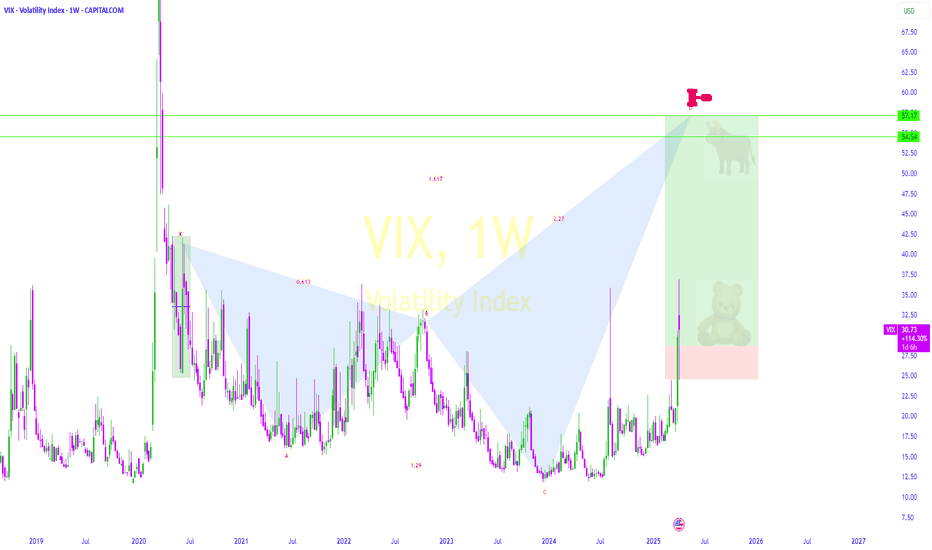
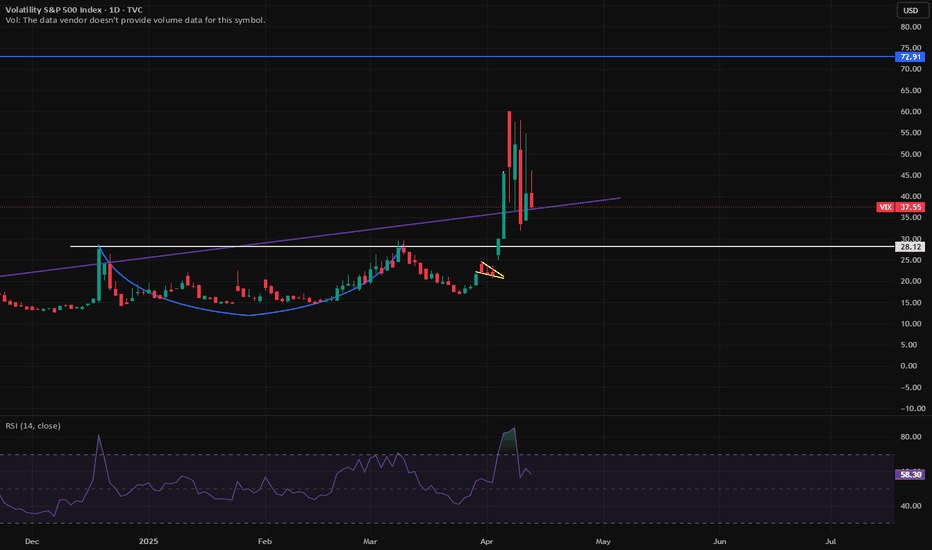
VIX stock Chart Fibonacci Analysis 042925Trading Idea
1) Find a FIBO slingshot
2) Check FIBO 61.80% level
3) Entry Point > 24/61.80%
Chart time frame: B
A) 15 min(1W-3M)
B) 1 hr(3M-6M)
C) 4 hr(6M-1year)
D) 1 day(1-3years)
Stock progress: C
A) Keep rising over 61.80% resistance
B) 61.80% resistance
C) 61.80% support
D) Hit the bottom
E) Hit the top
Stocks rise as they rise from support and fall from resistance. Our goal is to find a low support point and enter. It can be referred to as buying at the pullback point. The pullback point can be found with a Fibonacci extension of 61.80%. This is a step to find entry level. 1) Find a triangle (Fibonacci Speed Fan Line) that connects the high (resistance) and low (support) points of the stock in progress, where it is continuously expressed as a Slingshot, 2) and create a Fibonacci extension level for the first rising wave from the start point of slingshot pattern.
