Skeptic | RSI Masterclass: Unlock Pro-Level Trading Secrets!Hey traders, it’s Skeptic ! 😎 Ready to transform your trading? 95% of you are using the Relative Strength Index wrong , and I’m here to fix that with a game-changing strategy I’ve backtested across 200+ trades. This isn’t a generic RSI tutorial—it’s packed with real-world setups, myth-busting insights, and precise rules to trade with confidence. Join me to master the art of RSI and trade with clarity, discipline, and reason. Big shoutout to TradingView for this epic free tool! 🙌 Let’s dive in! 🚖
What Is RSI? The Core Breakdown
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) , crafted by Welles Wilder, is a momentum oscillator that measures a market’s strength by comparing average gains to average losses over a set period. Here’s the formula:
G = average gains over n periods, L = average losses.
Relative Strength (RS) = | G / L |.
RSI = 100 - (100 / (1 + RS)).
Wilder used a 14-period lookback , and I stick with it—it’s smooth, filters noise, and gives a crystal-clear read on buyer or seller momentum. Let’s get to the good stuff—how I use RSI to stack profits! 📊
My RSI Strategy: Flipping the Script
Forget what you’ve read in books like The Handbook of Technical Analysis by Mark Andrew Lim— overbought (70) and oversold (30) aren’t just for shorting or buying. I go long when RSI hits overbought, and it’s been a goldmine. I’ve backtested over 200 trades with this approach, and it’s my go-to confirmation for daily setups. Why does it work? When RSI hits overbought on my 15-minute entry chart, it signals explosive buyer momentum. Here’s what you get:
Lightning-Fast R/R: I hit risk/reward targets in 30 minutes to 2 hours on 15-minute entries (longer for 1-hour entries, depending on your timeframe).
Massive R/R Potential: An overbought RSI on 15-minute can push 1-hour and 4-hour RSI into overbought, driving bigger moves. I hold for R/Rs of 5 or even 10, not bailing early. 🚀
Rock-Solid Confirmation: RSI confirms my entry trigger. Take BTC/USD:
BTC bounces off a key support at 76,000, sparking an uptrend.
It forms a 4-hour box range, but price tests the ceiling more than the floor, hinting at a breakout.
Trigger: Break above the box ceiling at 85,853.57.
On 15-minute, a powerful candle breaks the ceiling, and RSI hits overbought—that’s my green light. I open a long.
Soon, 1-hour and 4-hour RSI go overbought, signaling stronger momentum. I hold, and BTC pumps hard, hitting high R/R in a short window.
This keeps trades fast and efficient—quick wins or quick stops mean better capital management and less stress. Slow trades? They’re a mental grind, pushing you to close early for tiny R/Rs. 😴
Pro Rules for RSI Success
Here’s how to wield RSI like a trading weapon:
Stick to the Trend : Use RSI in the direction of the main trend (e.g., uptrend = focus on longs).
Confirmation Only: Never use RSI solo for buy/sell signals. Pair it with breakouts or support/resistance triggers.
Fresh Momentum: RSI is strongest when it just hits overbought/oversold. If the move’s already rolling, skip it—no FOMO, walk away!
Customize Zones: Overbought (70) and oversold (30) can shift—it might show reactions at 65 or 75. Adjust to your market’s behavior.
Backtesting RSI: Your Path to Mastery
To make RSI yours, backtest it across at least 30 trades in every market cycle— uptrend, downtrend, and range. Test in volatile markets for extra edge. 😏 Key takeaways:
Range Markets Kill RSI: Momentum oscillators like RSI (or SMA) are useless in ranges—no momentum, no signal. Switch to ROC (Rate of Change) for ranges—I use it, and it’s a beast. Want an ROC guide? Hit the comments!
Overextended RSI Zones: On your entry timeframe (e.g., 15-minute), check higher timeframes (e.g., 4-hour) for past RSI highs/lows. These are overextended zones—price often rejects or triggers a range. Use them to take profits.
Final Vibe Check
This RSI masterclass is your key to trading like a pro—fast R/Rs, big wins, and unshakable confidence . At Skeptic Lab, we live by No FOMO, no hype, just reason. Guard your capital— max 1% risk per trade, no excuses. Want an ROC masterclass or more tools? Drop a comment! If this fired you up, smash that boost—it means everything! 😊 Got a setup or question? Hit me in the comments. Stay sharp, fam! ✌️
M-oscillator
Best Free Volatility Indicator on TradingView for Gold Forex
This free technical indicator will help you easily measure the market volatility on Forex, Gold or any other market.
It will show you when the market is quiet , when it's active and when it's dangerous .
We will go through the settings of this indicator, and you will learn how to set it up on TradingView.
Historical Volatility Indicator
This technical indicator is called Historical Volatility.
It is absolutely free and available on TradingView, MetaTrader 4/5 and other popular trading terminals.
TradingView Setup
Let me show you how to find it on TradingView and add it to your price chart.
Open a technical price chart on TradingView and open the "Indicators" menu (you will find it at the top of the screen).
Search "Historical Volatility" and click on it.
It will automatically appear on your chart.
"Length" parameter will define how many candles the indicator will take for measuring the average volatility. (I recommend keeping the default number, but if you need longer/shorter-term volatility, you can play with that)
Timeframe drop-down list defines what time frame the indicator takes for measuring the volatility. (I recommend choosing a daily timeframe)
And keep the checkboxes unchanged .
How to Use the Indicator
Now, let me show you how to use it properly.
Wider the indicator and analyse its movement at least for the last 4 months.
Find the volatility range - its low levels will be based on the lower boundary of the range, high levels will be based on its upper boundary.
This is an example of such a range on USDCAD pair.
When the volatility stays within the range, it is your safe time to trade.
When volatility approaches its lows, it may indicate that the market might be slow .
Highs of the range imply that the market is very active
In-between will mean a healthy market.
The Extremes
The violation of a volatility range to the downside is the signal that the market is very slow . This would be the recommended period to not trade because of high chance of occurrence of fakeouts.
An upward breakout of a voliatlity range is the signal of the extreme volatility . It will signify that the market is unstable , and it will be better to let it calm down before placing any trade.
Volatility Analysis
That is how a complete volatility analysis should look.
At the moment, volatility reached extreme levels on CADJPY pair.
The best strategy will be to wait till it returns within the range.
Remember This
With the current geopolitical uncertainty and trade wars, market volatility reaches the extreme levels.
Such a volatility is very dangerous , especially for newbie traders.
Historical volatility technical indicator will help you to easily spot the best period for trading and the moment when it is better to stay away.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Altcoins in Focus: Aptos, KAIA, and Ravencoin (RVN)Amid Bitcoin’s rapid growth and renewed interest in Ethereum, investors are increasingly turning their attention to altcoins—alternative cryptocurrencies showing strong potential for sharp gains. As of early June 2025, Aptos (APT), KAIA, and Ravencoin (RVN) stand out for their price surges and growing interest from major exchanges and analysts.
Aptos, a next-generation blockchain platform developed by former Meta (ex-Diem) engineers, has secured its place among the top 50 by market cap. In recent days, the token broke through a resistance level at $9.20, signaling a possible continuation of the uptrend. Its appeal lies in its scalability and its unique MoveVM architecture, which makes it attractive for developers in DeFi and NFT applications.
KAIA, a new token in the AI and metaverse ecosystem, gained over 15% this week following a Binance listing and integration with several major Web3 projects. Investors see KAIA as a potential “new Render,” focusing on neural computation and digital identity infrastructure.
Ravencoin (RVN), a long-time presence in the crypto space, is regaining popularity. With its focus on asset tokenization and copyright protection on the blockchain, RVN surged 14% after announcing partnerships with several independent music platforms.
The rise of these altcoins demonstrates that there is room in the crypto world not just for the giants, but also for innovative, purpose-driven projects capable of capturing market and user interest.
HA-RSI + Stochastic Ribbon: The Hidden Gem for Trend & MomentumNavigating volatile markets requires more than just raw price action. The Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator blends the power of smoothed candlesticks with momentum insights to give traders a clearer picture of trend strength and reversals.
At Xuantify , we use the Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator as a hybrid momentum and trend tool. While the indicator calculations are based on Heikin Ashi values to smooth out noise and better capture trend dynamics, the chart itself displays standard candlesticks (real price data) . This ensures that all signals are aligned with actual market structure, making it easier to execute trades with confidence and clarity.
This dual-layer approach gives us the best of both worlds: clarity from smoothing and precision from real price action. MEXC:SOLUSDT.P
🧠 How We Use It at Xuantify
At Xuantify , we integrate the Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator into our multi-layered strategy framework. It acts as a trend confirmation filter and a momentum divergence detector , helping us avoid false breakouts and time entries with greater precision. We pair it with volume and volatility metrics to validate signals and reduce noise. Note the Stochastic Ribbon Overlay as shown in the chart, very accurate for momentum.
⭐ Key Features
Heikin Ashi Smoothing : Filters out market noise for clearer trend visualization.
RSI-Based Oscillation : Measures momentum shifts with precision.
Color-Coded Bars : Instantly identify bullish/bearish momentum.
Dynamic Signal Zones : Customizable overbought/oversold thresholds.
Stochastic Ribbon Overlay : A powerful multi-line stochastic system that enhances momentum analysis and trend continuation signals.
💡 Benefits Compared to Other Indicators
Less Whipsaw : Heikin Ashi smoothing reduces false signals common in traditional RSI.
Dual Insight : Combines trend and momentum in one visual.
Better Divergence Detection : Easier to spot hidden and regular divergences.