When the current price goes over 61.80% level , that can be a good entry point, especially if the SMA 100 and 200 curves are gathered together at 61.80%, it is a very good entry point.
As a great help, tradingview provides these Fibonacci speed fan lines and extension levels with ease. So if you use the Fibonacci fan line, the extension level, and the SMA 100/200 curve well, you can find an entry point for the stock market. At least you have to enter at this low point to avoid trading failure, and if you are skilled at entering this low point, with fibonacci6180 technique, your reading skill to chart will be greatly improved.
If you want to do day trading, please set the time frame to 5 minutes or 15 minutes, and you will see many of the low point of rising stocks.
If want to prefer long term range trading, you can set the time frame to 1 hr or 1 day.
VIX trade ideas
VIX Bullish Watch OutBased on Chart current at P. High (Previous High) Act as strong support I strongly believe VIX will go Up and market will go Down from here.
Significant Resistance are P. High and Take Profit Lines.
Once Resistance reached Watch out for VIX going down.
Once VIX Down Market Is Up and Vice Versa Watch out.
Take Care.
VIX Set Up for a Big Move: Aggressive Institutional Call BuyingSummary:
The VIX has officially broken major resistance, and institutional players are making large bets on rising volatility over the next 1–2 months. The combination of the technical breakout and heavy call buying strongly suggests a potential VIX surge toward 30–35.
🔥 Technical Analysis:
Key Resistance at 23.50 (red line) was cleanly broken and is now acting as support.
VIX currently at 25.16, maintaining position above all key short-term moving averages.
Price is sandwiched between the 50 EMA (26.22) and 23.50 support, suggesting coiled energy ready to break either direction — currently favoring the upside.
RSI remains neutral at ~45, meaning plenty of room for volatility expansion without technical exhaustion.
Past behavior shows that after VIX clears major resistance and holds, sharp expansions typically follow.
📊 Institutional Option Flow:
Today's VIX option flow highlights aggressive accumulation of May calls:
12,000 contracts bought on 21 Strike Calls (May 21 expiration) — $4.08M bet.
8,000 contracts bought on 22 Strike Calls (May 21 expiration) — $2.28M bet.
Significant accumulation at the 30 Strike Calls across multiple timestamps — over $3M total premium.
Additional layering into higher strikes for June and July expirations (34C, 40C, 60C, 70C), indicating expectations for extreme moves.
💬 Key Insight:
These are large block trades, aggressively executed at the ask, suggesting real conviction rather than passive hedging.
🚀 Projected Outlook:
Level Importance
23.50 Confirmed support after breakout
26.22 (50 EMA) Minor resistance — currently being tested
29.41 (20 EMA) Short-term breakout target
30–35 zone Primary upside target if VIX momentum continues
If VIX sustains above 23.50 and breaks the 50 EMA cleanly, we can expect a fast push to the 30–35 range, especially if external catalysts (economic data, geopolitical risk) align.
📣 Final Thoughts:
The technical setup and the institutional option flow are both aligned — something that doesn't happen often.
Volatility is coiling above support, and big money is positioning for an explosive move.
Whether you're managing risk or looking for opportunity, it's time to pay attention to volatility.
✍️ Chart and flow analysis by @brownian. Thank goodness I am not your financial advisor, else you would be living in your car.
📅 April 28, 2025
#Volatility #VIX #OptionsFlow #TechnicalAnalysis #EMAAnalysis #TradingView #QQQ #SPY #SPX #NASDAQ
NASDAQ:QQQ
AMEX:SPY
VIX Breakout Trade: Targeting 31.22!🚀 📈
Description:
Today, I spotted a bullish breakout on VIX from a falling wedge pattern.
Entry is around 25.05, with a stop-loss below 24.00.
First target is 28.18, second target is 31.22.
High risk-reward setup as volatility may surge!
Always manage risk carefully. 📊
VIX is a VIXjust having a little fun in a chat about how i chart the VIX. i say a VIX is a VIX. when we are spiking, we are spiking and we should become cautious if we don't know how to manage in that environment (intense bearish environment). this recent spike has proven that there are bullish moments that can be gleamed, but you have to be clear about your targets .
if someone has more to add about VIX royalty, please do share. otherwise, pick one to monitor if that is even your thing. no need to clutter your toolbox with VIX concepts... says me.
shout out to @BradMatheny. your work is amazing. thank you for sharing a bit here and there. i'm going to make time to learn more from you.
tootles
VIX, the paroxysm of fear is behind us The international equity market suffered a bearish shock between the beginning of February and the beginning of April, against the backdrop of the trade war. The trade war known as “reciprocal tariffs” initiated by the Trump Administration caused the MSCI World stock index to fall by over 20%.