Visual Simplicity : Clean, intuitive design for faster decision-making.
⚙️ Settings That Matter
RSI Length : Default is 14, but we often test 10 or 21 for different timeframes.
Smoothing Type : EMA vs. SMA – EMA reacts faster, SMA is smoother.
Overbought/Oversold Levels : 70/30 is standard, but 80/20 can reduce noise in trending markets.
📊 Enhancing Signal Accuracy
Combine with Volume Oscillators to confirm momentum strength.
Use Price Action Zones to validate oscillator signals.
Look for Divergences between price and oscillator for early reversal clues.
🧩 Best Combinations with This Indicator
MACD : For cross-confirmation of momentum shifts.
Bollinger Bands : To identify volatility squeezes and breakouts.
Support/Resistance Levels : For contextual trade entries and exits.
⚠️ What to Watch Out For
Lag in Strong Trends : Like all smoothed indicators, it may react slightly late.
Over-Optimization : Avoid curve-fitting settings to past data.
Standalone Use : Best used in conjunction with other tools, not in isolation.
🚀 Final Thoughts
The Heikin Ashi RSI Oscillator is a powerful hybrid tool that simplifies complex market behavior into actionable insights. At Xuantify, it’s a core part of our strategy toolkit, helping us stay ahead of the curve with clarity and confidence.
🔔 Follow us for more educational insights and strategy breakdowns!
We regularly share deep dives into indicators, trading psychology, and backtested strategies. Stay tuned and level up your trading game with us!
SMI vs. Stochastic: Which One Gives You the Edge?Momentum indicators are essential tools in every trader’s arsenal—but not all are created equal. While the Stochastic Oscillator has been a go-to for decades, the Stochastic Momentum Index (SMI) offers a more refined and reliable way to read market momentum.
In this post, we’ll break down the key differences between these two indicators, how we use them at Xuantify , and why the SMI might just give you the edge you’ve been looking for.
🧠 How We Use It at Xuantify
We’re always looking for tools that offer greater precision and less noise . While the Stochastic Oscillator is one of the most commonly used tools for spotting overbought and oversold conditions, the Stochastic Momentum Index (SMI) gives us a clearer, smoother view of momentum —especially in volatile or choppy markets.
We use the SMI to refine our entries and exits , particularly when trading breakouts or reversals. MEXC:ETHUSDT.P
⭐ Key Features
Stochastic Oscillator : Measures the closing price relative to the high-low range. Simple and responsive. Great for spotting short-term reversals.
Stochastic Momentum Index (SMI) : Measures the distance of the current close from the midpoint of the high-low range. Smoother and more centered around zero. Better at filtering out false signals.
💡 Benefits Compared to Other Indicators
Stochastic Oscillator vs. SMI:
Signal Smoothness: Moderate vs. High
Noise Filtering: Low vs. Excellent
Centered Oscillation: No vs. Yes (around 0)
Best Use Case: Range-bound markets vs. Trend shifts & momentum confirmation
False Signal Risk: Higher vs. Lower
The SMI is especially useful when you want to avoid whipsaws and get a more reliable read on momentum .
⚙️ Settings That Matter
Stochastic Oscillator : %K = 14, %D = 3
SMI : Length = 14, Signal Smoothing = 3, Double Smoothing = 3
You can adjust the SMI smoothing values to match the volatility of the asset— lower smoothing for fast markets , higher for slower ones.
📊 Enhancing Signal Accuracy
Enhance SMI signals by combining them with:
Trend filters like EMAs or Supertrend
Volume confirmation
Support/resistance zones
Divergence spotting for early trend reversals
This layered approach helps us avoid false positives and stay aligned with the broader trend .
🧩 Best Combinations with This Indicator
SMI + EMA Crossovers: Confirm momentum with trend direction
SMI + RSI Divergence: Spot early reversals with confluence
SMI + Volume Profile: Validate momentum near key price levels
⚠️ What to Watch Out For
Lag in fast markets: SMI’s smoothing can delay signals slightly
Over-optimization: Avoid excessive tweaking of parameters
Not ideal alone: Best used with confluence tools for confirmation
🚀 Final Thoughts
The Stochastic Oscillator is a classic for a reason—but the Stochastic Momentum Index is a refined evolution . We’ve found that SMI gives us cleaner signals , better momentum clarity , and fewer false alarms —especially when paired with smart filters.
If you're looking to upgrade your momentum toolkit , the SMI might just be your edge.
🔔 Follow us for more educational insights and strategy breakdowns!
We break down indicators, strategies, and market psychology to help you trade smarter—not harder.
Color Your Trades: MACD 4C vs the Classic📊 Coloring Momentum: Comparing Standard MACD vs MACD 4C
Momentum indicators are a trader’s compass—but not all compasses are created equal. In this post, we compare the classic MACD with the visually enhanced MACD 4C , a four-color histogram tool that adds clarity and nuance to trend and momentum analysis.
Let’s break down how both tools work, how we use them at Xuantify, and how you can decide which one fits your strategy best.
🔍 What Are These Indicators?
Standard MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is a time-tested momentum indicator that plots the difference between two EMAs (typically 12 and 26) and a signal line (usually a 9 EMA of the MACD line). It’s simple, effective, and widely used.
MACD 4C , developed by vkno422 , builds on the classic MACD by introducing a four-color histogram and divergence detection , making it easier to interpret momentum shifts and trend strength visually.
Key Differences:
Standard MACD: Two lines + histogram (single color)
MACD 4C: Histogram only, but with four colors to show trend strength and direction
MACD 4C includes bullish/bearish divergence detection
🧠 How We Use Them at Xuantify
We use both indicators—but for different purposes.
1. Standard MACD – Clean Confirmation
We use it for classic trend confirmation and crossover signals . It’s great for traders who prefer minimalism and are comfortable interpreting line-based momentum.
2. MACD 4C – Visual Momentum Clarity
We use MACD 4C when we want a more intuitive, color-coded view of momentum. The four-color histogram helps us quickly spot trend strength, exhaustion, and divergence.
🧭 Color Coding in MACD 4C
MACD 4C uses four histogram colors (default settings):
Lime/Green : Bullish momentum building or continuing
Red/Maroon : Bearish momentum building or continuing
This makes it easier to:
Spot momentum shifts
Identify trend continuation
Detect divergence at a glance
⚙️ Settings That Matter
Both indicators allow customization, but MACD 4C offers more visual tuning:
MACD 4C:
Adjustable fast/slow MA and signal smoothing
Toggle divergence detection
Color-coded histogram for quick reads
Standard MACD:
Clean, minimal, and widely supported
Best for traders who prefer traditional setups
🔗 Best Combinations with These Indicators
We combine MACD tools with:
Structure Tools – BOS/CHOCH for context
Liquidity Zones – To spot where momentum may reverse
Volume Profile – To confirm strength behind moves
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) – For precision entries
⚠️ What to Watch Out For
Both indicators are lagging by nature—they rely on moving averages. MACD 4C’s divergence detection can help anticipate reversals, but it’s still best used as a confirmation tool , not a standalone signal.
🔁 Repainting Behavior
Both the standard MACD and MACD 4C are non-repainting . Once a histogram bar or crossover is printed, it remains fixed. This makes them reliable for real-time trading and backtesting .
⏳ Lagging or Leading?
These are lagging indicators , designed to confirm trends—not predict them. MACD 4C’s divergence feature adds a leading element , but it should always be used with structure and price action for confirmation.
🚀 Final Thoughts
If you’re a visual trader who wants more clarity from your momentum tools, MACD 4C is a powerful upgrade. If you prefer simplicity and tradition, the standard MACD still holds its ground.
Try both, test them in your strategy, and see which one sharpens your edge.
Understanding Williams %R In TradingThe Williams %R is a fast, sensitive momentum oscillator ideal for short-term trading strategies. It provides early signals of overbought and oversold conditions by comparing the current close to the high-low range over a defined lookback period (typically 14 bars).
By understanding where Williams %R fits among other oscillators, traders can better utilize it within a well-rounded, context-aware strategy.
✅ 1. What Are Momentum Indicators?
Momentum indicators are technical analysis tools used to measure the speed and strength of a price movement over time. Rather than focusing on absolute price direction, momentum indicators assess how quickly prices are changing and help traders identify potential turning points, continuation patterns, or overbought/oversold conditions.
They are particularly useful in sideways or ranging markets, where momentum shifts often precede breakouts or reversals.
Key characteristics of momentum indicators:
Often bounded within fixed ranges (e.g., 0–100 or -100 to 0)
Typically leading indicators, aiming to provide early entry/exit signals
Help spot divergence between price and momentum — a common sign of weakening trends
✅ 2. Understanding the Williams %R Indicator
≫ The Origin: Developed by Larry Williams
The Williams %R indicator was developed by Larry Williams, a renowned trader and author, in the late 1970s. Williams introduced this tool to identify potential market turning points by measuring a security’s momentum relative to its recent high-low range.
Originally intended for short-term futures trading, the indicator has since become a staple for both day traders and swing traders across various markets, including stocks, forex, and crypto.
Larry Williams famously used this indicator in his trading system when he won the 1987 World Cup Trading Championship, turning $10,000 into over $1 million in a single year—demonstrating its real-world impact when used effectively.
≫ Formula Breakdown
The Williams %R formula is as follows:
Williams %R= = (HighestHigh − Close) / (HighestHigh - LowerLow) × −100
Highest High = The highest price over the lookback period (typically 14 periods)
Lowest Low = The lowest price over the same lookback period
Close = The current closing price
This formula normalizes the current price within its recent trading range and expresses it as a negative percentage between 0 and -100.
Example:
If price is at the highest point in the range → %R = 0 (overbought)
If price is at the lowest point in the range → %R = -100 (oversold)
This inverted scale (compared to RSI) helps traders see how close the current price is to the top or bottom of the recent range, providing clues about potential reversal zones.
Williams %R in Pinescript:
//@version=5
indicator("Custom Williams %R", overlay=false)
length = input.int(14, title="Period")
highestHigh = ta.highest(high, length)
lowestLow = ta.lowest(low, length)
williamsR = (highestHigh - close) / (highestHigh - lowestLow) \* -100
plot(williamsR, title="%R", color=color.purple)
hline(-20, "Overbought", color=color.red)
hline(-80, "Oversold", color=color.green)
≫ Key Settings: 14-Period Default and Customizations
The default setting for Williams %R is 14 periods, which Larry Williams originally recommended. However, this lookback period can be customized based on your trading style and timeframe.
Here’s how different settings can be applied:
❖ Intraday Trading (5-minute to 15-minute charts):
Use a 9 to 14-period setting for faster, more responsive signals.
Ideal for scalpers or short-term traders seeking quick entries and exits.
❖ Swing Trading (1-hour to Daily charts):
Stick with the standard 14 to 21-period range.
Balances sensitivity and reliability; helps capture short- to mid-term reversals.
❖ Position/Long-Term Trading (Weekly charts or higher):
Use 21-period or longer to smooth out signals and reduce noise.
Best for spotting high-conviction turning points with less frequent trades.
🔁 Customization Tip:
You can also use multiple %R settings (e.g., 14 and 50) together to analyze short-term momentum inside longer-term trend cycles, adding depth and context to your strategy.
≫ Interpretation: Overbought and Oversold Conditions
The Williams %R scale ranges from 0 to -100 and is interpreted as follows:
❖ Overbought: %R above -20
Indicates that price is near the top of its recent range
Suggests potential for a pullback or reversal downward
❖ Oversold: %R below -80
Indicates price is near the bottom of its recent range
Suggests potential for a bounce or reversal upward
⚠️ Important: Overbought does not mean “time to sell” and oversold does not mean “time to buy.” These are conditions, not signals. Use them with confirmation tools like support/resistance zones, candlestick patterns, volume analysis, divergences and more.
✅ 3. Using Williams %R Effectively
≫ Entry Signals
Williams %R can be used to time entries based on shifts in momentum, especially around key overbought and oversold zones.
❖ Overbought/Oversold Reversals
This is the most common use of Williams %R - identifying turning points when price reaches extreme levels in its recent range:
Overbought Zone (above -20):
Signals potential bearish reversal
Look for confluence with resistance levels or bearish candlestick patterns
Confirmation often comes as %R drops back below -20
Oversold Zone (below -80):
Indicates a possible bullish reversal
Stronger when aligned with support or demand zones
Confirmation often comes when %R climbs back above -80
⚠️ Note: These are signals of potential exhaustion, not guaranteed reversals. Always pair with price action context or volume.
❖ Pullback Continuations
Williams %R can also support trend-following strategies by identifying momentum retracements within an ongoing trend:
In an uptrend, wait for Williams %R to dip below -80 (short-term oversold) and then re-enter above -80 as the trend resumes
In a downtrend, look for a rally where %R rises above -20 (short-term overbought), then re-enters below -20 to confirm trend continuation
This technique helps you buy the dip or sell the rally with better timing and risk control.
≫ Exit Signals
Williams %R can also guide exit timing by showing when momentum is weakening, especially as price moves away from extremes.
❖ Returning to Neutral Zones
When Williams %R moves back toward the -50 midpoint, it can signal that the current move is losing steam.
In a long position, if %R returns from oversold to above -50 but then flattens or dips again, it may be time to take profit
In a short position, if %R rises from overbought back below -50, it suggests selling pressure is decreasing
Exiting before full reversals can help you lock in gains while reducing risk exposure.
❖ Crossovers at Extremes
Some traders look for quick crossovers back through key thresholds (-80 and -20) as exit or reversal alerts:
If %R drops from above -20 back below it, the overbought condition may be ending
If %R rises from below -80 back above it, the oversold condition may be ending
These sharp shifts often precede momentum flips, making them useful for both exit timing and new trade setups in the opposite direction.
❖ False Signal Filtering Techniques
Williams %R can produce false signals, especially in trending or volatile markets. To improve signal quality, consider these filters:
Use with Trend Filters:
Apply moving averages (e.g., 50- or 200-period MA) to define trend direction and avoid counter-trend trades
Only trade overbought signals in a downtrend and oversold signals in an uptrend
Add Price Action Confirmation: Look for candlestick patterns (e.g., engulfing, pin bars) or support/resistance reactions before acting on %R signals
Volume Analysis: Confirm signals with volume spikes or divergences to validate strength or weakness in a move
Multiple Timeframe Confluence: Use Williams %R on a higher timeframe (e.g., 4H or daily) to establish the broader context, then align trades on a lower timeframe
Avoid during High Volatility Events: News releases and earnings reports can create erratic spikes that cause misleading %R readings
❖ Best Market Conditions: Ranging vs Trending Markets
Williams %R performs best under specific market conditions. Understanding when to use it—and when to avoid it—is key to success.
Ranging Markets: Ideal Conditions
Williams %R excels in sideways or consolidating markets
In ranges, price frequently oscillates between support and resistance, making overbought/oversold signals highly effective
Reversals from the -20 or -80 zones often align with the top and bottom of a trading range
Trending Markets: Use With Caution
During strong trends, Williams %R can stay in the overbought or oversold zone for extended periods
This makes reversal signals less reliable and more prone to false exits
In trending conditions, it’s better to:
Use Williams %R for pullback entries
Combine it with a trend filter to stay on the dominant side of momentum
✅ 4. Optimizing the Period Setting (5, 9, 14, 21, etc.)
The length of the lookback period in Williams %R significantly affects signal behavior:
Shorter periods (5, 9):
Produce faster, more frequent signals
Best for scalping and intraday trading
More sensitive but can result in higher noise and false signals
Default period (14):
Balanced responsiveness
Suitable for swing trading and multi-hour charting
Longer periods (21+):
Generate fewer but more stable signals
Best for position trading or slower-moving markets
Reduced noise but may lag in volatile conditions
🔍 To optimize:
Test various period values under consistent rules (e.g., entry/exit and risk management stay the same)
Compare outcomes across different market environments (trending, ranging, volatile)
✅ 4. Key Takeaways
Williams %R is a momentum oscillator that measures the close relative to the recent high-low range on a scale from 0 to -100.
It was developed by Larry Williams to help identify short-term overbought and oversold market conditions.
A reading above -20 suggests overbought conditions, while a reading below -80 indicates oversold conditions.
The default 14-period setting balances signal responsiveness and stability for most traders.
Shorter periods generate faster signals with more noise, while longer periods produce smoother signals with more lag.
Williams %R works best in ranging or sideways markets rather than strongly trending environments.
Traders can use %R for reversal signals or to confirm pullbacks within a broader trend.
Filtering signals with price action, support/resistance, or volume improves accuracy.
The indicator is not meant to be used in isolation and requires confirmation before acting on signals.
Backtesting across different timeframes and period settings is essential for identifying optimal usage.
Performance metrics such as win rate, R:R ratio, and drawdown help evaluate the indicator’s reliability.
Williams %R is easy to code and automate in platforms like TradingView using Pine Script.
The indicator adds value when used as part of a broader, disciplined trading system.
Williams %R is a simple yet deeply insightful momentum oscillator. While often overlooked in favor of more complex indicators, it provides a unique lens into market sentiment and price extremes. Its greatest strength lies in its clarity — helping traders time entries and exits with greater confidence when paired with context.
RSI 101: The Secret of RSI’s WMA45 Line and How to Use ItIn my trading method, I use the WMA45 line together with RSI to help spot the trend more clearly.
Today, I’ll share with you how it works and how to apply it — whether you're doing scalping or swing trading.
Why WMA45?
WMA (Weighted Moving Average) is a type of moving average where recent prices are given more importance.
WMA45 simply means it takes the average of the last 45 candles (could be 45 minutes, 45 hours, or 45 days depending on your chart).
Because it moves slower than RSI, it helps reduce the “noise” and gives you a better idea of the real trend.
This idea is not new — many traders have tested RSI strategies also use this line. I just applied and adjusted it in my own way.
👉 How to set it up on TradingView (very simple):
What WMA45 Tells You
Trending
This line shows you the overall direction of the market:
📉 If WMA45 is going down, the price is likely going down.
📈 If WMA45 is going up, the price is likely going up.
Also, the steeper the line, the stronger the trend is:
Looking at the example above, the WMA45 line starts from the same level in two different phases, but the slope is different. The steeper line shows a larger price range.
This happens because the price was more volatile, which caused the RSI to move more sharply, and that, in turn, made the WMA45 slope steeper.
In multi-timeframe analysis, when the trend on the higher timeframe is strong (shown by a steep WMA45 line), the RSI on the lower timeframe will usually move within a tighter range and react more accurately to key levels.
If you’re not sure what these key RSI levels are, check out my previous post here:
For example, in a strong downtrend on H1, RSI on M5 might not even reach 50:
✅ What does this mean for trading?
Use WMA45 on higher timeframes to define trend bias.
On lower timeframes, watch RSI responses at key zones for optimal entries.