Now, since the States have entered into a sequence of trade diplomacy, the equity market has rebounded and volatility has dropped one floor.
Can we say that the paroxysm of fear is behind us, based on the prism of technical analysis of the financial markets?
To answer this question, we'd like to take a look at two interesting charts.
1) Firstly, the implied volatility chart of the stocks that make up the SP 500 index, the VIX. The nickname of this index is “the fear index”. Its calculation is based on the price of call and put options on the stocks making up the SP500 index. Remember that the S&P 500 is considered the benchmark index of Western finance
2) The second chart of interest is a quantitative analysis of financial markets. Quantitative analysis of financial markets is one of the disciplines of technical analysis of financial markets, and here it concerns the percentage of SP 500 stocks above the 50-day moving average.
It is precisely the application of technical analysis to these two charts that allows us to argue in favour of a selling paroxysm reached during the first fortnight of April.
For the VIX, the fear index has been rejecting downwards since the 60 level, with a chartist “black cloud cover” structure (Japanese candlestick terminology) and a bearish resolution of the RSI technical indicator from its weekly overbought zone. This signal historically signified that the paroxysm of fear was over.
For the percentage of S&P 500 stocks above the 50-day moving average, the quantitative bullish signal is very convincing. Historically, every time this percentage has fallen below the 20% threshold in an abrupt fashion, only to rise back up again, it has signalled the final phase of the bear market, and that's what's happening again this April 2025, as you can see on the chart below.
CONCLUSION: Through the prism of technical analysis of the financial markets, a number of clues point to a paroxysm of fear reached in the first half of April. Of course, only the fundamentals and the outcome of trade diplomacy can confirm that the low point is well and truly behind us.
DISCLAIMER:
This content is intended for individuals who are familiar with financial markets and instruments and is for information purposes only. The presented idea (including market commentary, market data and observations) is not a work product of any research department of Swissquote or its affiliates. This material is intended to highlight market action and does not constitute investment, legal or tax advice. If you are a retail investor or lack experience in trading complex financial products, it is advisable to seek professional advice from licensed advisor before making any financial decisions.
This content is not intended to manipulate the market or encourage any specific financial behavior.
Swissquote makes no representation or warranty as to the quality, completeness, accuracy, comprehensiveness or non-infringement of such content. The views expressed are those of the consultant and are provided for educational purposes only. Any information provided relating to a product or market should not be construed as recommending an investment strategy or transaction. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
Swissquote and its employees and representatives shall in no event be held liable for any damages or losses arising directly or indirectly from decisions made on the basis of this content.
The use of any third-party brands or trademarks is for information only and does not imply endorsement by Swissquote, or that the trademark owner has authorised Swissquote to promote its products or services.
Swissquote is the marketing brand for the activities of Swissquote Bank Ltd (Switzerland) regulated by FINMA, Swissquote Capital Markets Limited regulated by CySEC (Cyprus), Swissquote Bank Europe SA (Luxembourg) regulated by the CSSF, Swissquote Ltd (UK) regulated by the FCA, Swissquote Financial Services (Malta) Ltd regulated by the Malta Financial Services Authority, Swissquote MEA Ltd. (UAE) regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority, Swissquote Pte Ltd (Singapore) regulated by the Monetary Authority of Singapore, Swissquote Asia Limited (Hong Kong) licensed by the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) and Swissquote South Africa (Pty) Ltd supervised by the FSCA.
Products and services of Swissquote are only intended for those permitted to receive them under local law.
All investments carry a degree of risk. The risk of loss in trading or holding financial instruments can be substantial. The value of financial instruments, including but not limited to stocks, bonds, cryptocurrencies, and other assets, can fluctuate both upwards and downwards. There is a significant risk of financial loss when buying, selling, holding, staking, or investing in these instruments. SQBE makes no recommendations regarding any specific investment, transaction, or the use of any particular investment strategy.
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. The vast majority of retail client accounts suffer capital losses when trading in CFDs. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Digital Assets are unregulated in most countries and consumer protection rules may not apply. As highly volatile speculative investments, Digital Assets are not suitable for investors without a high-risk tolerance. Make sure you understand each Digital Asset before you trade.
Cryptocurrencies are not considered legal tender in some jurisdictions and are subject to regulatory uncertainties.