When holding positions, WMA45 helps determine whether to stay in the trade.
Moving Sideways
Here’s something important to note: when WMA45 is flat, RSI will keep crossing back and forth over it.
Depending on where WMA45 is flat, RSI tends to move within that range and creates different sideways price patterns. Here are the main types:
Around 50 → price moves in a box: According to RSI theory, the 50 level is the balance between buyers and sellers. RSI fluctuating around this causes price to move sideways in a rectangular box range.
Above 50 → price goes up in a rising channel: Above 50 is where buyers dominate sellers. RSI operating in this zone will continually create bullish candles pushing the price upward.
Below 50 → price goes down in a falling channel: Below 50 is where sellers dominate buyers. RSI in this zone will consistently form lower highs and lower lows, pushing the price downward.
Trend Reversal of WMA45
WMA45 is calculated from the average of 45 candles, so it's almost impossible for it to reverse direction suddenly. When it's sloping (trending), it takes time for RSI to fluctuate enough to "flatten" it before it can reverse.
As shown in the example, after WMA45 slopes up, before it turns downward, RSI must cross back and forth through it to reduce the steepness => flatten it => then reverse.
Does this align with Dow Theory? It represents the phases: Trend > Sideway > Trend. Sideway is when the WMA45 line is flattened.
✅ What does this mean for trading?
After a trend forms, if you want to enter a counter-trend trade, patiently wait for WMA45 to flatten to confirm the previous trend has ended.
Dynamic Support and Resistance
In addition to being a trend indicator for RSI, WMA45 also serves as a dynamic support/resistance level for RSI.
You will often observe RSI reacting when it encounters the WMA45 line.
In an uptrend, WMA45 acts as support for RSI.
In a downtrend, WMA45 acts as resistance for RSI.
Notably, if the reactions occur at higher RSI values, the resulting price support is stronger. Conversely, if reactions happen at lower RSI values, the price is pushed down further.
In the above example, in the first reaction around RSI 60s, RSI dropped by 9.6 points and price dropped by 12 points. In the second reaction at RSI 40s, RSI dropped similarly, but the price dropped by 25 points.
✅ What does this mean for trading?
You can use WMA45 as an entry zone for your trade: Wait for reactions with WMA45 on the higher timeframe, then switch to a lower timeframe to find a trade entry.
Use WMA45 as a take-profit or stop-loss level: For a short trade near WMA45, you can stop out if RSI crosses above it.
When monitoring these reactions, pay attention to the number of reactions—more reactions require more caution in trading.
Some Trade Setups Using WMA45 and RSI
1. Intraday trading
Trend: Follow the trend on the H1 chart.
Entry zone: At WMA45 of H1.
Entry confirmation: 2 methods:
On M5: when WMA45 of RSI is already flattened, and RSI has crossed above WMA45.
On M5: when a divergence appears in RSI.
2. Scalping
With the RSI’s reaction to WMA45, even on smaller timeframes (M1, M5), you can scalp when RSI touches WMA45.
When WMA45 has a slope and RSI returns to touch it, you can enter a trade with SL behind the candle close (10–20 pips to avoid stop hunts and spread), and TP to the nearest peak.
As mentioned, the first touch gives the best reaction.
My trading system is entirely based on RSI, feel free to follow me for technical analysis and discussions using RSI.
Technical Analysis Indicators Cheat SheetHello, traders! 🦾
This cheat sheet provides a comprehensive overview of the most widely used technical analysis indicators. It is designed to support traders in analyzing trends, momentum, volatility, and volume.
Below, you’ll find a handy screenshot of this Cheat Sheet that you can save and peek at whenever you need a quick, friendly refresher on your trading indicators. ;)
1. Trend Indicators
These tools identify the direction and strength of price movements, critical for trend-following strategies.
Moving Averages (MA)
Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) smooth price data to highlight trends. Crossovers (e.g., 50-day vs. 200-day MA) signal potential trend shifts.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) – Tracks the difference between two EMAs, paired with a signal line to generate trade signals. A bullish crossover occurs when MACD rises above the signal line.
Parabolic SAR. Places dots above or below the price to indicate trend direction. Dots below the price suggest an uptrend; above, a downtrend.
ADX (Average Directional Index)
Measures trend strength (0–100). Values above 25 confirm a robust trend; below 20 indicate consolidation.
2. Momentum Indicators (Oscillators)
These indicators assess price movement speed and highlight overbought or oversold conditions.
RSI (Relative Strength Index)
Ranges from 0 to 100, with values above 70 indicating overbought conditions and below 30 indicating oversold. The divergence between the RSI and price can signal impending reversals.
Stochastic Oscillator –Compares closing price to the price range over a period (0–100). Above 80 is overbought; below 20, oversold. %K and %D line crossovers provide precise trade signals.
CCI (Commodity Channel Index) – Measures price deviation from its average. Readings above +100 indicate overbought; below -100, oversold.
Williams %R – Similar to Stochastic, it measures distance from the period’s high (0 to 100). Above -20 is overbought; below -80, oversold.
3. Volatility Indicators
These tools quantify price fluctuation ranges to optimize trade timing.
Bollinger Bands – Comprises a 20-day SMA and two bands (±2 standard deviations). Narrow bands reflect low volatility; wide bands indicate high volatility. A price touching the outer bands may signal a reversal or trend continuation, depending on the context.
ATR (Average True Range) – Calculates the average price range over a period to gauge volatility. Higher ATR values denote greater market movement.
4. Volume Indicators
Volume-based indicators validate price movements and highlight market participation.
OBV (On-Balance Volume) – Cumulates volume to confirm price trends. The rising OBV, alongside rising prices, supports an uptrend. OBV divergence from price may foreshadow reversals.
Volume Oscillator – Compares two volume moving averages to evaluate buying or selling pressure. Positive values suggest stronger buying. It typically confirms breakouts or assesses the sustainability of a trend.
Chaikin Money Flow (CMF) – It analyzes money flow based on price and volume. Positive CMF indicates buying pressure; negative, selling pressure.
5. Other Key Indicators. Advanced Tools for Deeper Market Analysis.
Ichimoku Cloud – Combines five lines and a “cloud” to assess trend, momentum, and support/resistance. Price above the cloud signals an uptrend; below, a downtrend. Cloud thickness reflects the strength of support or resistance levels.
Fibonacci Retracement – Maps potential support and resistance using Fibonacci ratios (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%).
Pivot Points – Derives support (S1, S2) and resistance (R1, R2) levels from the prior period’s high, low, and close.
Skills to Sharpen for Smarter Trading
Successful traders often find that combining indicators from different categories yields better results. For instance, pairing a trend-based EMA with a momentum indicator like RSI can help confirm signals more reliably — much like crafting the perfect coffee blend, where balance is everything.
Many also realize that stacking similar tools, such as using both RSI and Stochastic, tends to clutter the picture rather than clarify it. A focused set of indicators usually proves more effective.
Another common practice is backtesting setups on historical data to understand how strategies perform in specific markets and timeframes. It’s a way to rehearse before stepping onto the stage.
Ultimately, those who see consistent results tend to integrate indicators into a coherent strategy rather than reacting to every signal. That clarity often makes all the difference
Many of these indicators, from MACD to Bollinger Bands, are readily available on platforms like TradingView, making it easy to apply them to your charts.
Subscribe and let us know which of these indicators intrigues you the most so we can explore it further in our next post!
Good luck! 👏
What If Trump’s Tariffs Are Actually Bullish for SPX ?Hello Traders 🐺
In this idea, I want to take a closer look at SPX and break down why the new U.S. tariffs and Trump’s economic policies could either boost or damage the U.S. economy in the coming months. So make sure to stay with me until the very end.
🔍 Let’s start with the chart:
As you can see, SPX is currently holding above a weekly support level, marked by the orange ascending trendline. So far, so good. However, we’re also seeing a massive bearish divergence on the RSI — and in my opinion, this was one of the key reasons behind the recent Black Monday-style selloff.
⚠️ But here’s the deal: If SPX breaks below this orange trendline, the next strong support is around 3375 — aligned with the 0.5 Fibonacci level and the monthly blue trendline inside our green support zone.
🤔 Should we be bearish on SPX and the U.S. economy?
That’s the big question… and it’s tricky to answer right now. Let’s break it down.
🔧 1. Tariffs and Trump: What’s really going on?
We’re currently in a pause phase of the ongoing tariff war — with countries negotiating to avoid escalation. But here’s the catch: markets hate uncertainty, and that’s why we saw panic selling recently.
Still, most people miss the bigger picture here.
The U.S. has long been a consumer-driven economy, importing heavily from other nations. Meanwhile, U.S. producers have struggled to compete — both domestically and internationally — due to low tariffs at home and high tariffs abroad.
So what do Trump’s new tariffs do?
✅ They level the playing field for U.S. companies at home
✅ They push other countries to lower their tariffs through negotiation
✅ They reduce dependency on foreign imports and support domestic production
In short, if combined with smart monetary policy, these moves could actually help revive U.S. manufacturing and strengthen the economy in the mid-to-long term.
📉 Final thoughts on SPX:
I personally don’t believe the bearish breakdown is coming — but as a trader, I focus on reality, not preference. Right now, we’re still holding above major support, and unless that breaks, the bullish scenario remains in play.
Let me know what you think about this macro setup in the comments.
And as always remember:
🐺 Discipline is rarely enjoyable, but almost always profitable 🐺
🐺 KIU_COIN 🐺
Best Technical Indicator to Identify Order Block & Imbalance
Your ability to correctly identify Order Blocks on a price chart is essential for profitable trading Smart Money Concept.
In this article, I will show you a great technical indicator that will help you to spot Order Blocks on any financial market.
First, in brief, let me give you my definition of Order Block.
The problem is that in SMC trading there is no one single definition of that and many traders interpret it differently.
To me, an Order Block is a specific zone on a chart from where a strong price movement initiates and where a significant imbalance between supply and demand occurs .
This imbalance should strictly originate from a liquidity zone.
That definition implies that in order to identify an Order Block zone, one should learn to properly identify the imbalance and liquidity zones.
And again, there is no precise definition of an imbalance on a price chart. To me, a bullish imbalance is a formation of a bullish engulfing candle - the one that engulfs a range of previous bearish candle with its body.
Above is the example of a valid Order Block on GBPUSD.
A bearish imbalance is a formation of a bearish engulfing candle - the one that engulfs a range of a previous bullish candle with its body.
Above, you can see the example of an Order Block on USDCAD, based on a bearish imbalance.
There is one technical indicator that will help you to recognize such Order Blocks. It is called " All Candlestick Patterns" on TradingView.
Open settings of the indicator and make it show ONLY Engulfing Candles and choose "No Detection" in "Detect Trends Based on".
After that, hide the indicator and first, Identify the liquidity zones on a chart and wait for a test of one of these zones.
Here is a test of a liquidity zone on NZDUSD on an hourly time frame.
After that, turn on the indicator, and wait for its signal.
You can see that after some time, the price formed a bullish imbalance with a bullish engulfing candle. The indicator highlight that candle.
The Order Block zone will be based on the lowest low of 2 candles and the high of a bearish candle preceding the imbalance.
One more example. We see a test of a significant liquidity zone on EURAUD on a 4H time frame.
We turn on the indicator and look for a signal.
A bearish imbalance is formed and the indicator immediately notifies us.
An Order Block Zone in that case will be the area based on the highest high of 2 candles and the low of a bullish candle preceding the imbalance .
Of course, there will be the rare cases when the indicator will miss the imbalances. But while you are learning to recognize Order Blocks, this indicator will definitely help you a lot!
Thank you for reading!
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
RSI 101: Revealing the Special Characteristics of RSIWhy does RSI have support and resistance levels at 40 and 60?
Why does divergence happen between RSI and price?
What is RSI momentum?
All the characteristics of RSI (that I know) will be explained here.
Formula and Meaning
If you are using TradingView, you probably already know what RSI is and what "overbought" and "oversold" mean. So, I won’t repeat it here. Instead, I’ll dive deeper into the true nature of RSI, giving you a different perspective.
You can skip the mathematical formula of RSI, it’s already discussed everywhere online. Just remember this ratio table:
Here’s how I explain the table:
At RSI = 50, the average gain equals the average loss (I'll call this the buy/sell ratio). This is a balanced point. Buyers and sellers are equally strong.
At RSI ~ 60 (66.66), the buy/sell ratio = 2/1. Buyers are twice as strong as sellers.
At RSI ~ 40 (33.33), the buy/sell ratio = 1/2. Sellers are twice as strong as buyers.
At RSI = 80, the buy/sell ratio = 4/1. Buyers are four times stronger.
At RSI = 20, the buy/sell ratio = 1/4. Sellers are four times stronger.
The formula shows that when RSI reaches 80 or 20, the buyer or seller is extremely strong — about four times stronger — confirming a clear trend.
At these levels, some Trading strategies suggest placing a Sell or Buy based on the overbought/oversold idea.
But for me, that’s not the best way. The right approach is: when a trend is clearly formed, we should follow it.
I'll explain why right below.
Look at this chart showing RSI changes with the buy/sell ratio:
When RSI > 50:
When RSI < 50:
You can see that the higher RSI goes, the slower it climbs, but the high buy/sell ratio makes price move up faster.
Similarly, when RSI goes lower, it drops slower but price drops faster.
That’s why at overbought (RSI=80) or oversold (RSI=20) areas, you need to be careful. Even a small RSI moving can lead to big price changes, easily hitting your stop loss.
On the other hand, if you follow the trend and wait for RSI to pull back, you will trade safer and more profitably.
RSI Key Levels
Here are some special RSI levels I personally find useful when observing FX:XAUUSD :
(These levels are relative. They might vary with different timeframes or trading pairs. Check historical data to find the right ones for you. On bigger timeframes like M15 or above, the accuracy is better.)
RSI = 20
When RSI hits 20, sellers dominate. This confirms a trend reversal to bearish.
RSI = 80
When RSI hits 80, buyers dominate. This confirms a trend reversal to bullish.
RSI = 40
This is a sensitive level. Sellers start gaining the upper hand (sell/buy = 2/1).
If buyers lose 40, they lose their advantage.
So RSI >= 40 is "buyer territory". In an uptrend, RSI usually stays above 40.
RSI = 40 acts as support in an uptrend.
RSI = 60
Same idea. RSI <= 60 is "seller territory".
RSI = 60 acts as resistance in a downtrend.
40 and 60 are considered the key levels of RSI.
Now you guys know why RSI has support/resistance around 40/60!
RSI Range
As you know, RSI moves between 0 and 100.
Since RSI >= 40 is buyer territory, we can see the relationship between price and RSI:
When RSI stays above 40, price tends to move in an uptrend:
When RSI stays below 60, price tends to move in a downtrend:
When RSI stays between 40 and 60, buyers and sellers are balanced, and price moves sideways in a box:
When RSI is moving, It creates a RSI Range.
Whenever the trend switches between the three states — uptrend, sideways, and downtrend — a Range Shift is formed.
At first, RSI moves in 40-60 range, price moves sideways. A strong price move pushes RSI to 80. Later, RSI stays above 50, helping price grow strongly. When momentum fades, RSI returns to 40-60 and price moves sideways again.
Note:
RSI reflects Dow Theory by showing the stages of accumulation, growth, and distribution.
And as you see, when RSI touches key levels, the trend often pulls it back.
RSI Momentum
Price momentum means how fast price changes.RSI momentum represents the change in the strength between buying and selling forces.
When RSI > 50:
If price falls, RSI shows high momentum — RSI drops fast but price drops slowly.
If price rises, RSI shows low momentum — RSI rises slowly but price rises fast.
For example, at first RSI is above 50.
Price drops from (a) to (b) by 44 units, RSI drops from (Ra) to (Rb) by 25 units.
Later, RSI drops from (Rb) to (Rc) (also 25 units) but price drops from (b) to (c) by 73 units.
When RSI < 50:
If price falls, RSI has low momentum — RSI drops slowly but price falls fast.
If price rises, RSI has high momentum — RSI rises fast but price rises slowly.
RSI and Price Divergence
Divergence happens when price and RSI move in opposite directions:
Price goes up but RSI goes down, or vice versa.
Why does divergence happen?
In a strong downtrend, price forms a bottom at point (1), and RSI drops to level (r1).
When a price pullback happens, price pushes up to a peak at point (2), and RSI also bounces back to level (r2).
Because the downtrend is strong, after completing the pullback (1-2), price continues to make a lower bottom at point (3).
At this point, remember the behavior of RSI momentum when RSI is below 50:
It takes a large price drop (from 2 to 3) to cause a small RSI drop (from r2 to r3).
Meanwhile, even a small price increase (from 1 to 2) causes a large RSI rise (from r1 to r2).
Since the distance (1-2) is smaller than (2-3), but the RSI move (r1-r2) is bigger than (r2-r3), divergence is created.
Divergence shows that the current trend is very strong, not a complete signal of a trend reversal.
(I might share with you how to spot a complete RSI reversal signal in future posts.)
As shown in the example above, after forming bottom (5) and creating a bullish divergence between (3-5) and (r3-r5), price still kept dropping sharply while RSI kept rising.
In these areas, if you keep trying to catch a reversal just based on divergence, you will likely need to DCA or cut your losses many times.
That’s why the most important thing in trading is always to follow the trend.
RSI Exhaustion
RSI Exhaustion happens when RSI keeps getting rejected by a resistance or support zone and can’t break through.
After a strong downtrend, RSI recovers but stalls around the 5x zone.
It tries many times but fails, showing buying power is weakening.
Then the downtrend continues:
Exhaustion near high or low RSI levels creates stronger divergences than exhaustion in the middle range:
Double or triple tops/bottoms on RSI (M or W shapes) basically indicate RSI exhaustion.
RSI Can Identify Trend Strength
In an uptrend:
If RSI pulls back to a higher level before going up again, the trend is stronger.
The pullback should not fall too deep (below 40).
Example:
First rally: RSI drops to 60 before rising again → strong rally (273 units).
Second rally: RSI drops to 50 before rising again → weaker rally (94 units).
Same idea for a downtrend:
If RSI pullbacks to 50 then drops again, the downtrend is stronger than if it pullbacks to 60.
RSI Support and Resistance
Besides 40-60 acting as support/resistance, RSI also reacts to old tops and bottoms it created.
Why does this happen?
RSI is calculated from closing prices.
On a higher timeframe, the candle close price is a high/low or support/resistance price on lower timeframes.
When RSI moves in a trend on a higher timeframe, it maintains a buy/sell ratio, forcing lower timeframe RSI to oscillate within a range.
Example:
On H4, RSI stays above 40 → uptrend.
It makes H1 RSI move between 30-80.
Sharp RSI tops/bottoms react even stronger because they show strong buying/selling forces.
Summary
When looking at the price chart, we can see that price can rise or fall freely without any defined boundaries.