The use of Internet-based systems can involve high risks, including, but not limited to, fraud, cyber-attacks, network and communication failures, as well as identity theft and phishing attacks related to crypto-assets.
VIX – “Liquidity Pool Bounce & Reversal Setup”🟢 VIX – “Liquidity Pool Bounce & Reversal Setup”
📅 Date: April 22, 2025
⏰ Multi-Timeframe Analysis (12h, 1D, 1h, 30m, 5m)
🔎 Global Context:
The Volatility Index (VIX) is reacting to a clear institutional liquidity zone (blue area) across multiple timeframes (12h, 1D, 1h), aligning with a mean reversion move following the explosive rally earlier this month. We’re seeing multiple signs of a potential bullish reversal:
Previous lows + demand zone confluence
Multiple CHoCH (Change of Character) events on lower timeframes
Implied divergence from equities (not shown here, but inferred)
Strong rejection from the institutional block (26.345–26.600)
🔍 Technical Analysis & Justification:
📌 Wyckoff & Smart Money Concepts (SMC):
On 30m and 1h charts, we observe several CHoCH and BOS events suggesting a transition from redistribution into accumulation.
The latest bearish move failed to break the weak low zone (26.345), indicating a liquidity grab trap.
📌 Fibonacci & Moving Averages:
Price touched the 78.6%–88.6% retracement from the previous bullish leg.
EMAs 8/21 (Orange/Blue) are about to cross bullish on 5m and 30m – a typical trigger for a new impulsive move.
EMA200 (White) still hovers above – likely target of the first bullish push.
📌 Volume Profile (implicit):
Most of the recent consolidation occurred in the 27.00–27.40 imbalance zone, which now acts as a magnet for price during retracement.
📌 Liquidity & Order Flow Concepts:
The 26.345–26.600 range served as a Weak Low and was swept clean – classic liquidity trap behavior.
📈 Trade Parameters:
🟢 Entry (Buy): 26.795
🔒 Stop-Loss (SL): 26.345 (below last liquidity sweep)
🎯 Take Profit 1 (TP1): 27.390 (inefficiency zone + EMA200)
🎯 Take Profit 2 (TP2): 28.150 (1h/30m order block)
🧮 Risk-Reward Ratio (RR):
TP1: ~1.6
TP2: ~3.0
📊 Confidence Level: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High-probability setup)
🧠 Strategic Summary:
This is a classic reversal play based on liquidity absorption and structural shift (CHoCH), supported by multi-timeframe alignment. A bullish engulfing or strong reaction inside the blue zone confirms the entry bias. If price breaks above 27.00 with volume, momentum may carry it towards 28.00+ swiftly.
⚠️ Risk Disclaimer: Trading involves risk. Only trade with capital you can afford to lose. Always manage your exposure wisely.
💬 What do you think of this setup? Do you see confluence with your strategy? Let’s discuss below! 👇
Technical Analysis of VIX Dynamics:As we predicted, the small crab (retail traders) jumped from the ocean depths (high VIX zone) but failed to break the golden resistance at 29 due to panic and stress.
Now the mother crab (institutions) is preparing to surface. If successful, this could crush the VIX and dramatically shift market sentiment - just like we originally envisioned in our crab market theory."
VIX drop before the next ZOOM upWhat we experienced last week was absolutely insane in terms of volatility. The beauty of all of this is that it's still a trend and many of these spikes are quite predictable. We all knew about the days the tariffs that were going to hit, right? Why didn't you get into UVIX when I called this out days in advance. It's fine, you will have another shot! Actually, we're in line for many many more spikes which is the great thing. Volatility is your friend!
I'll be posting weekly and will be giving away a Free trading alert that has been backtested for the last 3 years over the next week. 2025 will be awesome!
Expect VIX to drop a bit more, great to get in on the SVIX and then let's analyze the next trend and take on UVIX on the upside! This is so easy....
VIX is readying for a golden shot#vix the volatility index is consolidating in falling megaphone channel for another impulsive wave. TVC:VIX had the 1st wave when trade wars begin (But i warned you 3 months ago with VIX chart) then 2nd wave of correction in progress and when 2nd wave consolidation is done, 3rd wave far more cruel than 1st wave will set sail. Beware with your high risk positions, just a warning. Not financial advice. DYOR.
Long Strategy for VIX: Eyeing Stabilization Amid Persistent Vola
- Key Insights: The VIX has exhibited significant fluctuations over the last
week, peaking at levels above 55 before settling in the 37–40 range. This
suggests that although fear has eased, market uncertainty remains elevated.