However, RSI operates differently: it always moves within a fixed range from 0 to 100.
During its movement, RSI forms specific patterns that reflect the behavior of price.
Because RSI has a clear boundary, identifying its characteristics and rules becomes easier compared to analyzing pure price action.
By studying RSI patterns, we can make better assumptions and predict future price trends with higher accuracy.
I have shared with you the core characteristics of RSI, summarized as follows:
Besides overbought (80) and oversold (20), RSI respects 40 and 60.
40 is support level in an uptrend. 60 is resistance level in a downtrend.
In an uptrend, RSI stays above 40.
In a downtrend, RSI stays below 60.
An RSI Range-Shift leads to a trend change.
RSI Divergence shows strong trends.
Double or triple tops/bottoms show RSI exhaustion → potential reversals.
The higher the RSI level, the slower it moves, but the faster the price rises.
The lower the RSI level, the slower it moves, but the faster the price falls.
A strong uptrend can be identified when RSI moves within a higher range or shows continuous bearish divergences.
A strong downtrend can be identified when RSI moves within a lower range or shows continuous bullish divergences.
RSI reacts to its old tops and bottoms.
Sharper RSI peaks show stronger selling.
Sharper RSI bottoms show stronger buying.
In the next parts, I’ll show you how to apply these RSI's Characteristics to trend analysis, multi-timeframe analysis, and trading strategies, that you might have never seen before.
I trade purely with RSI. Follow me for deep dives into RSI-based technical analysis and discussions!
RSI 101: Scalping Strategy with RSI DivergenceFX:XAUUSD
I'm an intraday trader, so I use the H1 timeframe to identify the main trend and the M5 timeframe for entry confirmation.
How to Determine the Trend
To determine the trend on a specific timeframe, I rely on one or more of the following factors:
1. Market Structure
We can determine the trend by analyzing price structure:
Uptrend: Identified when the market consistently forms higher highs and higher lows. This means price reaches new highs in successive cycles.
Downtrend: Identified when the market consistently forms lower highs and lower lows. Price gradually declines over time.
2. Moving Average
I typically use the EMA200 as the moving average to determine the trend. If price stays above the EMA200 and the EMA200 is sloping upwards, it's considered an uptrend. Conversely, if price is below the EMA200 and it’s sloping downwards, it signals a downtrend.
3. RSI
I'm almost use RSI in my trading system. RSI can also indicate the phase of the market:
If RSI in the 40–80 range, it's considered an uptrend.
If RSI in 20 -60 range, it's considered a downtrend.
In addition, the WMA45 of the RSI gives us additional trend confirmation:
Uptrend: WMA45 slopes upward or remains above the 50 level.
Downtrend: WMA45 slopes downward or stays below the 50 level.
Trading Strategy
With this RSI divergence trading strategy, we first identify the trend on the H1 timeframe:
Here, we can see that the H1 timeframe shows clear signs of a new uptrend:
Price is above the EMA200.
RSI is above 50.
WMA45 of RSI is sloping upward.
To confirm entries, move to the M5 timeframe and look for bullish RSI divergence, which aligns with the higher timeframe (H1) trend.
RSI Divergence, in case you're unfamiliar, happens when:
Price forms a higher high while RSI forms a lower high, or
Price forms a lower low while RSI forms a higher low.
RSI divergence is more reliable when the higher timeframe trend remains intact (as per the methods above), indicating that it’s only a pullback in the bigger trend, and we’re expecting the smaller timeframe to reverse back in line with the main trend.
Stop-loss:
Set your stop-loss 20–30 pips beyond the M5 swing high/low.
Or if H1 ends its uptrend and reverses.
Take-profit:
At a minimum 1R (risk:reward).
Or when M5 ends its trend.
You can take partial profits to optimize your gains:
Take partial profit at 1R.
Another part when M5 ends its trend.
The final part when H1 ends its trend.
My trading system is entirely based on RSI, feel free to follow me for technical analysis and discussions using RSI.
What Is Momentum – And Why It’s Not Just a Trend IndicatorMost traders follow price — candles, trendlines, support/resistance. But there’s another layer that often tells the story before the price moves: momentum.
⸻
🔍 In this post, you’ll learn:
• What momentum really measures
• Why it’s not the same as price direction
• How momentum can signal a shift before the chart confirms it
• Why combining momentum with structure improves timing
⸻
📈 Momentum ≠ Direction
Price can be rising while momentum is fading. That’s often a clue of an upcoming slowdown or reversal — long before the price turns. Similarly, price can be flat, while momentum builds in one direction. That’s tension… and tension leads to moves.
⸻
🔥 Why Momentum Matters:
• It reveals intensity, not just direction
• It can act as a leading indicator — not lagging
• Momentum divergences often hint at hidden accumulation or distribution
• Tracking it helps you avoid late entries or false breakouts
⸻
🔧 Takeaway for traders:
If you’re only watching price, you’re only seeing half the picture.
Momentum shows what’s driving the move, and when that drive starts weakening.
⸻
💬 What’s your favorite momentum indicator? RSI, %R, CCI, or something else?
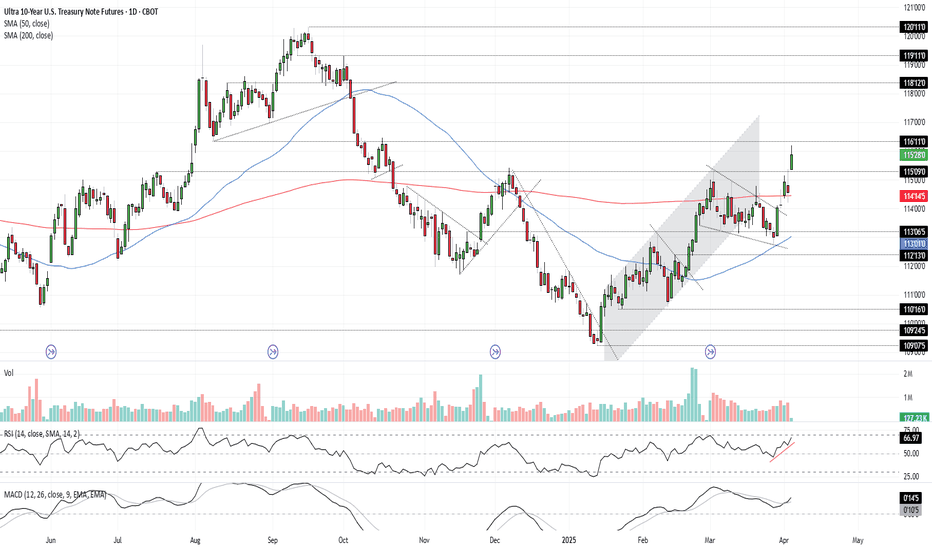
Bonds Don’t Lie: The Signal is ClearU.S. 10-year Treasuries are a crucial cog in the global financial machine, serving as a benchmark borrowing rate, a tool for asset valuation, and a gauge of the longer-term outlook for U.S. economic growth and inflation.
As such, I keep a close eye on 10-year note futures, as they can offer clues on directional risks for bond prices and yields. The price action over the past few days has sent a clear and obvious signal as to where the risks lie: prices higher, yields lower.
Futures had been grinding lower within a falling wedge for several weeks but broke higher last Friday on decent volumes following soft U.S. household spending data. It has since extended bullish the move, reclaiming the 200-day moving average before surging above key resistance at 115’09’0 after Trump’s reciprocal tariff announcement on Wednesday.
RSI (14) is trending higher but isn’t yet overbought, while MACD has crossed the signal line above 0, confirming the bullish momentum signal. That favours further upside, putting resistance at 116’11’0 and 118’12’0 on the immediate radar. For those who prefer it expressed in yield terms, that’s around 4% and 3.8% respectively.
Good luck!
DS
How to Set Multiple TPs...for BeginnersHey Rich Friends,
I wanted to share how I find multiple TPs for my Forex trades using free tools and only 1 technical indicator. This strategy is perfect for beginners because it is easy to follow and has clear confirmations for entering and exiting a trade in profit, even if it hits your Stop Loss.
I keep my charts clean and let price action do the talking. Here's my setup:
✅ Session Breaks & Horizontal Lines – I mark the previous day’s highs, lows, and key levels to identify potential areas of interest.
✅ Stochastic for Entries & Exits – I use the Stochastic indicator to time my trades when the price reacts at my key levels (80 and 20 are very important here!)
✅ Horizontal Lines = Potential TPs – Instead of setting a take profit, I let the market tell me when to exit based on price action around these levels.
Less noise, more precision. Drop a "7" if you made it to the end of the video and let me know if it was helpful!
Peace and Profits,
Cha
Use RSI Like a GoldmanYou might be wondering, do the traders at Goldman Sachs use the Relative Strength Index (RSI)? The answer is, perhaps they do, and perhaps they don’t. However, based on my experience, I can confidently say that even the most seasoned and professional traders rely on RSI from time to time.
While it may not be their sole tool for decision-making, it’s often included in their broader strategy due to its effectiveness in identifying overbought or oversold conditions in the market. RSI is one of many technical indicators that can serve as a helpful signal in navigating market trends, and even the best traders find it useful on occasion.
When trading with technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), having a clear and structured approach is crucial to maximizing its effectiveness. While RSI can be a powerful tool for identifying potential trend reversals, it’s essential to understand the right conditions and context in which to use it.
Below are some key principles and guidelines that can help you apply RSI more effectively in your trading strategy. Whether you’re a swing trader or a day trader, these tips can help you avoid common pitfalls and make more informed decisions in the market.
⚙️ Keep Settings Simple
Keep the RSI settings minimal to avoid confusion. Stick to the standard 14-period lookback, which is widely used and reliable for most market conditions.
📉📈 Ensure Divergence Occurs Outside of Key Levels
Divergence should only be considered when the RSI reaches extreme levels, typically above 70 (overbought) or below 30 (oversold). This helps to identify potential trend reversals. Divergence at neutral levels (like between 40–60) may not be as effective.
🔥 Base Divergence on Candle Closes, Not Wicks
Always look for divergence based on the closing price of candles. Divergence created by wick movements is unreliable and can lead to false signals. Stick to the body of the candle to ensure accuracy.
⏳ Watch the Lookback Period
The RSI’s default lookback period is 14, and divergence with a gap of more than 14 candles is generally less reliable. Wider gaps often signal weak price momentum and a higher chance of failure, so focus on shorter, more recent divergences for better results.
💧 Liquidity Must Be Taken Before Entering Trades
Liquidity is essential when confirming trade setups:
The first high or low should take out liquidity from higher time frames (such as range highs and lows).
The subsequent highs or lows should take out local liquidity, which can be identified by overbought or oversold RSI conditions. Ensure there’s a clear market structure shift before entering trades.
⏰ Timeframe Considerations for Different Trade Types
For swing trades, focus on longer timeframes like the 4-hour chart to capture larger market moves and trends.
For day trades, the 15-minute timeframe is ideal for capturing short-term price action and finer market details.
🔄 Use Divergences for Trend Reversals, in Confluence with Other Analysis
RSI divergence is best used to identify potential trend reversals. However, it should not be used in isolation. Always look for confluence with other technical analysis methods (such as support/resistance levels, moving averages, or candlestick patterns) to increase the reliability of the signal. Combining multiple tools enhances the accuracy of your trade setups.
Stay sharp, stay ahead, and let’s make those moves. Until next time, happy trading!
Can we enhance the most popular Indicator on TradingView?I describe my implementation of the TTM Squeeze indicator, first coded by Lazybear and that became the most popular indicator on TradingView.
There's gotta be a reason for that to be the most popular, right? I wanted to find out and make it much easier to navigate as well as adding to it with my own touch.
Hope you enjoy it.
Divergence Trading Explained For Beginners -DAX Pullback TradeTrading divergence in the Forex or Stock market can be an important tool. Learn how to identify divergences & practically apply them to your technical analysis to increase your edge & profits in the financial markets.
In this video you'll learn
What is a bullish and bearish divergence
How to use divergence to spot potential reversals in the market
How to use volume to identify key levels of reversals
How to measure out a "Kill Zone"
What are tweezer tops & tweezer bottoms & why they are important
How to use the Fibonacci retracement tool
How to use the Relative Strength Index (RSI Indicator)
Your Trading Coach - Akil
Understanding RSI In TradingThis article takes a deep dive into the Relative Strength Index (RSI), a powerful tool for traders at any level. We’ll break down how RSI works, how to interpret it, and how to use it effectively in your trading strategies. Plus, we’ll touch on the math behind it. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just getting started, this guide will give you the insights you need to make RSI a valuable part of your trading toolkit.
Understanding Oscillators in Trading
An oscillator is a technical indicator that moves between two extremes, usually ranging from 0 to 100. Traders use oscillators to spot overbought and oversold conditions in the market. An overbought signal suggests that excessive buying has driven prices too high and may not be sustainable, while an oversold signal indicates the opposite—excessive selling that could lead to a potential rebound. By tracking these price oscillations, traders can anticipate trend reversals and make more informed decisions.
Key Functions of Oscillators:
Momentum Analysis: Oscillators gauge the speed and strength of price movements, offering insights into an asset’s momentum.
Volatility Detection: They help identify periods of high or low volatility, enabling traders to adjust their strategies accordingly.
Trend Confirmation: When combined with other technical indicators, oscillators can validate or reveal emerging trends in the market.
Introduction to the RSI Indicator
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum-based technical indicator used to assess the strength of recent price movements and identify overbought or oversold conditions in an asset. It helps traders spot potential trend reversals by oscillating between 0 and 100. An RSI above 70 suggests the asset may be overbought, while a reading below 30 indicates it may be oversold.
By the end of this, you'll be an RSI expert!
Interpreting RSI Readings
RSI values above 70 suggest that an asset is overbought, meaning it has likely experienced a sharp price increase and may be due for a correction. On the other hand, RSI values below 30 indicate that the asset is oversold, implying a steep price drop and the possibility of a rebound.
However, it's important to remember that RSI isn't foolproof and can occasionally give false signals. To increase accuracy, it's best to use RSI in combination with other technical indicators and fundamental analysis.
Overbought: An RSI reading above 70 signals that the asset may be overbought and due for a correction. This could present a potential selling opportunity, but traders should be cautious, as false signals can occur.
Oversold: An RSI reading below 30 indicates that the asset may be oversold and due for a rebound. This can signal a potential buying opportunity, but again, traders should be cautious of possible false signals.
Divergence: Divergence happens when the RSI moves in the opposite direction of the price. For instance, if the price makes new highs while the RSI forms lower highs, this could point to a potential trend reversal.
Support and Resistance: The RSI can also help identify support and resistance levels. If the RSI consistently bounces off the 30 level, it may indicate a support level. Conversely, if the RSI repeatedly fails to break through the 70 level, this could signal a resistance level.
RSI and Divergence
Divergence happens when the RSI moves in the opposite direction of the asset's price, often signaling a potential trend reversal. For example, if the price is hitting new highs but the RSI forms lower highs, it could indicate a bearish divergence, suggesting a possible sell signal.
A common example of bearish divergence is when the price of an asset makes higher highs, but the RSI forms lower highs. This suggests weakening buying momentum, even as the price continues to rise. It can be a sign that the uptrend may be losing steam, with a reversal to the downside potentially on the horizon.
On the other hand, bullish divergence occurs when the price is making lower lows, but the RSI is making higher lows. This indicates that selling pressure is subsiding, and the asset may be primed for a rebound to the upside. Traders can use this pattern to time their entries for long positions.
RSI divergence can help traders identify overbought or oversold conditions, enabling them to make more effective decisions about entry and exit points. However, divergence should always be used alongside other technical and fundamental analysis for confirmation before acting on the signal.
Calculating the RSI Indicator
Calculating the RSI is straightforward once you break it down. The goal is to determine the average gains and losses over a set period, typically 14 days. This helps assess the strength of price movements and identify overbought or oversold conditions. While the math may sound complex, understanding the formula is key to using the tool effectively.
The RSI formula is:
RSI = 100 - (100 / (1 + (Average Gains / Average Losses)))
This calculation provides valuable insights into the relative strength of an asset’s price movements.
Factors Affecting the RSI Calculation
The RSI calculation can be influenced by several factors, with the length of the time period being the most significant. A shorter period (e.g., 5 days) results in a more volatile RSI that responds quickly to price changes, while a longer period (e.g., 20 days) creates a smoother RSI, filtering out short-term fluctuations. The ideal time period depends on your trading style and the volatility of the market you're analyzing.
Why the RSI Indicator is Powerful
Identifies Overbought and Oversold Conditions: The RSI helps traders recognize when an asset is overbought or oversold, allowing them to time their entries and exits more effectively.
Detects Divergences: Divergences between the RSI and price can signal potential trend reversals, giving traders an early warning to adjust their positions accordingly.
Flexible and Customizable: Traders can adjust the RSI’s period to match their trading style and the specific market conditions, making it a highly versatile tool for technical analysis.
Widely Adopted and Well-Understood: The RSI is one of the most popular technical indicators, with a wealth of resources and analysis available to assist traders in interpreting its signals.
Practical Application in Real Life
Here are a few effective strategies where RSI can be combined with other technical indicators for a more comprehensive analysis:
Example 1: RSI + Support/Resistance + Moving Averages
Scenario:
You are analyzing a stock that has been in an uptrend, with the price currently approaching a key resistance level at $100. The 50-period moving average is also trending upwards, confirming the bullish trend.
The RSI is at 75, indicating an overbought condition.
As the price nears the resistance level, the RSI starts to flatten, suggesting the upward momentum might be weakening.
You wait for the price to fail to break above the $100 resistance level and the RSI to drop below 70, signaling a potential reversal. This provides a clearer sell signal, as both the price and RSI align with the idea that a correction could be coming.
Why this works:
By using both RSI and moving averages with support and resistance, you have a solid confirmation of the potential reversal, as it combines trend analysis with overbought conditions.
Example 2: RSI + SFP (Swing Failure Pattern) + Price Action
Scenario:
You’re monitoring a currency pair that recently made a new low, breaking through a previous swing low at 1.1500. However, the price quickly reverses and fails to sustain the breakdown, bouncing back above the previous low, forming an SFP.
At the same time, the RSI is below 30, but it starts to turn upward, forming a bullish divergence (higher lows on the RSI while the price makes lower lows).
This divergence and the SFP setup suggest that the selling pressure is decreasing, and a potential reversal to the upside could be imminent.
Why this works:
The Swing Failure Pattern highlights the false breakdown, and the RSI divergence confirms that momentum is shifting. This combination increases the likelihood of a successful trade when entering on the potential reversal.