Historically, the current environment indicates potential opportunities for
a long position if volatility trends continue to moderate. Market
participants should monitor the 32–34 support zone, as a breach below this
could signal improved sentiment and reduced risk-off positioning.
- Price Targets:
* **Next Week Targets (T1, T2)**: T1 = 43.5, T2 = 47.3
* **Stop Levels (S1, S2)**: S1 = 36.2, S2 = 34.8
- Recent Performance: Over the past week, the VIX demonstrated extreme
volatility, briefly surging above 55 early in the week, reflecting intense
fear driven by macroeconomic uncertainty and geopolitical factors. By week’s
end, it had declined to the 37–40 range as market panic subsided somewhat.
Despite this moderation, the index remains well above its historical
average, indicating ongoing caution.
- Expert Analysis: Analysts emphasize that the sharp decline from the midweek
peak signals reduced panic and a potential shift to stabilization. However,
elevated levels above 20 suggest continued risk-off sentiment, with hedging
activity still prominent among institutional investors. Current levels are
reminiscent of volatility spikes seen in major crises, often preceding
medium-term recovery in equities. Traders may expect a possible rally in
equity markets if the VIX trends lower toward the critical 32–34 support
zone, which would further confirm easing fear.
- News Impact: VIX movements this week were influenced by a mix of macroeconomic
concerns and geopolitical risks, which drove it to its highest levels since
COVID. Sentiment began to improve in the latter part of the week as the S&P
500 rebounded from oversold conditions, aligning with historical trends
where elevated fear is followed by equity recoveries. While the decline in
the VIX reflects reduced panic, market risks remain, warranting caution
amidst wider price swings.
Market Insight: VIX Index WatchHold onto your life jackets, folks! The volatility index (a.k.a. the Shark VIX) has emerged from the depths at a slippery 0.88 and is now eyeing the ominous 1.138! 📈💔
Why does that matter? Well, if it's anything like a shark spotting in the ocean, it usually means it’s about to get choppy! 🦈💥 Expect some serious splashes ahead as we ride these market waves!
So, if you prefer calm seas over shark-infested waters, it might be time to brace yourself for a fun (read: bumpy) ride! 🎢 Don’t worry; we’ll keep the floaties handy!
Swim smart, invest wisely! 🌊💸**
"When the VIX is low, look out below!""When the VIX is low, look out below!"
+
FEDs motto "Higher for longer"
=
Fed rate hikes to go: 2-3 left
it is pivot time, change of market dynamic from "bad news is good news" to "bad news is bad news".
state of economy is not good and it will start sinking in to investors and public
Path to 100 VIXI wrote this note on TVC:VIX a few days ago:
www.tradingview.com
And am now expanding it a bit more.
As someone who was working middle office during the original 2016 Trump Election, Brexit, during the Taper Tantrum and a few other major events - I want to lay out my principles on trading the VIX because spikes like this bring a lot of "first time" VIX traders to something that trades like NOTHING ELSE in the market.
This is not a stock in a short squeeze, this is not a generic index.
This is like nothing you've ever traded before. In fact, I'd encourage you to take advantage of TradingView's chart options and instead look at the chart of -1*$TVC:VIX.
That alone should give you pause.
----------------------------------
So - let's start with the principles of the finance business as laid out in the masterclass which was the movie "Margin Call" .
"John Tuld: There are three ways to make a living in this business: be first, be smarter, or cheat."
1. Be First.
You are not first if you are buying above the historic average of VIX 20-21.
If you were buying CBOE:UVXY since Jan 2025, you'd be up 175% right now and likely looking to re-balance into your desired long term asset positions.
2. Be Smarter.
* Are you taking into consideration the VIXEX Cycle?
* Do you know the effect of VIXEX before or after monthly OpEx?
* Do you know the current implied volatility curve of options ON the VIX?
* Do you know that of the last 4 times the VIX has hit 50, it went on to 80+ 50% of the time after that?
* Yes, I've seen the charts going around about forward S&P X year returns but did you know that after the VIX spike to 80 in October 2008, the market (in a decreasing volatility environment) went on a further 35% decline in the next 4-5 months?
* Where is the MOVE? What are the bond indexes & bond volatility measures doing? And if you don't yet understand that equities ALWAYS reacts to what is going on in the rates / yield world... you'll find out eventually. I hope.
3. Cheat
When things start going wrong, everyone wants an easy solution.
That's why its called a relief rally. It feels like relief - the bottom is in, the worst part is over.