Key Takeways
The RSI is an essential tool for traders looking to spot overbought or oversold conditions and potential trend reversals. By mastering how to interpret RSI readings and incorporating them into your strategies, you can improve your decision-making and potentially boost your trading results. For a more balanced approach, always use RSI alongside other technical indicators and fundamental analysis.
what is the most effective indicator?There isn’t a single "most effective" trading indicator that works for everyone, as effectiveness depends on your trading style, strategy, and the market conditions. However, some indicators are considered more versatile or reliable when used correctly. Here's a breakdown to help you choose:
Most Effective for Trends:
Moving Averages (EMA or SMA):
Simple and effective for identifying trends.
Works well in trending markets but less reliable in sideways or choppy markets.
Pro Tip: Combine short-term and long-term moving averages for crossovers.
Ichimoku Cloud:
A comprehensive indicator that provides trend direction, support/resistance, and momentum.
Effective but requires practice to interpret correctly.
Most Effective for Overbought/Oversold Levels:
Relative Strength Index (RSI):
One of the most popular and effective indicators for spotting overbought or oversold conditions.
Works well in both trending and range-bound markets when combined with other tools.
Stochastic Oscillator:
Similar to RSI but includes %K and %D lines for crossovers.
Effective for momentum confirmation.
Most Effective for Volatility:
Bollinger Bands:
Great for identifying periods of high or low volatility and potential breakout zones.
Useful for sideways (range-bound) markets and trend reversals.
Average True Range (ATR):
Excellent for setting stop-loss levels and identifying market volatility trends.
Works well in conjunction with trend indicators.
Most Effective for Momentum:
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD):
Ideal for spotting trend reversals and momentum shifts.
Effective when used with a confirmation indicator like RSI.
Parabolic SAR:
Simple for identifying trend direction and potential exit points.
Works best in trending markets.
Combination for Higher Effectiveness:
Trend + Momentum: Combine EMA with MACD to identify trends and entry/exit points.
Overbought/Oversold + Volume: Use RSI with Volume Indicators (e.g., OBV) to confirm breakouts or reversals.
Volatility + Trend: Use Bollinger Bands with Ichimoku Cloud to spot breakout opportunities with clear trend guidance.
combined guide for both the **Regime Classifier** and **kNN Here’s the combined guide for both the **Regime Classifier** and **kNN (k-Nearest Neighbors)** indicators with emojis, tailored for your TradingView chart description:
---
### **🔑 Individual Lesson Steps**
#### **Lesson 1: What is a Regime Classifier?**
👽 **Defining Market Regimes**
- A **market regime** refers to distinct market conditions based on price behavior and volatility.
- **Types of Market Regimes:**
- 🚀 **Advance** (Uptrend)
- 📉 **Decline** (Downtrend)
- 🔄 **Accumulation** (Consolidation)
- ⬆️⬇️ **Distribution** (Topping/Bottoming Patterns)
👾 **Why it Matters:**
- Identifying market regimes helps traders tailor their strategies, manage risk, and make more accurate decisions.
---
#### **Lesson 2: Anatomy of the Regime Classifier Indicator**
👽 **Core Components**
- **Median Filtering:** Smooths out price data to capture significant trends.
- **Clustering Model:** Classifies price trends and volatility into distinct regimes.
- **Volatility Analysis:** Analyzes price volatility with rolling windows to detect high and low volatility phases.
👾 **Advanced Features:**
- **Dynamic Cycle Oscillator (DCO):** Tracks price momentum and cyclic behavior.
- **Regime Visualization:** Color-coded display of market conditions to make trends and patterns clearer.
---
#### **Lesson 3: Configuring the Regime Classifier Indicator**
👽 **Customization Settings**
- **Filter Window Size:** Adjusts sensitivity for detecting trends.
- **ATR Lookback Period:** Determines how far back the volatility is calculated.
- **Clustering Window & Refit Interval:** Fine-tunes how the indicator adapts to new market conditions.
- **Dynamic Cycle Oscillator Settings:** Tailors lookback periods and smoothing factors.
👾 **Why It’s Useful:**
- Customizing these settings helps traders optimize the indicator for different trading styles (e.g., scalping, swing trading, long-term investing).
---
#### **Lesson 4: Using the Indicator for Regime-Based Trading Strategies**
👽 **Adapt Strategies Based on Regimes**
- **Advance Regime:** Focus on long positions and trend-following strategies.
- **Decline Regime:** Prioritize short positions or hedging strategies.
- **Accumulation Regime:** Watch for breakout opportunities.
- **Distribution Regime:** Look for trend reversals or fading trends.
👾 **Using the Dynamic Cycle Oscillator for Confirmation:**
- 🌡️ **Overbought/Oversold Conditions:** Identify potential reversals.
- 🔄 **Trend Momentum:** Confirm if the trend is gaining or losing strength.
---
#### **Lesson 5: Combining Volatility and Price Trends for High-Confidence Trades**
👽 **Interpreting Volatility Clusters**
- 🔥 **High Volatility:** Indicates caution, risk management, or hedging opportunities.
- 🌿 **Low Volatility:** Suggests consolidation or trend continuation.
👾 **How Volatility Clusters Interact with Price Trends:**
- Combine trend direction with volatility analysis to refine trade entries and exits for more precise decisions.
---
#### **Lesson 6: Backtesting and Live Application**
👽 **Validate Using Historical Data**
- Guide traders on **backtesting** strategies using historical data to see how the indicator would have performed.
👾 **Real-Time Application:**
- Implement the Regime Classifier in **live markets** to monitor ongoing price conditions and gain actionable insights.
---
### **🔑 kNN (k-Nearest Neighbors) Indicator Lesson Steps**
#### **Lesson 1: What is kNN?**
👽 **Defining kNN**
- **k-Nearest Neighbors** is a machine learning algorithm that makes predictions based on the proximity of data points.
- It identifies the nearest neighbors of a data point and classifies it according to the majority class of those neighbors.
👾 **Why it Matters:**
- **kNN** helps traders forecast price movement, trends, and potential reversals by analyzing historical data.
---
#### **Lesson 2: Anatomy of the kNN Indicator**
👽 **Core Components**
- **Training Data:** Historical price data used to identify the neighbors of a point.
- **Distance Metric:** Determines the closeness of data points (e.g., Euclidean distance).
- **k Parameter:** The number of nearest neighbors to consider for predictions.
👾 **Advanced Features:**
- **Distance Calculation:** Helps assess how similar current price movement is to historical patterns.
- **Prediction:** The majority of the nearest neighbors determines the expected price movement (up or down).
---
#### **Lesson 3: Configuring the kNN Indicator**
👽 **Customization Settings**
- **k (Number of Neighbors):** Adjust to control how many historical data points influence predictions.
- **Distance Metric:** Choose from Euclidean, Manhattan, or other metrics based on data characteristics.
- **Window Size:** Defines how many data points (e.g., time periods) are used for analysis.
👾 **Why It’s Useful:**
- Tuning these settings allows traders to adjust the sensitivity and precision of predictions, optimizing for various trading styles.
---
#### **Lesson 4: Using the kNN Indicator for Predictive Trading Strategies**
👽 **Predicting Price Movements**
- Use **kNN** to identify trend directions and price reversals based on historical proximity.
- **Uptrend Prediction:** Identify moments where the nearest neighbors suggest a continuation of the trend.
- **Downtrend Prediction:** Signal when the majority of neighbors point toward price decline.
👾 **Using Predictions to Enhance Trade Entries:**
- Use **kNN** signals in conjunction with **Regime Classifier** regimes to validate and enhance entry and exit points.
---
#### **Lesson 5: Combining kNN Predictions with Regime Classifier for Precision**
👽 **Refining Trade Confidence**
- Cross-reference **kNN predictions** (uptrend/downtrend) with **Regime Classifier’s** regime identification for higher precision trades.
- **Example:** If **kNN** predicts an uptrend and the **Regime Classifier** signals an **Advance** regime, you can confidently go long.
---
#### **Lesson 6: Backtesting and Live Application**
👽 **Validate Predictions with Historical Data**
- Backtest using **kNN** on past price data to measure accuracy in predicting trends and reversals.
- **Real-Time Application:** Implement **kNN** in live markets alongside **Regime Classifier** for comprehensive decision-making.
---
### **🔄 Combined Lessons for Advanced Mastery**
#### **Combo 1: Regime Identification and kNN Predictions for Strategy Optimization**
💡 **Objective:** Combine market regime identification with kNN predictions to refine trading strategies.
- Merge **Lesson 1 (Understanding Regimes)** and **Lesson 1 (What is kNN?)**.
- **Practical Exercise:** Use both indicators to identify regimes and predict price trends in live charts.
---
#### **Combo 2: Customization, Practical Usage, and Enhanced Predictions**
💡 **Objective:** Equip traders to fine-tune both indicators for their unique strategies.
- Merge **Lesson 3 (Settings Configuration for Regime Classifier)** and **Lesson 3 (kNN Indicator Configuration)**.
- Walkthrough: Customize settings and combine both indicators to predict price trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
---
#### **Combo 3: Comprehensive Trading Strategy with Regime Classifier and kNN**
💡 **Objective:** Build a full-fledged trading system using both indicators for market regime analysis and predictive signals.
- Combine **all lessons** for a complete, systematic trading approach:
- 🔍 **Identify market regimes**
- 🔄 **Use kNN predictions** to assess potential price movements
- 📈 **Combine with Dynamic Cycle Oscillator** for entry/exit timing
- 💥 **Execute trades** with a comprehensive strategy
---
These lessons and combos provide traders with the essential tools to master both the **Regime Classifier** and **k-Nearest Neighbors** indicators, from understanding the fundamentals to implementing advanced strategies and refining predictions for more accurate market analysis.