But that is what the really big players have the biggest opportunity to play with the day to day environment.
They know our heuristics. They encourage the formation of cargo cult style investing whether that's HODL in the cryptocurrencies or Bogleheads in the vanguard ETFs.
It's all the same and encourages you to forgot first principles thinking about things like:
1. Is this actually a good price or is it just relatively cheap to recent history?
2. Who's going to have to dilute to survive the next period of tighter lending, import costs from tariffs, or whatever the problem of the day is.
3. VIX correlation - volatility is just a description of the markets. Its not a description of the direction. There is periods where volatility is positively correlated to the price movement (like during earnings beats). Know about this and know when it changes.
4. Etc.
Some have pointed out that is more appropriately a measure of liquidity in the SPX.
When VIX is low, that means there is lots of "friction" to price movement. It means that there is tons of orders on the L2 book keeping the current price from moving in any direction too quickly.
When VIX is high, that means there is very low "friction" to price movement. It means there are very few orders on the L2 book and market makers can "cheat" by appearing to create a low volume rally and then rug pull that price movement very quickly (not via spoofing, more just dynamic management of gamma & delta hedging requirements).
Additionally - volume itself becomes deceptive. Volume is just indicating that a trade happened.
Its not telling you to what degree the spread between the bid and ask has blown out to 1x, 2x, or 5x normal and that trades are executing only at the highest slippage prices in that spread.
All of these things are considerations that the market makers can use to make a "buy the dip" situation that works heavily to their advantage.
TLDR: "If you can't spot the sucker in your first half hour at the table, then you are the sucker"
----------------------------------
So - why / when would VIX go to 100?
In 2020, its easy to forget that a culmination of things stopped the crash at -35%.
* March 17, 2020 VIXEX wiped out a significant amount of long volatility positions.
* March 20, 2020 Opex wiped out a significant proportion of the short term put positions
* March 20, 2020 Fed Reserve announced to provide "enhanced" (i.e. unlimited) liquidity to the
markets starting Monday March 23, 2020.
* April 6th, 2020 Peak of Implied Volatility (point where options "most expensive") - which meant that buyers / sellers started providing more & more liquidity following this point.
In 2025, we have yet to see:
* Any motion towards intervention from the Fed for liquidity.
* Any motion from the significant fundamental investors (we're not close to an attractive P/S or P/E on most stocks for Buffett & Co to start buying)
* Any significant motion from companies on indicating strategies about capital raises, layoffs, or other company level liquidity reactions.
* Any "reset" of options in either volatility or hedging. Numbers below as of April 9, 2025:
- SPY 2.8M Put OI for April 17
- VIX 3.5M Call OI for April 16
Just an example but maybe IF we see those clear and NOT get re-bought for May Opex... we might be ready to call a top here at 50 VIX.
Otherwise.... we're just at another stop on the path to 100.
VIX - Extreme fear in the market: a unique opportunity?Extreme fear in the market: a unique opportunity?
An analysis of the most significant
VIX spikes (1987-2025) and subsequent stock market performance.
The VIX (Volatility Index) is an indicator that reflects the level of fear or uncertainty in the market based on expectations of volatility in the S&P 500 Index.
The VIX's 118% surge from April 4 to April 7, 2025 was the fifth largest 3-day surge in market history.
This surge 🚀 reflects the high level of uncertainty that has developed in the markets.
It is very difficult to make informed investment decisions during such periods.
But we can rely on historical patterns.
After the 20 largest VIX spikes, the S&P 500 Index has consistently delivered exceptional returns:
- After 1 year: 16.5% (vs. 12% in normal periods)
- After 3 years: 45.9% (vs. 39.5% in normal periods)
- After 5 years: 83.0% (vs. 74.4% in normal periods)
The difference in returns over the 4 years is 10.2% above average.
Over the past 40 years, there has only been one negative return (the 2007 spike before the financial crisis), while most extreme fear events have become outstanding buying opportunities. For example, the August 2011 spike was followed by an impressive 117% return over the next five years.
When market panic reaches extreme levels, institutional capital typically steps in against retail sales, setting the stage for stronger long-term growth. History shows that these moments of maximum fear often represent optimal entry points for patient investors.
It is essential to realize that historical patterns do not always hold true in the future. Each crisis has unique characteristics and causes that can lead to different outcomes.
These statistics provide good mathematical expectations, not guarantees.
This has always been the case in the market, and proper handling of math expectations and risk management are the foundations of profitable strategies.
Best regards EXCAVO
_____________________
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.